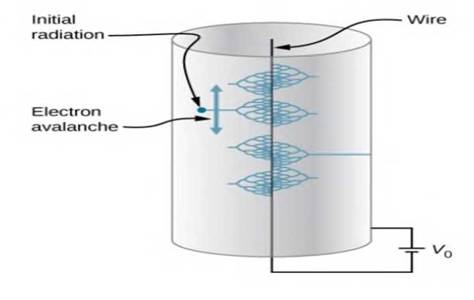
Problem 7.1CYU: Check Your Understanding If Q has a mass of 4.00 g , what is the speed of Q at r2 ? Problem 7.2CYU: Check Your Understanding What is the potential energy of Q relative to the zero reference at... Problem 7.3CYU: Check Your Understanding Is the electrical potential energy of two point charges positive or... Problem 7.4CYU: Check Your Understanding How much energy does a 1.5-V AAA battery have that can move 100C ? Problem 7.5CYU: Check Your Understanding How many electrons would go through a 24.0-W lamp? Problem 7.6CYU: Check Your Understanding How would this example change with a positron? A positron is identical to... Problem 7.7CYU: Check Your Understanding From the examples, how does the energy of a lightning strike vary with the... Problem 7.8CYU: Check Your Understanding What is the potential inside the metal sphere in Example 7.10? Problem 7.9CYU: Check Your Understanding What is the potential on the x-axis? The z-axis? Problem 7.10CYU: Check Your Understanding What is the potential on the axis of a nonuniform ring of charge, where the... Problem 7.11CYU: Check Your Understanding Which coordinate system would you use to calculate the electric field of a... Problem 7.12CYU: Check Your Understanding What are the equipotential surfaces for an infinite line charge? Problem 1CQ: Would electric potential energy be meaningful if the electric field were not conservative? Problem 2CQ: Why do we need to be careful about work done on the system versus work done by the system in... Problem 3CQ: Does the order in which we assemble a system of point charges affect the total work done? Problem 4CQ: Discuss how potential difference and electric field strength are related. Give an example. Problem 5CQ: What is die strength of the electric field in a region where the electric potential is constant? Problem 6CQ: If a proton is released from rest in an electric field, will it move in the direction of increasing... Problem 7CQ: Voltage is the common word for potential difference. Which term is more descriptive, voltage or... Problem 8CQ: If the voltage between two points is zero can a test charge be moved between them with zero net work... Problem 9CQ: Wliat is the relationship between voltage and energy? More precisely, what is the relationship... Problem 10CQ: Voltages are always measured between two points Why? Problem 11CQ: How are units of volts and electron-volts related? How do they differ? Problem 12CQ: Can a particle move in a direction of increasing electric potential, yet have its electric potential... Problem 13CQ: Compare the electric dipole moments of charges +Q separated by a distance d and charges +Q/2... Problem 14CQ: Would Gauss’s law be helpful for determining the electric field of a dipole? Why? Problem 15CQ: In what region of space is the potential due to a uniformly charged sphere the same as that of a... Problem 16CQ: Can the potential of a nonuniformly charged sphere be the same as that of a point charge? Explain. Problem 17CQ: If the electric field is zero throughout a region, must the electric potential also be zero in that... Problem 18CQ: Explain why knowledge of E(x, y, z) is not sufficient to determine V(x,y,z). What about the other... Problem 19CQ: If two points are at the same potential, are there any electric field lines connecting them? Problem 20CQ: Suppose you have a map of equipotential surfaces spaced 1.0 V apart. What do die distances between... Problem 21CQ: Is the electric potential necessarily constant over the surface of a conductor? Problem 22CQ: Linder electrostatic conditions, the excess charge on a conductor resides on its surface. Does this... Problem 23CQ: - Can a positively charged conductor be at a negative potential? Explain. Problem 24CQ: Can equipotential surfaces intersect? Problem 25CQ: Why are the metal support rods for satellite network dishes generally grounded? Problem 26CQ: (a) Why are fish reasonably safe in an electrical storm? (b) Why are swimmers nonetheless ordered to... Problem 27CQ: What are the similarities and differences between the processes in a photocopier and an... Problem 28CQ: About what magnitude of potential is used to charge the drum of a photocopy machine? A web search... Problem 29P: Consider a charge Q1(1+5.0C) fixed at a site with another charge Q2 (Charge +3.0C , mass 6.0g )... Problem 30P: Two charges Q1(1+2.00C) and Q2(+2.00C are placed symmetrically along the x-axis at x=3.00cm .... Problem 31P: