
Experimental Organic Chemistry: A Miniscale & Microscale Approach (Cengage Learning Laboratory Series for Organic Chemistry)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080461
Author: John C. Gilbert, Stephen F. Martin
Publisher: Brooks Cole
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 7.3, Problem 4E
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The stepwise mechanism using curved arrow to show the electron’s flow for the below isomerization needs to be determined.
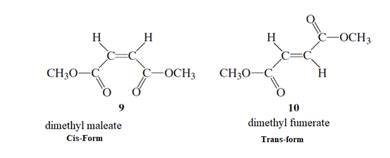
Concept Introduction :
The isomerism procedure includes the isomers. It is known as the molecules that contain the similar molecular formula but they generally own a dissimilar atom’s arrangement in space. Below are the two kinds:
- Constitutional isomers: They are known as the compounds within which the several atoms are linked or attached in a dissimilar manner. They are also known as the structural isomers:
- Stereoisomers: These are the compounds that vary on the basis of positioning in space. Below are two types:
- Enantiomers: These are the compounds that are generally a mirror image of one another and these mirror images are also known as non-superimposable.
- Diastereomers: These are the compounds that are not the mirror images of one another. Also, these compounds are also non-superimposable. They are of two kinds: cis and trans:
- Cis-isomers are the isomers that generally have atoms that are concerned with the similar side of a bond.
- Instead, the trans-isomers are the compounds which contain atoms concerned with opposite sides of a bond.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please help me with #2b & #3 using the data.
Heparin is used as an anti-coagulant. A risk of heparin use is thrombocytopenia, or low platelet
count. This risk is minimized with the use of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH), therefore it is
desirable to separate LMWH from higher molecular weight heparins. The method of choice to do
this is molecular exclusion chromatography. Below is a chromatogram from a molecular exclusion
chromatographic run. Peaks ranging from A to J are clearly distinguishable. The heparin mixture
that was analyzed had anywhere from 6 to 30 repeat units of monomer (where the heparin with 30
repeat units would be roughly five times the size of the heparin with six repeat units).
a. Which letter most likely represents the peak with 6 repeat units given these heparin polymers
were separated with molecular exclusion chromatography?
b. Explain your reasoning describing the mechanism of retention in molecular exclusion
chromatography.
100
80
60
60
Relative Abundance
40
40
E
GH
20
20
B
A
36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50
50…
HELP NOW PLEASE ! URGENT!
Chapter 7 Solutions
Experimental Organic Chemistry: A Miniscale & Microscale Approach (Cengage Learning Laboratory Series for Organic Chemistry)
Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 1ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 3ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 5ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 6ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 7ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 9ECh. 7.2 - Prob. 10E
Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 1ECh. 7.3 - Prob. 2ECh. 7.3 - Prob. 3ECh. 7.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 7.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 7.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 7.3 - Prob. 7ECh. 7.3 - Prob. 8ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 1ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 2ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 3ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 5ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 6ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 7ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 8ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 9ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 10ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 11ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 12ECh. 7.4 - Prob. 13ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 1ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 2ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 3ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 4ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 5ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 6ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 7ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 8ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 9ECh. 7.6 - Prob. 10E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
- 13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Seven Name Reactions in One - Palladium Catalysed Reaction (047 - 053); Author: Rasayan Academy - Jagriti Sharma;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5HEKTpDFkqI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY