
Concept explainers
At the beginning of the month, Arthur’s Olde Consulting Corporation had two jobs in process that had the following costs assigned from previous months:
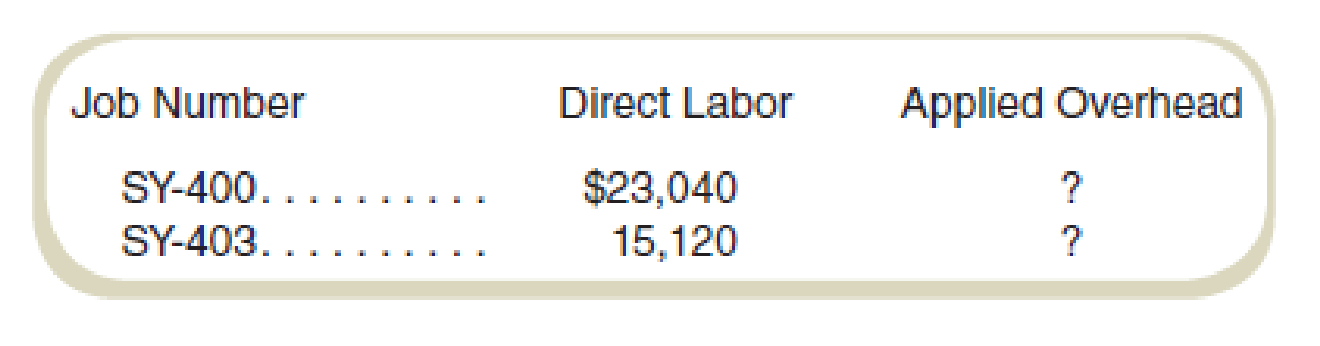
During the month, Jobs SY-400 and SY-403 were completed but not billed to customers. The completion costs for SY-400 required $25,200 in direct labor. For SY-403, $72,000 in labor was used.
During the month, the only new job, SY-404, was started but not finished. Total direct labor costs for all jobs amounted to $148,320 for the month.
Required
- a. What are the costs of Jobs SY-400 and SY-403 at (1) the beginning of the month and (2) when completed?
- b. What is the cost of Job SY-404 at the end of the month?
- c. How much was under- or overapplied service overhead for the month?
a.
Find the costs of jobs SY-400 and SY-403 at the beginning of the month and when completed.
Answer to Problem 40E
The costs of jobs SY-400 and SY-403 at the beginning of the month and when completed are as follows:
| Costs of jobs SY-400 and SY-403 at the beginning of the month | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| SY-400 | $ 36,864 |
| SY-403 | $ 24,192 |
Table: (1)
| Costs of jobs SY-400 and SY-403 during the month | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| SY-400 | $ 77,184 |
| SY-403 | $ 139,392 |
Table: (2)
Explanation of Solution
Job costing: Job costing is a method of tracking and allocating costs to different jobs in the manufacturing process. This method of costing is used in entities where different jobs are incurred in each period.
The costs of jobs SY-400 and SY-403 at the beginning of the month and when completed are as follows:
| Costs of jobs SY-400 and SY-403 at the beginning of the month | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| SY-400 | $ 36,864 (1) |
| SY-403 | $ 24,192 (2) |
Table: (3)
| Costs of jobs SY-400 and SY-403 during the month | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| SY-400 | $ 77,184 (3) |
| SY-403 | $ 139,392 (4) |
Table: (4)
Working Note 1:
Compute the cost of job SY- 400 at the beginning of the month:
Working Note 2:
Compute the cost of job SY- 403 at the beginning of the month:
Working note 3:
Compute the cost of job SY- 400 during the month:
Working note 4:
Compute the cost of job SY- 403 during the month:
b.
Find the cost of job SY-404 at the end of the month.
Answer to Problem 40E
The cost of job SY-404 at the end of the month is $81,792.
Explanation of Solution
Job costing: Job costing is a method of tracking and allocating costs to different jobs in the manufacturing process. This method of costing is used in entities where different jobs are incurred in each period.
Compute the cost of job SY- 404 at the end of the month:
Thus, the value of the cost of job SY-404 at the end of the month is $81,792.
Working note 5:
Compute the direct labor of job SY-404:
c.
Find the under or over-applied service overhead for the month.
Answer to Problem 40E
The value of under-applied overhead is $1,008.
Explanation of Solution
Over-applied overheads: This is the amount of overhead which arises when the amount of actual overheads is less than the amount of overheads applied.
Compute the under or over-applied service overhead for the month:
Thus, the value of under-applied overhead is $1,008.
Working note 6:
Applied overheads are 60% of actual direct labor.
Hence,
Compute the overhead applied during the month:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