To form a hydrogen atom, a proton is fixed at a point and an electron is brought from far away to a... Problem 32P: (a) What is the average power output of a heart defibrillator that dissipates 400 J of energy in... Problem 33P: Find the ratio of speeds of an electron and a negative hydrogen ion (one having an extra election)... Problem 34P: An evacuated tube uses an accelerating voltage of 40 kV to accelerate electrons to hit a copper... Problem 35P: Show that units of V/m and N/C for electric field strength are indeed equivalent. Problem 36P: What is the strength of the electric field between two parallel conducting plates separated by 1.00... Problem 37P: The electric field strength between two parallel conducting plates separated by 4.00 cm is 7.50104... Problem 38P: The voltage across a membrane forming a cell wall is 80.0 mV and the membrane is 9.00 nm thick. What... Problem 39P: Two parallel conducting plates are separated by 10.0 cm, and one of them is taken to be at zero... Problem 40P: Find the maximum potential difference between two parallel conducting plates separated by 0.500 cm... Problem 41P: An electron is to be accelerated in a uniform electric field having a strength of 2.00106 V/m. (a)... Problem 42P: Use die definition of potential difference in terms of electric field to deduce die formula for... Problem 43P: The electric field in a region is pointed away from the z-axis and the magnitude depends upon the... Problem 44P: Singly charged gas ions are accelerated from rest through a voltage of 13.0 V. At what temperature... Problem 45P: A 0.500-cm-diameter plastic sphere, used in a static electricity demonstration, has a uniformly... Problem 46P: How far from a 1.00C point charge is the potential 100 V? At what distance is it 2.00102V ? Problem 47P: If the potential due to a point charge is 5.00102 V at a distance of 15.0 m, what are the sign and... Problem 48P: In nuclear fission, a nucleus splits roughly in half, (a) What is the potential 2.001014 in from a... Problem 49P: A research Vail de Graaff generator has a 2.00-m- diameter metal sphere with a charge of 5.00 mC on... Problem 50P: An electrostatic paint sprayer has a 0.200-m-diameter metal sphere at a potential of 25.0 kV that... Problem 51P: (a) What is the potential between two points situated 10 cm and 20 cm from a 3.0C point charge? (b)... Problem 52P: Find the potential at points P1,P2,andP4 in the diagram due to the two given charges. Problem 53P: Two charges 20Cand+2.0C are separated by 4.0 cm on the z-axis symmetrically about origin, with the... Problem 54P: (a) Plot the potential of a uniformly charged 1-m rod with 1 C/m charge as a function of the... Problem 55P: Throughout a region, equipotential surfaces are given by z = constant. The surfaces are equally... Problem 56P: In a particular region, the electric potential is given by V=xy2z+4xy . What is the electric field... Problem 57P: Calculate the electric field of an infinite line charge, throughout space. Problem 58P: Two very large metal plates are placed 2.0 cm apart, with a potential difference of 12 V between... Problem 59P: A very large sheet of insulating material has had an excess of electrons placed on it to a surface... Problem 60P: A metallic sphere of radius 2.0 cm is charged with +5.0C charge, which spreads on the surface of the... Problem 61P: Two large charged plates of charge density 30C/m2 face each other at a separation of 5.0 mm. (a)... Problem 62P: A long cylinder of aluminum of radius R meters is charged so that it has a uniform charge per unit... Problem 63P: Two parallel plates 10 cm on a side are given equal and opposite charges of magnitude 5.0109 C. The... Problem 64P: The surface charge density on a long straight metallic pipe is . What is the electric potential... Problem 65P: Concentric conducting spherical shells carry charges Q and -Q, respectively. The inner shell has... Problem 66P: Shown below are two concentric spherical shells of negligible thicknesses and radii R1and R2The... Problem 67P: A solid cylindrical conductor of radius a is surrounded by a concentric cylindrical shell of inner... Problem 68P: (a) What is the electric field 5.00 m from die center of the terminal of a Van de Graaff with a... Problem 69P: (a) What is the direction and magnitude of an electric field that supports the weight of a free... Problem 70P: A simple and common technique for accelerating electrons is shown in Figure 7.46, where there is a... Problem 71P: In a Geiger counter, a thin metallic wire at the center of a metallic tube is kept at a high voltage... Problem 72P: The practical limit to all electric field in air is about 3.00106 N/C. Above this strength, sparking... Problem 73P: To form a helium atom, an alpha particle that contains two protons and two neutrons is fixed at one... Problem 74P: Find the electrostatic energy of eight equal charges (+3C) each fixed at the corners of a cube of... Problem 75P: The probability of fusion occurring is greatly enhanced when appropriate nuclei are brought close... Problem 76P: A bare helium nucleus has two positive charges and a mass of 6.641027kg . (a) Calculate its kinetic... Problem 77P: An election enters a region between two large parallel plates made of aluminum separated by a... Problem 78P: How far apart are two conducting plates that have an electric field strength of 4.50103 V/m between... Problem 79P: (a) Will the electric field strength between two parallel conducting plates exceed the breakdown... Problem 80P: Membrane walls of living cells have surprisingly large electric fields across them due to separation... Problem 81P: A double charged ion is accelerated to an energy of 32.0 keV by the electric field between two... Problem 82P: The temperature near the center of the Sun is thought to be 15 million degrees Celsius ( 1.5107oC )... Problem 83P: A lightning bolt strikes a tree, moving 20.0 C of charge through a potential difference of 1.00102... Problem 84P: What is the potential 0.5301010 m from a proton (the average distance between the proton and... Problem 85P: (a) A sphere has a surface uniformly charged with 1.00 C. At what distance from its center is the... Problem 86P: What are the sign and magnitude of a point charge that produces a potential of —2.00 V at a distance... Problem 87P: In one of the classic nuclear physics experiments at the beginning of the twentieth century, an... Problem 88AP: A 12.0-V battery-operated bottle warmer heats 50.0 g of glass, 2.50102 g of baby formula, and... Problem 89AP: A battery-operated car uses a 12.0-V system. Find the charge the batteries must be able to move in... Problem 90AP: (a) Find the voltage near a 10.0 cm diameter metal sphere that has 8.00 C of excess positive charge... Problem 91AP: A uniformly charged ring of radius 10 cm is placed on a nonconducting table. It is found that 3.0 cm... Problem 92AP: A glass ring of radius 5.0 cm is painted with a charged paint such that the charge density around... Problem 93AP: A CD disk of radius (R = 3.0 cm) is sprayed with a charged paint so that the charge varies... Problem 94AP: (a) What is the final speed of an electron accelerated from rest through a voltage of 25.0 MV by a... Problem 95AP: A large metal plate is charged uniformly to a density of a=2.0109C/m2 . How far apart are the... Problem 96AP: Your friend gets really excited by the idea of making a lightning rod or maybe just a sparking toy... Problem 97AP: (a) Find x L limit of the potential of a finite uniformly charged rod and show that it coincides... Problem 98AP: A small spherical pith ball of radius 0.50 cm is painted with a silver paint and then -10 C of... Problem 99AP: Two parallel conducting plates, each of cross-sectional area 400 cm2, are 2.0 cm apart and... Problem 100AP: A point charge of q=50108 C is placed at the center of an uncharged spherical conducting shell of... Problem 101AP: Earth has a net charge that produces an electric field of approximately 150 N/C downward at its... Problem 102AP: Point charges of 25.0/ C and 45. C are placed 0.500 m apart. At what point along die line between... Problem 103AP: What can you say about two charges q1and q2 if the electric field one-fourth of the way from q1to q2... Problem 104AP: Calculate the angular velocity of an electron orbiting a proton in the hydrogen atom, given the... Problem 105AP: An electron has an initial velocity of 5.00106m/s in a uniform 2.0010m/s electric field. The field... Problem 106CP: Three Na+ and three Cl ions are placed alternately and equally spaced around a circle of radius 50... Problem 107CP: Look up (presumably online, or by dismantling an old device and making measurements) the magnitude... Problem 108CP: Use the electric field of a finite sphere with constant volume charge density to calculate the... Problem 109CP: Calculate the electric field of a dipole throughout space from the potential. format_list_bulleted



 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




