
Concept explainers
John can take either of two routes (A or B) to LAX airport. At midday on a typical Wednesday the travel time on either route is
a.
Find the better route for John to reach at the airport in 54 minutes to pick up his spouse.
Answer to Problem 91CE
The better route for John to reach at the airport in 54 minutes to pick up his spouse is route A.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
It is given that the time on route A follows normal distribution with mean of 54 minutes, standard deviation of 6 minutes and the time on route B follows normal distribution with mean of 60 minutes, standard deviation of 3 minutes.
Normal distribution:
A continuous random variable X is said to follow normal distribution if the probability density function of X is,
Assume that the random variable X denotes the time to reach airport.
For route A:
It is given that
Now, the probability to reach at the airport in 54 minutes using route A, implies that
Probability value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain probability value using EXCEL is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.DIST(54,54,6,1)”.
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
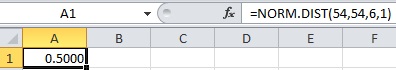
Therefore,
Thus, the probability to reach at the airport in 54 minutes using route A is 0.5.
For route B:
It is given that
Now, the probability to reach at the airport in 54 minutes using route B, implies that
Probability value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain probability value using EXCEL is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.DIST(54,60,3,1)”.
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
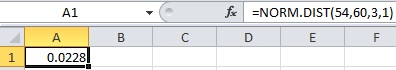
Therefore,
Thus, the probability to reach at the airport in 54 minutes using route B is 0.0228.
Therefore, there is more chance to reach airport by route A than by route B.
Thus, the better route for John to reach at the airport in 54 minutes to pick up his spouse is route A.
b.
Find the better route for John to reach at the airport in 66 minutes to pick up his spouse.
Answer to Problem 91CE
The better route for John to reach at the airport in 60 minutes to pick up his spouse is route A.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For route A:
It is given that
Now, the probability to reach at the airport in 66 minutes using route A, implies that
Probability value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain probability value using EXCEL is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.DIST(60,54,6,1)”.
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
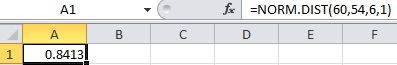
Therefore,
Thus, the probability to reach at the airport in 60 minutes using route A is 0.8413.
For route B:
It is given that
Now, the probability to reach at the airport in 60 minutes using route B, implies that
Probability value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain probability value using EXCEL is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.DIST(60,60,3,1)”.
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
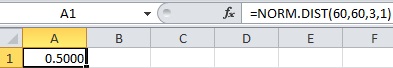
Therefore,
Thus, the probability to reach at the airport in 60 minutes using route B is 0.5.
Therefore, there is more chance to reach airport by route A than by route B.
Thus, the better route for John to reach at the airport in 60 minutes to pick up his spouse is route A.
c.
Find the better route for John to reach at the airport in 60 minutes to pick up his spouse.
Answer to Problem 91CE
The better route for John to reach at the airport in 66 minutes to pick up his spouse is route B.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Coefficient of variation:
Coefficient of variation for a random variable X is defined as,
It is better to use a random variable with lower CV.
For route A:
It is given that
Now, the probability to reach at the airport in 66 minutes using route A, implies that
Probability value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain probability value using EXCEL is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.DIST(66,54,6,1)”.
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
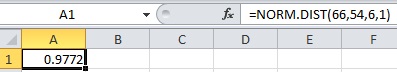
Therefore,
Thus, the probability to reach at the airport in 66 minutes using route A is 0.9972.
The CV for route A is,
For route B:
It is given that
Now, the probability to reach at the airport in 66 minutes using route B, implies that
Probability value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain probability value using EXCEL is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.DIST(66,60,3,1)”.
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
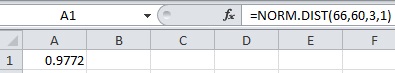
Therefore,
Thus, the probability to reach at the airport in 66 minutes using route B is 0.9972.
The CV for route B is,
Therefore, there is same chance to reach airport by route A and route B.
Now, the coefficient of variation for route B is less than route A.
