
Travels with My Ant: The Curtate and Prolate Cycloids
Earlier in this section, we looked at the parametric equations for a cycloid, which is the path a point on the edge of a wheel traces as the wheel rolls along a straight path. In this project we look at two different variations of the cycloid, called the curtate and prolate cycloids.
First, let’s revisit the derivation of the parametric equations for a cycloid. Recall that we considered a tenacious ant trying to get home by hanging onto the edge of a bicycle tire. We have assumed the ant climbed onto the tire at the very edge, where the tire touches the ground. As the wheel rolls, the ant moves with the edge of the tire (Figure 7.13).
As we have discussed, we have a lot of ?exibility when parameterizing a curve. In this case we let our parameter t represent the angle the tire has rotated through. Looking at Figure 7.13, we see that after the tire has rotated through an angle of t, the position of the center of the wheel,
Furthermore, letting
Then
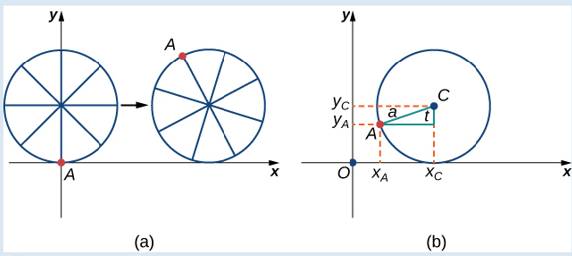
Figure 7.13 (a) The ant clings to the edge of the bicycle tire as the tire rolls along the ground. (b) Using geometry to determine the position of the ant after the tire has rotated through an angle of t.
Note that these are the same parametric representations we had before, but we have now assigned a physical meaning to the parametric variable t.
After a while the ant is getting dizzy from going round and round on the edge of the tire. So he climbs up one of the spokes toward the center of the wheel. By climbing toward the center of the wheel, the ant has changed his path of motion. The new path has less up—and-down motion and is called a curtate cycloid (Figure 7.14). As shown in the figure, we let b denote the distance along the spoke from the center of the wheel to the ant. As before, we let t represent the angle the tire has rotated through. Additionally, we let
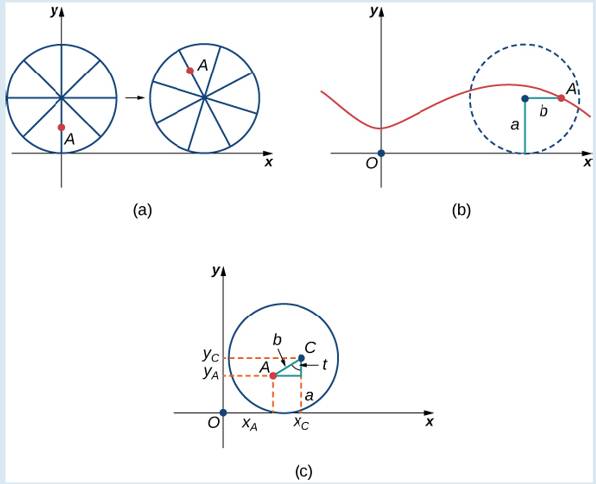
Figure 7.14 (a) The ant climbs up one of the spokes toward the center of the wheel. (b) The ant’s path of motion after he climbs closer to the center of the wheel. This is called a curtate cycloid. (c) The new setup, now that the ant has moved closer to the center of the wheel.
5. What do you notice about your answer to part 3 and your answer to part 4?
Notice that the ant is actually traveling backward at times (the “loops” in the graph), even though the train continues to move forward. He is probably going to be real1y dizzy by the time he gets home!
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
Calculus Volume 2
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardWhich degenerate conic is formed when a double cone is sliced through the apex by a plane parallel to the slant edge of the cone?arrow_forwardFor the problem below, what are the possible solutions for x? Select all that apply. 2 x²+8x +11 = 0 x2+8x+16 = (x+4)² = 5 1116arrow_forward
- For the problem below, what are the possible solutions for x? Select all that apply. x² + 12x - 62 = 0 x² + 12x + 36 = 62 + 36 (x+6)² = 98arrow_forwardSelect the polynomials below that can be solved using Completing the Square as written. 6m² +12m 8 = 0 Oh²-22x 7 x²+4x-10= 0 x² + 11x 11x 4 = 0arrow_forwardProve that the usual toplogy is firast countble or hot and second countble. ①let cofinte toplogy onx show that Sivast countble or hot and second firast. 3) let (x,d) be matricspace show that is first and second countble. 6 Show that Indiscret toplogy is firstand Second op countble or not.arrow_forward
- H.W For any events A and B, show that 1. P(AB)s P(A)≤ P(AUB)≤ P(A) + P(B)arrow_forwarda) Find the scalars p, q, r, s, k1, and k2. b) Is there a different linearly independent eigenvector associated to either k1 or k2? If yes,find it. If no, briefly explain.arrow_forwardPlz no chatgpt answer Plz Will upvotearrow_forward
- 1/ Solve the following: 1 x + X + cos(3X) -75 -1 2 2 (5+1) e 5² + 5 + 1 3 L -1 1 5² (5²+1) 1 5(5-5)arrow_forwardI need expert handwritten solution.to this integralarrow_forwardHow to understand and learn Laurent's serial and what's the point of Laurent's serial And what are the steps of a smooth solution for Laurentarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning





