
(Simulation: The Tortoise and the Hare) In this problem, you’ll recreate one of the truly great moments in history, namely the classic race of the tortoise and the hare. You’ll use random number generation to develop a simulation of this memorable event.
Our contenders begin the race at “square 1” of 70 squares. Each square represents a possible position along the race course. The finish line is at square 70. The first contender to reach or pass square 70 is rewarded with a pail of fresh carrots and lettuce. The course weaves its way up the side of a slippery mountain, so occasionally the contenders lose ground.
There’s a clock that ticks once per second. With each tick of the clock, your
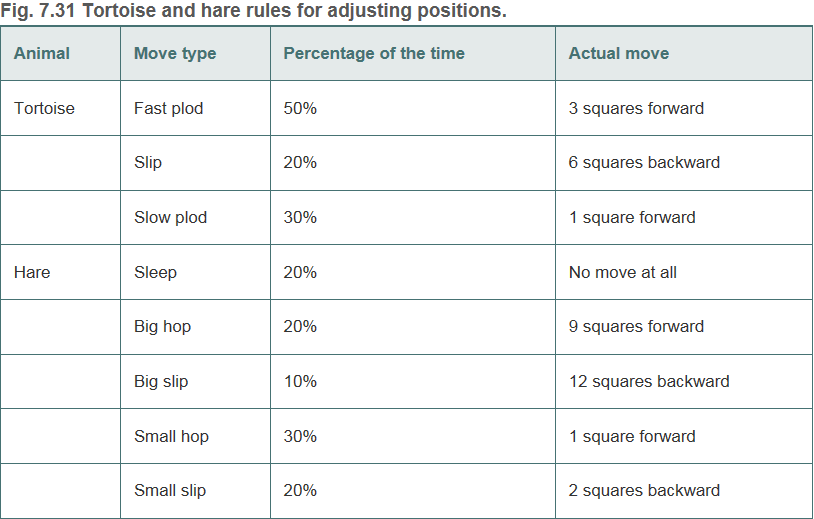
Use variables to keep track of the positions of the animals (i.e., position numbers are
Begin the race by printing
BANG !!!!!
AND THEY’RE OFF !!!!!
Then, for each tick of the clock (i.e., each iteration of a loop), print a 70-position line showing the letter T in the position of the tortoise and the letter H in the position of the hare. Occasionally, the contenders will land on the same square. In this case, the tortoise bites the hare and your program should print OUCH!!! beginning at that position. All print positions other than the T, the H, or the OUCH!!! (in case of a tie) should be blank.
After each line is printed, test whether either animal has reached or passed square 70. If so, then print the winner and terminate the simulation. If the tortoise wins, print TORTOISE WINS!!! H YAY!!! If the hare wins, print Hare wins. Yuch. If both animals win on the same tick of the clock, you may want to favor the turtle (the “underdog”), or you may want to print it’s a tie. If neither animal wins, perform the loop again to simulate the next tick of the clock. When you’re ready to run your program, assemble a group of fans to watch the race. You’ll be amazed at how involved your audience gets!
