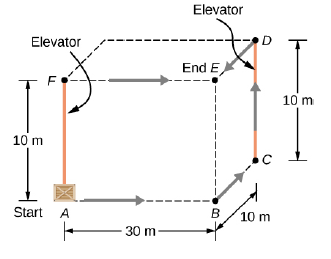
Problem 7.1CYU: Check Your Understanding Can kinetic friction ever be a constant force for all paths? Problem 7.2CYU: Check Your Understanding Can Earth’s gravity ever be a constant force for all paths? Problem 7.3CYU: Check Your Understanding Find the work done by the same force in Example 7.4 over a cubic path,... Problem 7.4CYU: Check Your Understanding The spring Example 7.5 is compressed 6 cm from its equilibrium length. (a)... Problem 7.5CYU: Check Your Understanding (a) A car and a truck each moving with the same kinetic energy. Assume that... Problem 7.6CYU: Check Your Understanding You are rowing a boat parallel to the banks of a river. Your kinetic energy... Problem 7.7CYU: Check Your Understanding suppose the radius of the loop-the-loop in Example 7.9 is 15 cm and the toy... Problem 7.8CYU: Check Your Understanding Estimate the power expended by a weightlifter raising a 150-kg barbell 2 m... Problem 1CQ: Give an example of something we think of as work in everyday circumstances that is not work in the... Problem 2CQ: Give an example of a situation in which there is a force and a displacement, but the force does no... Problem 3CQ: Describe a situation in 4iich a force is exerted for a long time but does no work. Explain. Problem 4CQ: A body moves in a circle at constant speed. Does the centripetal force that accelerates the body do... Problem 5CQ: Suppose you throw a ball upward and catch it when it returns at the same height. How much work does... Problem 6CQ: Why is it more difficult to do sit-ups while on a slant board than on a horizontal surface? (See... Problem 7CQ: As a young man, Tarzan climbed up a vine to reach his tree house. As he got older, he decided to... Problem 8CQ: A particle of m has a velocity of . Is its kinetic energy given by ? If not, what is the correct... Problem 9CQ: One particle has mass mand a second particle has mass 2m . The second particle is moving with speed... Problem 10CQ: A person drops a pebble of mass m1from a height h, and it hits the floor with kinetic energy K. The... Problem 11CQ: The person shown below does work on the lawn mower. Under what conditions would the mower gain... Problem 12CQ: Work done on a system puts energy into it. Work done by a system removes energy from it. Give an... Problem 13CQ: Two marbles of masses mand 2mare dropped from a height h. Compare their kinetic energies when they... Problem 14CQ: Compare the work required to accelerate a car of mass 2000 kg from 30.0 to 400 km/h with that... Problem 15CQ: Suppose you are jogging at constant velocity. Are you doing any work on the environment and vice... Problem 16CQ: Two forces act to double the speed of a particle, initially moving with kinetic energy of 1 J. One... Problem 17CQ: Most electrical appliances are rated in watts. Does this rating depend on how long the appliance is... Problem 18CQ: Explain, in terms of the definition of power, why energy consumption is sometimes listed in... Problem 19CQ: A spark of static electricity, such as that you might receive from a doorknob on a cold dry day, may... Problem 20CQ: Does the work done in lifting an object depend on how fast it is lifted? Does the power expended... Problem 21CQ: Can the power expended by a force be negative? Problem 22CQ: How can a 50-W light bulb use more energy than a 1000-W oven? Problem 23P: Work How much work does a supermarket checkout attendant do on a can of sip he pushes 0.600 m... Problem 24P: A 75.0-kg person climbs stairs, gaining 2.50 m in height. Find the work done to accomplish this... Problem 25P: (a) Calculate the work done on a 1500-kg elevator car by its cable to lift it 40.0 m at constant... Problem 26P: Suppose a car travels 108 km at a speed of 30.0 m/s, and uses 2.0 gal of gasoline. Only 30 of the... Problem 27P: Calculate the work done by an 85.0-kg man who pushes a crate 4.00 m up along a ramp that makes an... Problem 28P: How much work is done by the boy pulling his sister 30.0 m in a wagon as shown below? Assume no... Problem 29P: A shopper pushes a grocery cart 20.0 m at constant speed on level ground, against a 35.0 N... Problem 30P: Suppose the ski patrol lowers a rescue sled and victim, having a total mass of 90.0 kg, down a 60.00... Problem 31P: A constant 20-N force pushes a small ball in the direction of the force over a distance of 