
Concept explainers
To find: the conclusion about the thermostat manufacturer’s claim, explain.
Answer to Problem 18E
It is convincing evidence that the thermostat manufacturer’s claim is false.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
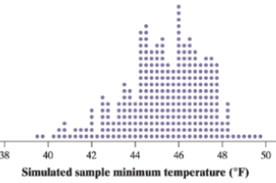
It is observed that every dot in the given dot plot represents a sample minimum temperature for a simple random sample with 10 reading. It is also observed that there are no dots above 40 in the given dot plot and there are 2 dots to the left of 40. This is indicating that is not possible that the population minimum is 40, because there are 2 samples that have a smaller sample minimum.
This is then indicating that there is enough convincing evidence that the thermostat manufacturer is false.
Chapter 7 Solutions
PRACTICE OF STATISTICS F/AP EXAM
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Precalculus
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Given the following sample data values: 7, 12, 15, 9, 15, 13, 12, 10, 18,12 Find the following: a) Σ x= b) x² = c) x = n d) Median = e) Midrange x = (Enter a whole number) (Enter a whole number) (use one decimal place accuracy) (use one decimal place accuracy) (use one decimal place accuracy) f) the range= g) the variance, s² (Enter a whole number) f) Standard Deviation, s = (use one decimal place accuracy) Use the formula s² ·Σx² -(x)² n(n-1) nΣ x²-(x)² 2 Use the formula s = n(n-1) (use one decimal place accuracy)arrow_forwardTable of hours of television watched per week: 11 15 24 34 36 22 20 30 12 32 24 36 42 36 42 26 37 39 48 35 26 29 27 81276 40 54 47 KARKE 31 35 42 75 35 46 36 42 65 28 54 65 28 23 28 23669 34 43 35 36 16 19 19 28212 Using the data above, construct a frequency table according the following classes: Number of Hours Frequency Relative Frequency 10-19 20-29 |30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 From the frequency table above, find a) the lower class limits b) the upper class limits c) the class width d) the class boundaries Statistics 300 Frequency Tables and Pictures of Data, page 2 Using your frequency table, construct a frequency and a relative frequency histogram labeling both axes.arrow_forwardTable of hours of television watched per week: 11 15 24 34 36 22 20 30 12 32 24 36 42 36 42 26 37 39 48 35 26 29 27 81276 40 54 47 KARKE 31 35 42 75 35 46 36 42 65 28 54 65 28 23 28 23669 34 43 35 36 16 19 19 28212 Using the data above, construct a frequency table according the following classes: Number of Hours Frequency Relative Frequency 10-19 20-29 |30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 From the frequency table above, find a) the lower class limits b) the upper class limits c) the class width d) the class boundaries Statistics 300 Frequency Tables and Pictures of Data, page 2 Using your frequency table, construct a frequency and a relative frequency histogram labeling both axes.arrow_forward
- A study was undertaken to compare respiratory responses of hypnotized and unhypnotized subjects. The following data represent total ventilation measured in liters of air per minute per square meter of body area for two independent (and randomly chosen) samples. Analyze these data using the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis test. Unhypnotized: 5.0 5.3 5.3 5.4 5.9 6.2 6.6 6.7 Hypnotized: 5.8 5.9 6.2 6.6 6.7 6.1 7.3 7.4arrow_forwardThe class will include a data exercise where students will be introduced to publicly available data sources. Students will gain experience in manipulating data from the web and applying it to understanding the economic and demographic conditions of regions in the U.S. Regions and topics of focus will be determined (by the student with instructor approval) prior to April. What data exercise can I do to fulfill this requirement? Please explain.arrow_forwardConsider the ceocomp dataset of compensation information for the CEO’s of 100 U.S. companies. We wish to fit aregression model to assess the relationship between CEO compensation in thousands of dollars (includes salary andbonus, but not stock gains) and the following variates:AGE: The CEOs age, in yearsEDUCATN: The CEO’s education level (1 = no college degree; 2 = college/undergrad. degree; 3 = grad. degree)BACKGRD: Background type(1= banking/financial; 2 = sales/marketing; 3 = technical; 4 = legal; 5 = other)TENURE: Number of years employed by the firmEXPER: Number of years as the firm CEOSALES: Sales revenues, in millions of dollarsVAL: Market value of the CEO's stock, in natural logarithm unitsPCNTOWN: Percentage of firm's market value owned by the CEOPROF: Profits of the firm, before taxes, in millions of dollars1) Create a scatterplot matrix for this dataset. Briefly comment on the observed relationships between compensationand the other variates.Note that companies with negative…arrow_forward
- 6 (Model Selection, Estimation and Prediction of GARCH) Consider the daily returns rt of General Electric Company stock (ticker: "GE") from "2021-01-01" to "2024-03-31", comprising a total of 813 daily returns. Using the "fGarch" package of R, outputs of fitting three GARCH models to the returns are given at the end of this question. Model 1 ARCH (1) with standard normal innovations; Model 2 Model 3 GARCH (1, 1) with Student-t innovations; GARCH (2, 2) with Student-t innovations; Based on the outputs, answer the following questions. (a) What can be inferred from the Standardized Residual Tests conducted on Model 1? (b) Which model do you recommend for prediction between Model 2 and Model 3? Why? (c) Write down the fitted model for the model that you recommended in Part (b). (d) Using the model recommended in Part (b), predict the conditional volatility in the next trading day, specifically trading day 814.arrow_forward4 (MLE of ARCH) Suppose rt follows ARCH(2) with E(rt) = 0, rt = ut, ut = στει, σε where {+} is a sequence of independent and identically distributed (iid) standard normal random variables. With observations r₁,...,, write down the log-likelihood function for the model esti- mation.arrow_forward5 (Moments of GARCH) For the GARCH(2,2) model rt = 0.2+0.25u1+0.05u-2 +0.30% / -1 +0.20% -2, find cov(rt). 0.0035 ut, ut = στει,στ =arrow_forward
- Definition of null hypothesis from the textbook Definition of alternative hypothesis from the textbook Imagine this: you suspect your beloved Chicken McNugget is shrinking. Inflation is hitting everything else, so why not the humble nugget too, right? But your sibling thinks you’re just being dramatic—maybe you’re just extra hungry today. Determined to prove them wrong, you take matters (and nuggets) into your own hands. You march into McDonald’s, get two 20-piece boxes, and head home like a scientist on a mission. Now, before you start weighing each nugget like they’re precious gold nuggets, let’s talk hypotheses. The average weight of nuggets as mentioned on the box is 16 g each. Develop your null and alternative hypotheses separately. Next, you weigh each nugget with the precision of a jeweler and find they average out to 15.5 grams. You also conduct a statistical analysis, and the p-value turns out to be 0.01. Based on this information, answer the following questions. (Remember,…arrow_forwardBusiness Discussarrow_forwardCape Fear Community Colle X ALEKS ALEKS - Dorothy Smith - Sec X www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQ1w4xc5zw7yX8A9Q43nt5P1XWJWARE... Section 7.1,7.2,7.3 HW 三 Question 21 of 28 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 5 of Unlimited The proportion of phones that have more than 47 apps is 0.8783 Part: 1 / 2 Part 2 of 2 (b) Find the 70th The 70th percentile of the number of apps. Round the answer to two decimal places. percentile of the number of apps is Try again Skip Part Recheck Save 2025 Mcarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