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK C HOW TO PROGRAM
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
- Which one of the 4 Entities mention in the diagram can have a recursive relationship? Order, Product, store, customer.arrow_forwardInheritance & Polymorphism (Ch11) There are 6 classes including Person, Student, Employee, Faculty, and Staff. 4. Problem Description: • • Design a class named Person and its two subclasses named student and Employee. • Make Faculty and Staff subclasses of Employee. • A person has a name, address, phone number, and e-mail address. • • • A person has a class status (freshman, sophomore, junior and senior). Define the status as a constant. An employee has an office, salary, and date hired. A faculty member has office hours and a rank. A staff member has a title. Override the toString() method in each class to display the class name and the person's name. 4-1. Explain on how you would code this program. (1 point) 4-2. Implement the program. (2 point) 4-3. Explain your code. (2 point)arrow_forwardSuppose you buy an electronic device that you operate continuously. The device costs you $300 and carries a one-year warranty. The warranty states that if the device fails during its first year of use, you get a new device for no cost, and this new device carries exactly the same warranty. However, if it fails after the first year of use, the warranty is of no value. You plan to use this device for the next six years. Therefore, any time the device fails outside its warranty period, you will pay $300 for another device of the same kind. (We assume the price does not increase during the six-year period.) The time until failure for a device is gamma distributed with parameters α = 2 and β = 0.5. (This implies a mean of one year.) Use @RISK to simulate the six-year period. Include as outputs (1) your total cost, (2) the number of failures during the warranty period, and (3) the number of devices you own during the six-year period. Your expected total cost to the nearest $100 is _________,…arrow_forward
- Which one of the 4 Entities mention in the diagram can have a recursive relationship? If a new entity Order_Details is introduced, will it be a strong entity or weak entity? If it is a weak entity, then mention its type (ID or Non-ID, also Justify why)?arrow_forwardPlease answer the JAVA OOP Programming Assignment scenario below: Patriot Ships is a new cruise line company which has a fleet of 10 cruise ships, each with a capacity of 300 passengers. To manage its operations efficiently, the company is looking for a program that can help track its fleet, manage bookings, and calculate revenue for each cruise. Each cruise is tracked by a Cruise Identifier (must be 5 characters long), cruise route (e.g. Miami to Nassau), and ticket price. The program should also track how many tickets have been sold for each cruise. Create an object-oriented solution with a menu that allows a user to select one of the following options: 1. Create Cruise – This option allows a user to create a new cruise by entering all necessary details (Cruise ID, route, ticket price). If the maximum number of cruises has already been created, display an error message. 2. Search Cruise – This option allows to search a cruise by the user provided cruise ID. 3. Remove Cruise – This op…arrow_forwardI need to know about the use and configuration of files and folders, and their attributes in Windows Server 2019.arrow_forward
- Southern Airline has 15 daily flights from Miami to New York. Each flight requires two pilots. Flights that do not have two pilots are canceled (passengers are transferred to other airlines). The average profit per flight is $6000. Because pilots get sick from time to time, the airline is considering a policy of keeping four *reserve pilots on standby to replace sick pilots. Such pilots would introduce an additional cost of $1800 per reserve pilot (whether they fly or not). The pilots on each flight are distinct and the likelihood of any pilot getting sick is independent of the likelihood of any other pilot getting sick. Southern believes that the probability of any given pilot getting sick is 0.15. A) Run a simulation of this situation with at least 1000 iterations and report the following for the present policy (no reserve pilots) and the proposed policy (four reserve pilots): The average daily utilization of the aircraft (percentage of total flights that fly) The…arrow_forwardWhy is JAVA OOP is really difficult to study?arrow_forwardMy daughter is a Girl Scout and it is time for our cookie sales. There are 15 neighbors nearby and she plans to visit every neighbor this evening. There is a 40% likelihood that someone will be home. If someone is home, there is an 85% likelihood that person will make a purchase. If a purchase is made, the revenue generated from the sale follows the Normal distribution with mean $18 and standard deviation $5. Using @RISK, simulate our door-to-door sales using at least 1000 iterations and report the expected revenue, the maximum revenue, and the average number of purchasers. What is the probability that the revenue will be greater than $120?arrow_forward
- Q4 For the network of Fig. 1.41: a- Determine re b- Find Aymid =VolVi =Vo/Vi c- Calculate Zi. d- Find Ay smid e-Determine fL, JLC, and fLE f-Determine the low cutoff frequency. g- Sketch the asymptotes of the Bode plot defined by the cutoff frequencies of part (e). h-Sketch the low-frequency response for the amplifier using the results of part (f). Ans: 28.48 2, -72.91, 2.455 KS2, -54.68, 103.4 Hz. 38.05 Hz. 235.79 Hz. 235.79 Hz. 14V 15.6ΚΩ 68kQ 0.47µF Vo 0.82 ΚΩ V₁ B-120 3.3kQ 0.47µF 10kQ 1.2k0 =20µF Z₁ Fig. 1.41 Circuit forarrow_forwarda. [10 pts] Write a Boolean equation in sum-of-products canonical form for the truth table shown below: A B C Y 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 a. [10 pts] Minimize the Boolean equation you obtained in (a). b. [10 pts] Implement, using Logisim, the simplified logic circuit. Include an image of the circuit in your report.arrow_forwardUsing XML, design a simple user interface for a fictional app. Your UI should include at least three different UI components (e.g., TextView, Button, EditText). Explain the purpose of each component in your design-you need to add screenshots of your work with your name as part of the code to appear on the interface-. Screenshot is needed.arrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781305480537Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781305480537Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





