
Concept explainers
Predict the bond angles for the following molecules: (a) BeCl2, (b) BCl3, (c) CCl4, (d) CH3Cl, (e) Hg2Cl2 (arrangement of atoms: ClHgHgCl), (f) SnCl2, (g) H2O2, (h) SnH4.
(a)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
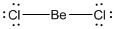
(b)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
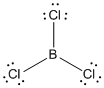
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
(c)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
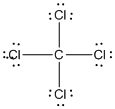
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
(d)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
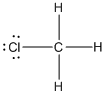
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
(e)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
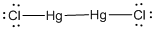
In the case of
(f)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
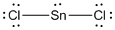
In the case of
(g)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
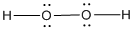
In the case of
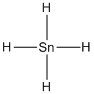
(h)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.103QP
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST VOL 1 W/CONNECT
- Draw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with one pen and all in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the oxidation of 3-bromo-cyclohexan-1-ol.arrow_forwardConvert the following Fischer projection to Haworth projections. show work and show the arrows please.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the substitution reaction converting an alcohol into an alkyl halide. If chirality is important to the reaction include it.arrow_forwardWrite, in words three different reactions we can use to make an alcohol.arrow_forwardDraw the reduction mechanism for the reduction of the aldehyde.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





