
Concept explainers
Predict the geometries of the following species using the VSEPR method: (a) PCl3, (b) CHCl3, (c) SiH4, (d) TeCl4.
(a)
Interpretation: For the given set of molecules the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
If the molecules (
The molecules of type
The molecules of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Answer to Problem 7.9QP
(a)
Trigonal pyramidal
Explanation of Solution
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (a)
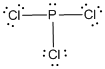
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 26.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 6 has to be subtracted with 26 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are three bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 20 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (a) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral since the
The molecular geometry for the given molecule is trigonal pyramidal due to the presence of one lone pair around the central atom.
(b)
Interpretation: For the given set of molecules the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
If the molecules (
The molecules of type
The molecules of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Answer to Problem 7.9QP
(b)
Tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (b)
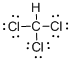
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 26.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 8 has to be subtracted with 26 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are four bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 18 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (b) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral as there is no lone pair of electron over the central metal atom and hence the molecular geometry for the given molecule is also Tetrahedral.
(c)
Interpretation: For the given set of molecules the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
If the molecules (
The molecules of type
The molecules of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Answer to Problem 7.9QP
Answer
(c)
Tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (c)
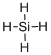
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 8.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 8 has to be subtracted with 8 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are four bonds in the skeletal structure.
There are no remaining electrons hence all the atoms in the molecules are fulfilled the octet rule that is each atom involves in bonding in order to fill their valence with eight electrons.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (c) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral since central atom does not contain any lone pair of electron with it.
The molecular geometry for the molecule is also tetrahedral as there are four atoms bonded with the central metal atom and there is absence of lone pair of electrons.
(d)
Interpretation: For the given set of molecules the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
If the molecules (
The molecules of type
The molecules of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Answer to Problem 7.9QP
(d)
See-saw shaped
Explanation of Solution
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (d)
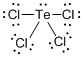
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 34.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 8 has to be subtracted with 8 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are four bonds in the skeletal structure.
Then the 26 electrons got after the subtractions should be placed over the atoms present in the molecule such that each atom contains eight electrons in the valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (d) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure shows that it contains five electron domains since it has 4 chlorine atoms and one lone pair with it.
The molecular geometry for the molecule is see-saw shape due to the present of that one lone pair of electron.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST VOL 1 W/CONNECT
- OH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forwardFor the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward
- 14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forwardΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward:0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forward
- Draw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