Thus, the better route for John to reach at the airport in 66 minutes to pick up his spouse is route B.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Applied Statistics in Business and Economics
- For context, the images attached below are a question from a June, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the images attached below (question and related graph) are from a February 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the images attached below are from a February 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forward
- For context, the image provided below is a question from a September, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the image below is from a January 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the image provided below is a question from a September, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forward
- Section 2.2 Subsets 71 Exercise Set 2.2 Practice Exercises In Exercises 1-18, write or in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. 1. {1, 2, 5} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} 2. {2, 3, 7} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} 3. {-3, 0, 3} {-4,-3,-1, 1, 3, 4} 4. {-4, 0, 4} 5. {Monday, Friday} {-3, -1, 1, 3} {Saturday, Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday} 6. {Mercury, Venus, Earth} {Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter} 7. {x/x is a cat} {xx is a black cat} {x|x is a pure-bred dog} ibrary mbers, ause the entire sual 8. {xx is a dog} 9. (c, o, n, v, e, r, s, a, t, i, o, n} {v, o, i, c, e, s, r, a, n, t, o, n} 10. [r, e, v, o, l, u, t, i, o, n} {t, o, l, o, v, e, r, u, i, n} 33. A = {x|x E N and 5 < x < 12} B = {x|x E N and 2 ≤ x ≤ 11} A_ B 34. A = {x|x = N and 3 < x < 10} B = A. {x|x = N and 2 ≤ x ≤ 8} B 35. Ø {7, 8, 9,..., 100} 36. Ø _{101, 102, 103, . . ., 200} 37. [7, 8, 9,...} 38. [101, 102, 103, ...} 39. Ø 40. { } { } e In Exercises 41-54, determine whether each statement is true or false. If…arrow_forwardA = 5.8271 ± 0.1497 = B 1.77872 ± 0.01133 C=0.57729 ± 0.00908 1. Find the relative uncertainty of A, B, and C 2. Find A-3 3. Find 7B 4. Find A + B 5. Find A B-B - 6. Find A * B 7. Find C/B 8. Find 3/A 9. Find A 0.3B - 10. Find C/T 11. Find 1/√A 12. Find AB²arrow_forwardWhy charts,graphs,table??? difference between regression and correlation analysis.arrow_forward
- You’re scrolling through Instagram and you notice that a lot of people are posting selfies. This piques yourcuriosity and you want to estimate the percentage of photos on Instagram that are selfies.(a) (5 points) Is there a “ground truth” for the percentage of selfies on Instagram? Why or why not?(b) (5 points) Is it possible to estimate the ground truth percentage of selfies on Instagram?Irrespective of your answer to the previous question, you decide to pull up n = 250 randomly chosenphotos from your friends’ Instagram accounts and find that 32% of these photos are selfies.(c) (15 points) Determine which of the following is an observation, a variable, a sample statistic (valuecalculated based on the observed sample), or a population parameter.• A photo on Instagram.• Whether or not a photo is a selfie.• Percentage of all photos on Instagram that are selfies.• 32%.(d) (5 points) Based on the sample you collected, do you think 32% is a reliable ballpark estimate for theground truth…arrow_forwardCan you explain this statement below in layman's terms? Secondary Analysis with Generalized Linear Mixed Model with clustering for Hospital Center and ICUvs Ward EnrolmentIn a secondary adjusted analysis we used generalized linear mixed models with random effects forcenter (a stratification variable in the primary analyses). In this analysis, the relative risk for the primaryoutcome of 90-day mortality for 7 versus 14 days of antibiotics was 0.90 (95% Confidence Interval [CI]0.78, 1.05).arrow_forwardIn a crossover trial comparing a new drug to a standard, π denotes the probabilitythat the new one is judged better. It is desired to estimate π and test H0 : π = 0.5against H1 : π = 0.5. In 20 independent observations, the new drug is better eachtime.(a) Find and plot the likelihood function. Give the ML estimate of π (Hint: youmay use the plot function in R)arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt  Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell




