
Concept explainers
Predict the geometries of the following ions: (a) NH4+, (b) NH2−, (c) CO32−, (d) ICl2−, (e) IC14−, (f) AlH4−, (g) SnCl5− (h) H3O+, (i) BeF42−.
(a)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
Tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (a)
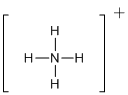
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 8.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 8 has to be subtracted with 8 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are four bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the structure does not have any electrons to be placed over the atoms since all the atoms have completed its valance shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (a) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral since the central atom
There exist no lone pair on central atom hence the molecular geometry for this molecule is also tetrahedral.
(b)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
(b)
Bent
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (b)
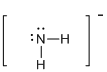
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 8.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 4 has to be subtracted with 8 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are two bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 4 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom have completed valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (b) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral.
Therefore, the molecular geometry for the given molecules is bent due to the presence of two lone pair of electrons with it.
(c)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
(c)
Trigonal planar
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (c)
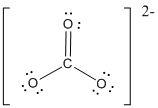
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 24.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 6 has to be subtracted with 24 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are three bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 18 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell then considering the valency of carbon one
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (c) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type trigonal planar since there are 3 oxygen atoms bonded with carbon in
There exist no lone pair on central atom hence the molecular geometry for this molecule is also trigonal planar.
(d)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
Answer
(d)
Linear
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (d)
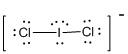
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 22 since it has one extra negative charge with it.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 4 has to be subtracted with 22 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are two bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 18 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (d) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral due to the presence of two lone pairs.
Therefore, the molecular geometry for the given molecule is bent because of the repulsions produced by the two lone pairs present in the central atom.
(e)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
(e)
Square planar
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (e)
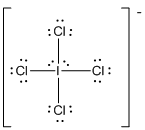
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 36.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 8 has to be subtracted with 36 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are four bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 28 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (e) using VSEPR.
Explanation:
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type octahedral since there are four
Therefore, the geometry for the molecule is square planar due to the presence of two lone pair of electrons.
(f)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
To predict: The geometry for the given molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
(f)
Tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (f)
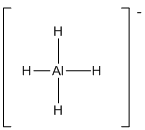
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 8 which include the presence one negative charge with it.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 8 has to be subtracted with 8 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are four bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, there are no electrons to be placed over the atoms.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (f) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral since there are four
There exist no lone pair on central atom hence the molecular geometry for this molecule is also tetrahedral.
(g)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
The geometry for the given molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
Solution
(g)
Trigonal bipyramidal
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (g)
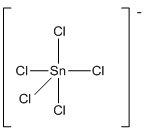
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 40 which include the presence one negative charge with it.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 10 has to be subtracted with 40 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are five bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 30 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (g) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type trigonal bipyramidal since there are five chlorine atoms bonded with the central atom.
There exists no lone pair on central atom hence the molecular geometry for this molecule is also trigonal bipyramidal.
(h)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
Answer
(h)
Trigonal pyramid
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (h)
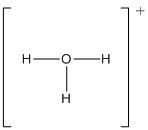
Explanation of Solution
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 8 which is included with the positive charge present in the given ion.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 6 has to be subtracted with 8 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are three bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 2 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (h) using VSEPR.
Explanation:
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral since there are three
Therefore, the molecular geometry for the given ion is trigonal pyramidal since there exist one lone pair over O atom which is bonded with three hydrogen atoms.
(i)
Interpretation: For the given set of ions the molecular geometry around the central metal should be predicted using VSEPR model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular geometry: It is defined as unique three dimensional arrangements of atoms around the central metal present in the molecule which is determined by using spectroscopic techniques and also by using Lewis structure or the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
The geometry for the given molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.10QP
(i)
Tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule (i)
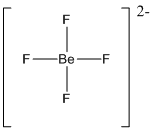
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is 32 which includes with the two negative charges present in the given ion.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the molecule with the total valence electrons such that 8 has to be subtracted with 32 as each bond contains two electrons with it and there are four bonds in the skeletal structure.
Finally, the 24 electrons got after subtractions has to be equally distributed over the fluorine atoms present in the molecule such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule (i) using VSEPR.
The electron domain for the given molecule is obtained by viewing the Lewis structure which is of type tetrahedral since central atom does not contain any lone pair of electron with it.
The molecular geometry for the molecule is also tetrahedral as there is no lone pair of electrons present in the given ion.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST VOL 1 W/CONNECT
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning



