
Concept explainers
The 10-ft cable AB is attached to two collars as shown. The collar at A can slide freely along the rod; a stop attached to the rod prevents the collar at B from moving on the rod. Neglecting the effect of friction and the weight of the collars, determine the distance a.
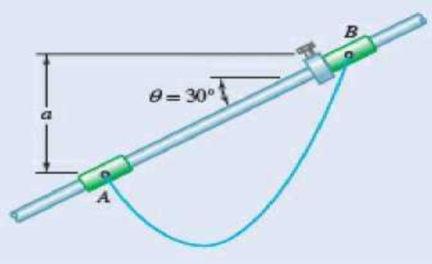
Fig. P7.147
Find the distance a.
Answer to Problem 7.147P
The distance a is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the cable AB is
The value of angle
The collar at A is slides freely and the collar at B is prevented from the moving.
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the cable assembly as in Figure 1.
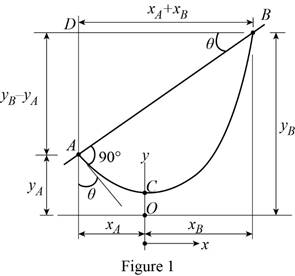
Refer the Equation 7.16 in the textbook.
Write the equation of the catenary cable as follows;
Differentiate the equation with x;
The slope at point A is;
The length of the portion AC is as follows:
The length of the portion CB is as follows:
Find the distance
Substitute 10 ft for L,
Find the distance
Find the distance
Consider the triangle ABD;
Find the value of
Find the distance a using the relation.
Use the trial and error procedure to find the value of a.
Consider the value of c and for the given value of
Trial 1:
Consider a trial value of 1.60 ft for c.
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 2.107 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 2.107 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 3.541 ft for
Substitute 2.107 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 2:
Consider a trial value of 1.70 ft for c.
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 2.239 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 2.239 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 3.622 ft for
Substitute 2.239 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 3:
Consider a trial value of 1.803 ft for c.
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and 2.374 ft for
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and 2.374 ft for
Substitute 1.803 ft for c and 3.694 ft for
Substitute 2.374 ft for
The calculated value of
Therefore, the value of c is 1.803 ft.
Substitute 3.606 ft for
Therefore, the distance a is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
VECTOR MECH....F/ENGNRS-STATICS -CONNECT
- The telescoping arm ABC of Prob. 6.93 can be lowered until end C is close to the ground, so that workers can easily board the platform.For the position when θ = -220°, determine (a) the force exerted at B by the single hydraulic cylinder BD, (b) the force exerted on the supporting carriage at A.arrow_forwardA spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and F of the linkage shown. Neglecting the weight of the spring and linkage, determine the force in the spring and the vertical motion of point G when a vertical downward 120-N force is applied (a) at point C ,( b) at points C and H.arrow_forwardIn order to unscrew the tapped faucet A, a plumber uses two pipe wrenches as shown. By exerting a 40-lb force on each wrench, at a distance of 10 in. from the axis of the pipe and in a direction perpendicular to the pipe and to the wrench, he prevents the pipe from rotating, and thus avoids loosening or further tightening the joint between the pipe and the tapped elbow C. Determine (a) the angle θ that the wrench at A should form with the vertical if elbow C is not to rotate about the vertical, (b) the force-couple system at Cequivalent to the two 40-lb forces when this condition is satisfied.arrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forwardProblem 4.51 The force-compression profile of a rubber bumper B is given by FB = Bx, where B = 3.5 x 10 lb/ft and x is the bumper's compression measured in the horizontal direction. Determine the expression for the potential energy of the bumper B. In addition, if the cruiser C weighs 70,00O lb and impacts B with a speed of 5 ft/s, determine the compression required to bring C to a stop. Model C as a particle and neglect C's vertical motion as well as the drag force between the water and the cruiser C. 5. 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 x (ft) Figure P4.51 FB (x105 lb)arrow_forwardA 20-m length of wire having a mass per unit length of 0.2 kg/m is attached to a fixed support at A and to a collar at B . Neglecting the effect of friction, determine (a) the sag h for which L = 15m, (b) the corresponding force P.arrow_forward
- A chairlift has been stopped in the position shown. Knowing that each chair weighs 567 N and that the skier in chair E weighs 765 N, determine the weight of the skier in chair F? (assume AB, BC and CD as 3 different strings/ropes) 6 m – 14 m - 24 m 8.25 m E 10 m C F D 10 marrow_forwardCollar A is connected as shown to a 50-lb load and can slide on a frictionless horizontal rod. Determine the distance x for which the collar is in equilibrium when P = 48 Ib. C 20 in. 50 Ibarrow_forwardPin B weighs 0.1kg and is free to slide in a horizontal plane along therotating arm OC and along the circular slot DE of radius b=500mm.Neglecting friction and assuming that θ= 15 rad/s andθ=250 rad/s2 for the position θ= 20o , determine for that position(a) the radial and transverse components of the resultant forceexerted on pin B, (b) the forces P and Q exerted on pin B,respectively, by rod OC and the wall of slot DE.arrow_forward
- help on this questionarrow_forwardA sailor is being rescued using a boatswain’s chair that is suspended from a pulley that can roll freely on the support cable ACB and is pulled at a constant speed by cable CD. Knowing that α =25° and β = 15° and that the tension in cable CD is 20 lb, determine (a) the combined weight of the boatswain’s chair and the sailor, (b) the tension in the support cable ACB.arrow_forwardQ2) A loaded Porter governor has four links each 200 mm long and are hinged at a distance of 40 mm from the axis of rotation. The mass of each ball is 2 kg and mass of the sleeve is 20 kg. The governor sleeve begins to rise at 300 r.p.m. when the links are at an angle of 35° to the vertical. Assuming the friction force to be constant, determine the minimum and maximum speed of rotation when the inclination of the arms to the vertical is 40°.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





