
a.
To determine:
The
Introduction:
Phenotype is the actual description of all the observable characteristic of an organism that is obtained from its genotype. The phenotype includes: appearance, behavior and development. In the question following terms are used to denote genotype.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
The following figure represents the cross between
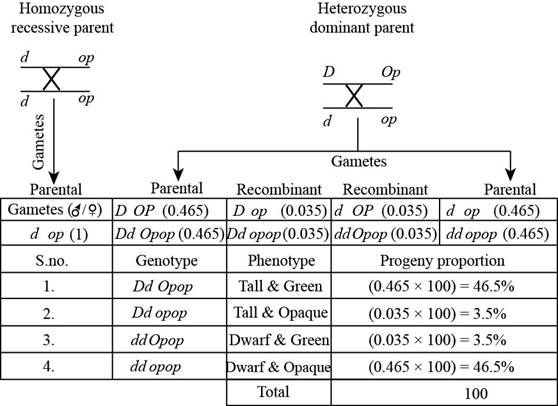
Fig. 1: The cross between
The cross in “Fig. 1” is between the homozygous recessive parent and heterozygous dominant parent. In this cross coupling will occur because of heterozygous dominant parent. In this two alleles are present on a same chromosome, so this lead to the production of four gametes.
Recombination frequency is 0.07 centiMorgan, so the parent frequency is
b.
To determine:
The phenotype and proportions of progeny produced by this crossing over
Introduction:
Phenotype is the actual description of all the observable characteristic of an organism that is obtained from its genotype. The phenotype includes: appearance, behavior and development. In the question following terms are used to denote genotype.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
The following figure represents the cross between
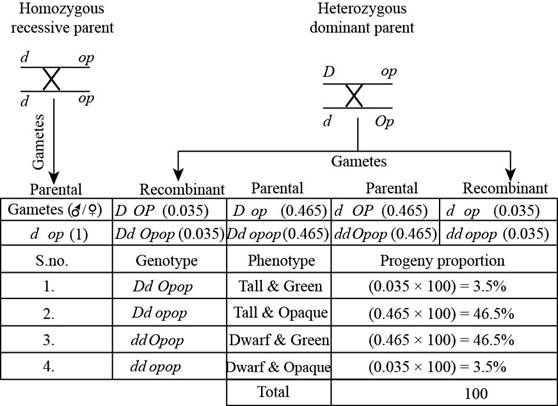
Fig. 2: The cross between
The cross in “Fig. 2” is between the homozygous recessive parent and heterozygous dominant parent. In this cross repulsion will occur because of heterozygous dominant parent. In this one allele is dominant and one is recessive, and both are present on a same chromosome, so this lead to the production of four gametes.
Recombination frequency is 0.07 centiMorgan, so the parent frequency is
c.
To determine:
The phenotype and proportions of progeny produced by this crossing over
Introduction:
Phenotype is the actual description of all the observable characteristic of an organism that is obtained from its genotype. The phenotype includes: appearance, behavior and development. In the question following terms are used to denote genotype.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
The following figure represents the cross between.
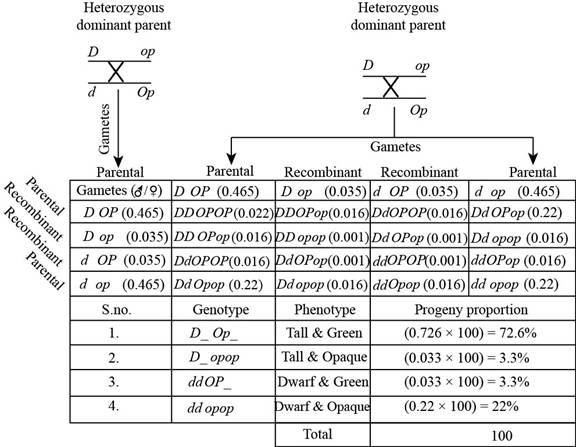
Fig. 3: The cross between.
The cross in “Fig. 3” is between the heterozygous dominant parents, genotype will have dominant allele on one chromosome and recessive allele on other chromosomes. In this cross repulsion will occur because of heterozygous dominant parent. In this one allele is dominant and one is recessive, and both are present on a same chromosome, so this lead to the production of four gametes.
Recombination frequency is 0.07 centiMorgan, so the parent frequency is
d.
To determine:
The phenotype and proportions of progeny produced by this crossing over
Introduction:
Phenotype is the actual description of all the observable characteristic of an organism that is obtained from its genotype. The phenotype includes: appearance, behavior and development. In the question following terms are used to denote genotype.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The following figure represents the cross between.
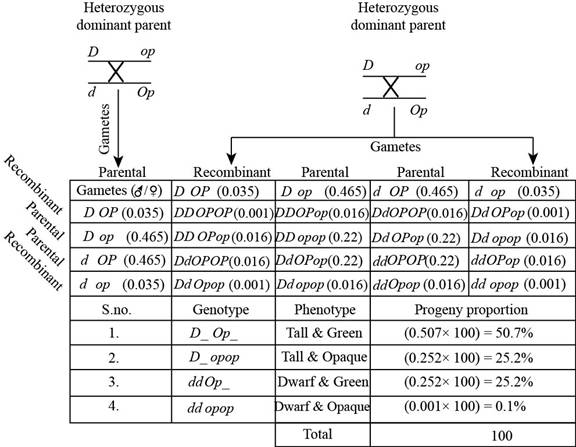
Fig. 4: The cross between.
The cross in “Fig.4” is between the heterozygous dominant parents. In this cross repulsion will occur because in this, genotype will have one dominant and one recessive allele on a chromosome, so this lead to the production of four gametes.
Recombination frequency is 0.07 centiMorgan, so the parent frequency is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Genetics: A Conceptual Approach
- Describe two different gene regulation mechanisms involving methylationarrow_forwardWhat is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forward
- Explain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardDescribe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





