
Concept explainers
Analysis of
Kansas Company uses a
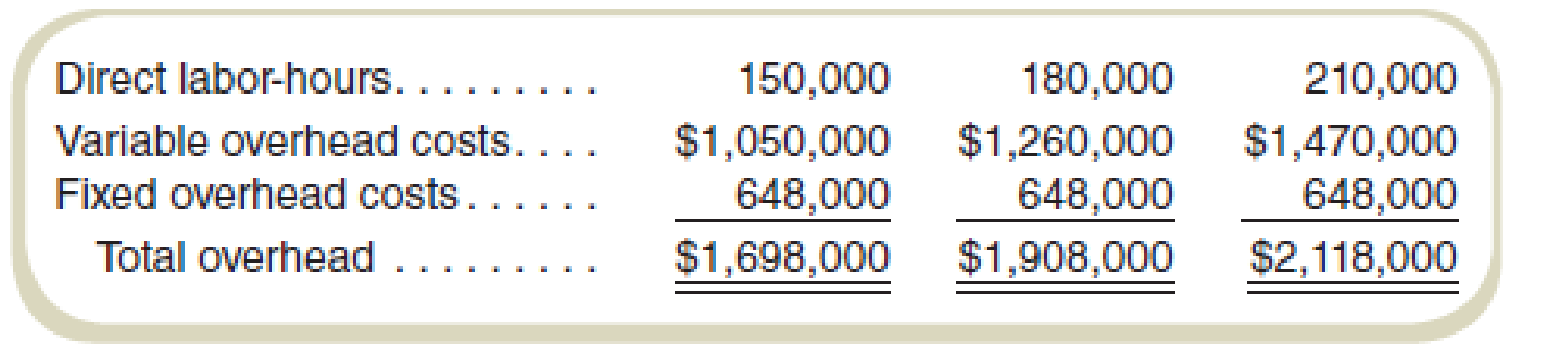
The expected volume is 180,000 direct labor-hours for the entire year. The following information is for March, when Jobs 6023 and 6024 were completed:
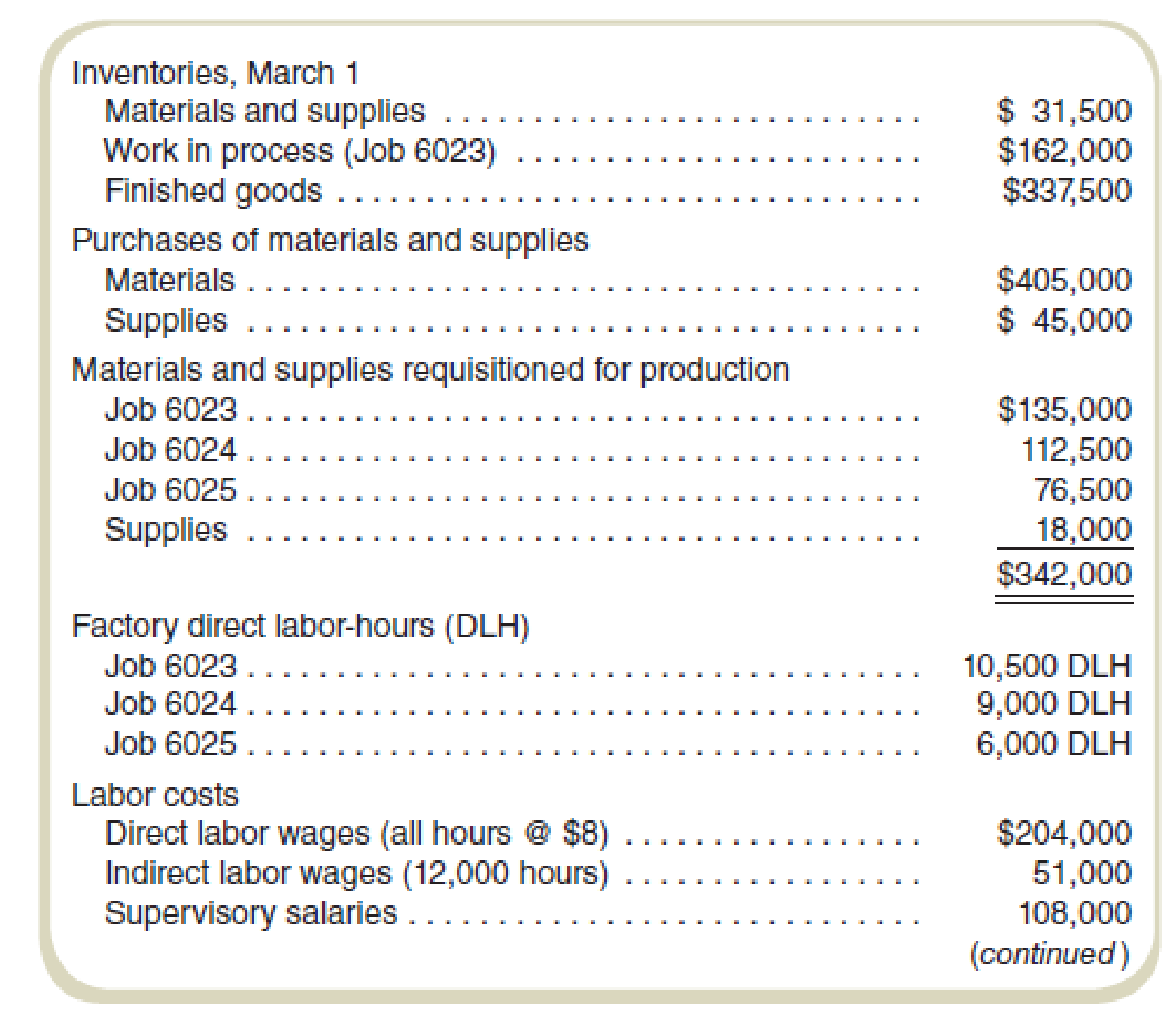

