
Concept explainers
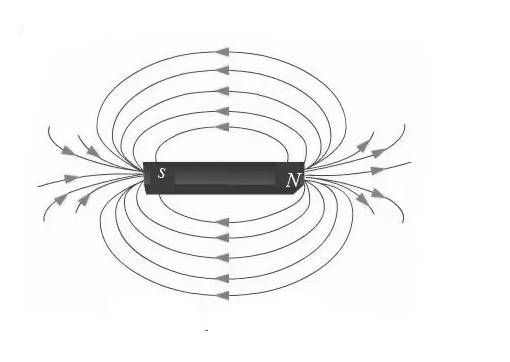
On an enlargement of the figure below, sketch field lines representing the magnetic field of the bar magnet. Show the field both inside and outside the magnet.
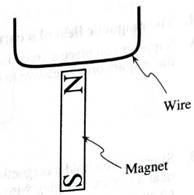
On the diagram, indicate the direction of the current through the wire when the circuit is complete.
Predict the direction of the force exerted on the wire by the magnet when the circuit is complete. Explain.
Check your prediction (Do not leave the battery connected for more than a few seconds. The battery and wires will become hot if the circuit is complete for too long.)
To Draw: Magnetic field due to a bar magnet.
The direction of current inside the circuit and the direction of force.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Direction of magnetic field is from north pole to south pole outside the magnet. There is no magnetic field inside the bar magnet.
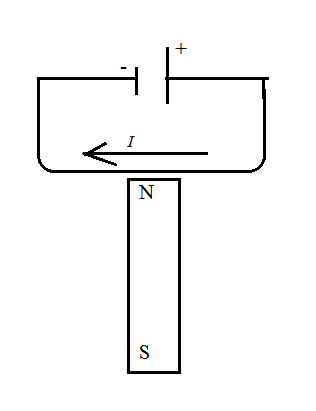
After closing the circuit, the current will flow from right to left. i.e. current will flow clockwise. This is because, the current induced in the circuit always opposes the change.
Direction of force can be calculated by using Fleming’s right-hand rule.
By this rule, three fingers of right hand are stretched such that thumb, first finger, middle finger are at 90 degrees to each other. If the first finger points along the direction of magnetic field, the middle finger points in the direction of the current, then the thumb will give the direction of force.
Applying this rule in the given condition, direction of force will be outside the paper.
Conclusion:
Direction of current is from right to left hand. The direction of force is out of the paper.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- If the car in the previous problem increases its power output by 10% (by pressing the gas pedal farther down), at what rate will the car accelerate? Hint: Consider the net force. In the previous problem the power was 31.8kWarrow_forwardWhat power is required (at the wheels) for a 1400 kg automobile to climb a 4% grade at a constant speed 30 m/s while it is opposed by drag and rolling resistance forces totaling 500 N?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- As a box is lifted against gravity and placed on a shelf, how does the work done by the lifter compare with the work done by gravity? What is the net work done on the box? What does this imply about its change in kinetic energy? Use definitions and mathematics from this chapter to answer these questions.arrow_forwardAs I carry a box up a flight of stairs, am I doing positive work or negative work on the box? Provide a mathematical explanation.arrow_forwardAs a ball falls under the influence of gravity, does gravity do positive work or negative work? Provide a mathematical explanation.arrow_forward
- Under what circumstances is it bad to describe kinetic energy as k = 1/2mv^2arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardAir temperature of 37 °C increases swimming pool temperature of 2.55 °C. What is the fraction of the water in the pool must evaporate during this time to carry enough energy to keep the temperature of the pool constant? 4186 J/(kg°C) = specific heat of water 2,430,000 (2.43 x 106) J/kg = latent heat of vaporization for the water in the pool.arrow_forward
- The iceberg requires 7.4 x 1020 Joules of energy to melt it completely. It absorbs energy from the Sun at a constant average rate of 88 Watts/m2. The total surface area of iceberg exposed to the sunlight is 12 billion (1.2 x 1010) square meters. How long will it take for sunlight to melt the entire iceberg in yearsarrow_forward1.0 kg block of ice to melt in the kitchen. The temperature in the kitchen is 31 °C. The ice starts out at 0 °C and takes an hour to melt and reach the same temperature as the surrounding room (31 °C). How much heat does the 1.0 kg of ice/water absorb from the room as it melts and heats up to 31 °C in Joules absorbed? Latent heat of fusion for water/ice is 334,000 J/kg Specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg°Carrow_forward5.84 If the coefficient of static friction between a table and a uni- form, massive rope is μ, what fraction of the rope can hang over the edge of the table without the rope sliding? 5.97 Block A, with weight Figure P5.97 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. 36.9° 1arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





