
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The plausible mechanism for the given transformations should be drawn and identified.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
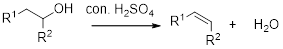
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.

In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction. Dehydration reaction will not go without acid (sulfuric acid).
(b)
Interpretation:
The plausible mechanism for the given transformations should be drawn and identified.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
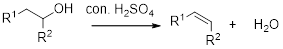
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.

In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction. Dehydration reaction will not go without acid (sulfuric acid).
(c)
Interpretation:
The plausible mechanism for the given transformations should be drawn and identified.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed via
E1 reaction is a unimolecular elimination reaction to produce alkene compounds in which carbocation is formed as an intermediate and it has stepwise mechanism.
E2 reaction is a bimolecular elimination reaction in which alkene compounds formed in a single step.
Example,
Alkenes are formed when alcohols are treated with strong acid via eliminating one β-proton and the
Alkenes are formed when
Curved arrows are used for drawing the mechanism of reaction.
The tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation.
(d)
Interpretation:
The plausible mechanism for the given transformations should be drawn and identified.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed via
E1 reaction is a unimolecular elimination reaction to produce alkene compounds in which carbocation is formed as an intermediate and it has stepwise mechanism.
E2 reaction is a bimolecular elimination reaction in which alkene compounds formed in a single step.
Example,
Alkenes are formed when alcohols are treated with strong acid via eliminating one β-proton and the
Alkenes are formed when alkyl halides are treated with bases via eliminating one β-proton and one α-halo group of the alkyl halide.
Curved arrows are used for drawing the mechanism of reaction.
The tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry 3rd.ed. Klein Evaluation/desk Copy
- -C = C - C - + Br₂ + I" -> -C-C-c -C = C -C- + Br² + I₂ -C=C Br I + Brū + Iz -7- C - C-C- I Br Mechanism; - C = c - c - + Br - Br > - C-c-c- Br -C-C-C- + 1 - - -Ċ-Ċ'-c' - Br Br Iarrow_forwardWrite the mechanism of the esterification reaction (please show the mechanism included line pairs and arrows)arrow_forwardHow do I break down the reaction shown on the chalkboard and explain it correctly using the bromonium ion mechanism, instead of the (disproven) carbocation-based mechanismarrow_forward
- ¿Qué the product is obtained from tetraethoxypropano and hidrazina?. Indicate the reason why the corresponding dial is used.arrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 is reacted with hydrazine, two isomeric products are formed. Indicate their structures and the major product.arrow_forwardIs it possible to obtain addition derivatives to nitrogen in position 2 of pyrazoles by reaction with electrophilic agents? Reason for this.arrow_forward
- Starting from 1,3-dicarbonyl derivatives to obtain isooxazoles and isothiazoles. Indicate whether synthetic methods exist.arrow_forwardIn the synthesis of benzotriazole, adding NaNO2 heats the solution. State the reason.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by treating benzotriazole with dimethyl sulfate or methyl iodide in a basic medium.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