Required
Answer the following questions:
- a. Compute the predetermined overhead rate (combined fixed and variable) to be used to apply overhead to individual jobs during the year. (Note: Regardless of your answer to requirement [a], assume that the predetermined overhead rate is $9 per direct labor-hour. Use this amount in answering requirements [b] through [e].)
- b. Compute the total cost of Job 6023 when it is finished.
- c. How much of
factory overhead cost was applied to Job 6025 during March? - d. What total amount of overhead was applied to jobs during March?
- e. Compute actual factory overhead incurred during March.
- f. At the end of the year, Kansas Company had the following account balances:

How would you recommend treating the overapplied overhead, assuming that it is not material? Show the new account balances in the following table:

a.
Compute the predetermined overhead rate to be used to apply overhead to individual jobs during the year fixed and variable both.
Answer to Problem 52P
The predetermined overhead rate to be used to apply overhead to individual jobs during the year fixed and variable both is $10.60.
Explanation of Solution
Predetermined overhead rate: The predetermined overhead rate is the rate computed for applying manufacturing overheads to the work-in-process inventory. This rate can be computed by dividing the total amount of manufacturing overheads by the base of allocation. The formula for calculating the predetermined overhead rate is:
Compute the predetermined overhead rate to be used to apply overhead to individual jobs during the year fixed and variable both:
Thus, the value of the predetermined overhead rate to be used to apply overheads to individual jobs during the year fixed and variable both is $10.60.
b.
Compute the total cost of Job 6023 when it is finished.
Answer to Problem 52P
The total cost of Job 6023 when it is finished is $475,500.
Explanation of Solution
Job costing: Job costing is a method of tracking and allocating costs to different jobs in the manufacturing process. This method of costing is used in entities where different jobs are incurred in each period.
Compute the total cost of Job 6023 when it is finished:
Thus, the value of the total cost of Job 6023 when it is finished is $475,500.
Working note 1:
Compute the direct labor:
Working note 2:
Compute the overhead applied:
c.
Find the value of factory overhead cost that was applied to Job 6025 during March.
Answer to Problem 52P
The value of factory overhead cost that was applied to Job 6025 during March is $54,000.
Explanation of Solution
Job costing: Job costing is a method of tracking and allocating costs to different jobs in the manufacturing process. This method of costing is used in entities where different jobs are incurred in each period.
Compute the value of factory overhead cost that was applied to Job 6025 during March:
Thus, the value of factory overhead cost that was applied to Job 6025 during March is $54,000.
d.
Find the total amount of overhead applied to jobs during March.
Answer to Problem 52P
The total amount of overhead applied to jobs during March is $229,500.
Explanation of Solution
Manufacturing overhead applied: the applied overheads refer to the overheads which have been allocated on the basis of the predetermined overhead rate.
Compute the total amount of overhead applied to jobs during March:
Thus, the total amount of overhead applied to jobs during March is $229,500.
e.
Compute the value of actual factory overhead incurred during March.
Answer to Problem 52P
The value of actual factory overhead incurred during March is $220,500.
Explanation of Solution
Overhead incurred: the amount of overheads which have actually occurred during a particular period of time. The overhead incurred are recorded at the end of the period when the overheads have been already applied to the jobs.
Compute the value of actual factory overhead incurred during March:
Thus, the value of actual factory overhead incurred during March is $220,500.
f.
Find the new account balances of the table given in the question and provide recommendations.
Answer to Problem 52P
New balances according to the given information in the question:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Over-applied overhead | $ - |
| Cost of goods sold | $ 2,937,000 |
| Work-in-process inventory | $ 114,000 |
| Finished goods inventory | $ 246,000 |
Table: (1)
It would not be recommended to prorate 0.1% of the cost of goods sold
Explanation of Solution
New balances according to the given information in the question:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Over-applied overhead | $ - |
| Cost of goods sold | $ 2,937,000 (3) |
| Work-in-process inventory | $ 114,000 |
| Finished goods inventory | $ 246,000 |
Table: (2)
The over-applied overheads are $3,000 which is 0.1% of the cost of goods sold. Hence, it would not be recommended to prorate such small percentage.
Working note 3:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT
- The per-unit cost of an item is its average total cost (= total cost/quantity). Suppose a new cell phone application costs $115,000 to develop and only $0.75 per unit to deliver to each cell phone customer. What will be the per-unit cost of the application if it sells 100 units? 1000 units? 1 million units?arrow_forwardcan you please this general accountingarrow_forwardPlease provide answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