5.0 m.... Problem 32P: A toy cart is pulled a distance of 6.0 m in a straight line across the floor. The force pulling the... Problem 33P: A 5.0-kg box rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and... Problem 34P: A sled plus passenger with total mass 50 kg is pulled 20 m across the snow (K=0.20) at constant... Problem 35P: Suppose that the sled plus passenger of the preceding problem is pushed 20 m across the snow at... Problem 36P: How much work does the force do on a particle as it moves from to Problem 37P: How much work is done against the gravitationaI force on a 5.0-kg briefcase when it is carried from... Problem 38P: It takes 500 J of work to compress a spring 10 cm. What is the force constant of the spring? Problem 39P: A bungee cord is essentially a very long rubber band that can stretch up to four times its... Problem 40P: A bungee cord exerts a nonlinear elastic force of magnitude where is the distance the cord is... Problem 41P: Engineers desire to model the magnitude of the elastic force of a bungee cord using the equation... Problem 42P: A particle moving in the xy -plane is subject to a force F(x,y)=(50Nm2)(xi+yj)( x 2 + y 2 )3/2 ,... Problem 43P: A particle moves along a curved path y(x)=(10m){1+cos[0.1m1]x} , from x=0 to x=10m , subject to a... Problem 44P: Kinetic Energy Compare the kinetic energy of a 20,000-kg truck moving at 110 km/h with that of an... Problem 45P: (a) How fast must a 3000-kg elephant move to have the same kinetic energy as a 65.0-kg sprinter... Problem 46P: Estimate the kinetic energy of a 90,000-ton aircraft carrier moving at a speed of at 30 knots. You... Problem 47P: Calculate the kinetic energies of (a) a 2000.0-kg automobile moving at 100.0 km/h; (b) an 80.-kg... Problem 48P: A 5.0-kg body has three times the kinetic energy of an 8.0-kg body. Calculate the ratio of the... Problem 49P: An 8.0-g bullet has a speed of 800 m/s. (a) What is its kinetic energy? (b) What is its kinetic... Problem 50P: (a) Calculate the force needed to bring a 950-kg car to rest from a speed of 90.0 km/h in a distance... Problem 51P: A car’s bumper is designed to withstand a 4.0-km/ h (1.1-m/s) collision with an immovable object... Problem 52P: Boxing gloves are padded to lessen the force of a blow. (a) Calculate the force exerted by a boxing... Problem 53P: Using energy considerations, calculate the average force a 60.0-kg sprinter exerts backward on the... Problem 54P: A 5.0-kg box has an acceleration of 2.0m/s2 when it is pulled by a horizontal force across a surface... Problem 55P: A constant 10-N horizontal force is applied to a 20-kg cart at rest on a level floor. If friction is... Problem 56P: In the preceding problem, the 10-N force is applied at an angle of 45 below the horizontal. What is... Problem 57P: Compare the work required to stop a 100-kg crate sliding at 1.0 m/s and an 8.0-g bullet traveling at... Problem 58P: A wagon with its passenger sits at the top of a hill. The wagon is given a slight push and rolls 100... Problem 59P: An 8.0-g bullet with a speed of 800 m/s is shot in to a wooden block and penetrates 20 cm before... Problem 60P: A 2.0-kg block starts with a speed of 10 m/s at the bottom of a plane inclined at 37 to the... Problem 61P: When a 3.0-kg block is pushed against a massless spring of force constant constant 4.5103N/m , the... Problem 62P: A small block of mass 200 g starts at rest at A, slides to B where its speed is then slides along... Problem 63P: A small object is placed at the top of an incline that is essentially frictionless. The object... Problem 64P: When released, a 100-g block slides down the path shown below, reaching the bottom with a speed of... Problem 65P: A 0.22LR-caliber bullet like that mentioned in Example 7.10 is fired into a door made of a single... Problem 66P: A sled stalls from rest at the top of a snow-covered incline that makes a 22 angle with the... Problem 67P: A person in good physical condition can put out 100 W of useful power for several hours at a... Problem 68P: What is the cost of operating a 3.00-W electric clock for a year if the cost of electricity is... Problem 69P: A large household air conditioner may consume 15.0 kW of power. What Is the cost of operating this... Problem 70P: (a) What is the average power consumption in watts of an appliance that uses 5.00kWh of energy per... Problem 71P: (a) What is the average useful power output of a person who does 6.00106J of useful work in 8.00 h?... Problem 72P: A 500-kg dragster accelerates from rest to a final speed of 110 m/s in 400 m (about a quarter of a... Problem 73P: (a) How long will it take an 850-kg car with a useful power output of 40.0 hp (1 hp equals 746 W) to... Problem 74P: (a) Fir the useful power output of an elevator motor that Lifts a 2500-kg load a height of 35.0 m in... Problem 75P: (a) How long would it take a 1.50105kg airplane with engines that produce 100 MW of power to reach a... Problem 76P: Calculate the power output needed for a 950-kg car to climb a 2.00 slope at a constant 30.0 m/s... Problem 77P: A man of mass 80 kg runs up a flight of stairs 20 m high in 10 s. (a) how much power is used to lift... Problem 78P: The man of the preceding problem consumes approximately 1.05107J (2500 food calories) of energy per... Problem 79P: An electron in a television tube is accelerated uniformly from rest to a speed of 8.4107 m/s over a... Problem 80P: Coal is lifted out of a mine a vertical distance of 50 m by an engine that supplies 500 W to a... Problem 81P: A girl pulls her 15-kg wagon along a flat sidewalk by applying a 10-N force at 37 to the horizontal.... Problem 82P: A typical automobile engine has an efficiency of 25 . Suppose that the engine of a 1000-kg... Problem 83P: When jogging at 13 km/h on a level surface, a 70-kg man uses energy at a rate of approximately 850... Problem 84AP: A cart is pulled a distance D on a flat, horizontal surface by a constant farce F that acts at an... Problem 85AP: Consider a particle on which several forces act, one of which is known to be constant in time: . As... Problem 86AP: Consider a particle on which several forces act, one of which is known to be constant in time: . As... Problem 87AP: Consider a particle on which several forces act, one of which is known to be constant in time: . As... Problem 88AP: Consider a particle on which a force acts that depends on the position of the particle. This force... Problem 89AP: A boy pulls a 5-kg cart with a 20-N force at an angle of 30 above the horizontal for a length of... Problem 90AP: A crate of mass 200 kg is to be bright from a site on the ground floor to a third floor apartment.... Problem 91AP: At hokey puck of mass 0.17 kg is shot across a rough floor with the roughness different at different... Problem 92AP: A horizontal force of 20 N is required to keep a 5.0 kg box traveling at a constant speed up a... Problem 93AP: A 7.0-kg box slides along a horizontal frictionless floor at 1.7 m/s and collides with a relatively... Problem 94AP: You are driving your car on a straight road with a coefficient of friction between the tires and the... Problem 95AP: A crate is being pushed across a rough floor surface. If no force is applied on the crate, the crate... Problem 96AP: Suppose a horizontal force of 20 N is required to maintain a speed of 8 m/s of a 50 kg crate. (a)... Problem 97AP: Grains from a hopper falls at a rate of 10 kg/s vertically onto a conveyor belt that is moving... Problem 98AP: A cyclist in a race must climb a 5 hill at a speed of 8 m/s. If the mass of the bike and the biker... Problem 99CP: Shown below is a 40-kg crate that is pushed at constant velocity a distance 8.0 m along a 30 Incline... Problem 100CP: The surface of the preceding problem is modified so that the coefficient of kinetic friction is... Problem 101CP: The force F(x) varies with position, as shown beolow Find the work done by this force on a particle... Problem 102CP: Find the work done by the same force in Example 7.4, between the same points, A=(0,0) and B=(2m,2m)... Problem 103CP: Answer the preceding problem using polar coordinates. Problem 104CP: Find the work done by the same force in Example 7.4, between the same points, A=(0,0) and B=(2m,2m)... Problem 105CP: Answer the preceding problem using polar coordinates. Problem 106CP: Constant power P is delivered to a car of mass m by its engine. Show that If air resistance can be... Problem 107CP: Suppose that the air resistance a car encounters is independent of its speed. When the car travels... Problem 108CP: Consider a linear spring, as in Figure 7.7(a), with mass M uniformly distributed along its length.... format_list_bulleted


 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




