
a.
To determine:
The
Introduction:
Test cross is the genetic cross between an individual that has dominant phenotype in specific trait to homozygous recessive for these specific traits. Test cross is used to identify the genotype of individual carrying dominant phenotype, and also used to check the linkage between the genes. In drosophila melanogaster, ebony eyes (e), and rough eyes (ro) are encoded by autosomal recessive gene that is present on chromosome they are separated by 20 map units. The gene that code for fork bristle (f) is X-linked recessive and assort independently of (e), and (ro).
a.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The cross between
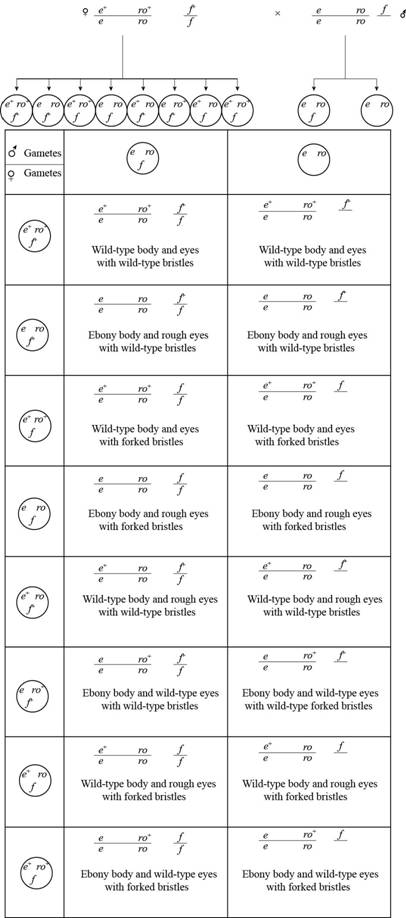
Fig.1: The cross between
Two autosomal genes in drosophila melanogaster, for body type and eyes are located 20 map unit apart from each other on chromosome 3.
Therefore, total percentage of recombinant would be 20 and non recombinant would be 80.
In females eight gametes are possible which will have four parental and four recombinants. Total percentage of recombinants is 20% so for each recombinant 5%. Similarly total percentage of non recombinant is 80% so each non recombinant will have 20%.
Given information is that, when drosophila is heterozygous for autosomal genes that are present in cis configuration with X-linked gene for heterozygous bristle. This female is crossed with homozygous recessive male for two autosomal genes and hemizygous for the X-linked gene.
The female are able to produce eight types of different gametes and these gametes are:
The result of the cross is:
The following table represents the expected proportion from the cross:
| Genotype | Body color | Eyes | Bristles | Proportion |
| Normal | Normal | Normal | 20% | |
| Normal | Normal | Forked | 20% | |
| Ebony | Rough | Normal | 20% | |
| Ebony | Rough | Forked | 20% | |
| Normal | Rough | Ebony | 5% | |
| Ebony | Normal | Normal | 5% | |
| Normal | Rough | Forked | 5% | |
| Ebony | Normal | Forked | 5% |
Table 1: The expected proportion from the cross.
b.
To determine:
The phenotype of progeny and their expected proportion when a female of each genotype is test crossed with the male
Introduction:
Test cross is the genetic cross between an individual that has dominant phenotype in specific trait to homozygous recessive for these specific traits. Test cross is used to identify the genotype of individual carrying dominant phenotype, and also used to check the linkage between the genes. In drosophila melanogaster, ebony eyes (e), and rough eyes (ro) are encoded by autosomal recessive gene that is present on chromosome they are separated by 20 map units. The gene that code for fork bristle (f) is X-linked recessive and assort independently of (e), and (ro).
b.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The cross between
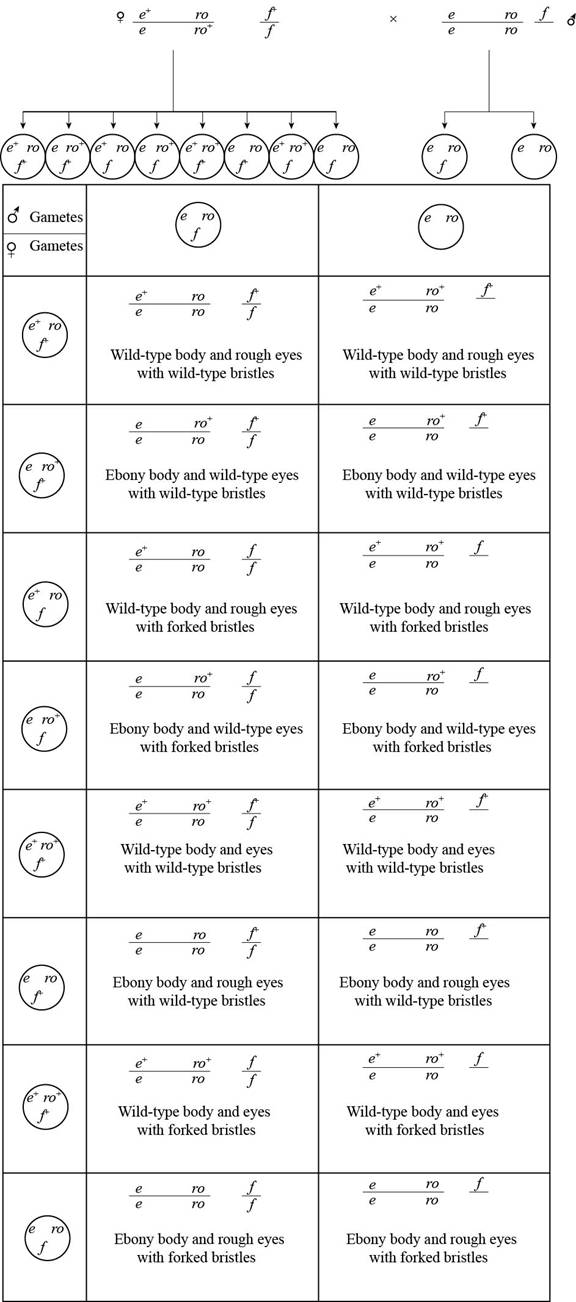
Fig. 2: The cross between
Given information is that, when drosophila is heterozygous for autosomal genes that are present in Tran’s configuration with X-linked gene for heterozygous bristle. This female is crossed with homozygous recessive male for two autosomal genes and hemizygous for the X-linked gene.
The female are able to produce eight types of different gametes and these gametes are:
The result of the cross is:
The following table represents the expected proportion from the cross:
| Genotype | Body color | Eyes | Bristles | Proportion |
| Normal | Rough | Normal | 20% | |
| Ebony | Normal | Normal | 20% | |
| Normal | Rough | Forked | 20% | |
| Ebony | Normal | Forked | 20% | |
| Normal | Normal | Normal | 5% | |
| Normal | Normal | Forked | 5% | |
| Ebony | Rough | Normal | 5% | |
| Ebony | Rough | Forked | 5% |
Table 2: The expected proportion from the cross.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Genetics: A Conceptual Approach 6E w/ SaplingPlus (Six-Month Access)
- What symbolic and cultural behaviors are evident in the archaeological record and associated with Neandertals and anatomically modern humans in Europe beginning around 35,000 yBP (during the Upper Paleolithic)?arrow_forwardDescribe three cranial and postcranial features of Neanderthals skeletons that are likely adaptation to the cold climates of Upper Pleistocene Europe and explain how they are adaptations to a cold climate.arrow_forwardBiology Questionarrow_forward
- ✓ Details Draw a protein that is embedded in a membrane (a transmembrane protein), label the lipid bilayer and the protein. Identify the areas of the lipid bilayer that are hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Draw a membrane with two transporters: a proton pump transporter that uses ATP to generate a proton gradient, and a second transporter that moves glucose by secondary active transport (cartoon-like is ok). It will be important to show protons moving in the correct direction, and that the transporter that is powered by secondary active transport is logically related to the proton pump.arrow_forwarddrawing chemical structure of ATP. please draw in and label whats asked. Thank you.arrow_forwardOutline the negative feedback loop that allows us to maintain a healthy water concentration in our blood. You may use diagram if you wisharrow_forward
- Give examples of fat soluble and non-fat soluble hormonesarrow_forwardJust click view full document and register so you can see the whole document. how do i access this. following from the previous question; https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/hi-hi-with-this-unit-assessment-psy4406-tp4-report-assessment-material-case-stydu-ms-alecia-moore.-o/5e09906a-5101-4297-a8f7-49449b0bb5a7. on Google this image comes up and i have signed/ payed for the service and unable to access the full document. are you able to copy and past to this response. please see the screenshot from google page. unfortunality its not allowing me attch the image can you please show me the mathmetic calculation/ workout for the reult sectionarrow_forwardIn tabular form, differentiate between reversible and irreversible cell injury.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





