
Use the following questions to check your understanding of some of the many types of visual information used in astronomy. For additional practice, try the Chapter 7 Visual Quiz at Mastering Astronomy.
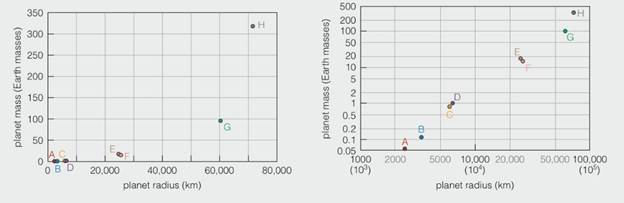
The plots above show the masses of the eight major planets on the vertical axis and their radial on the horizontal axis. The plot on the left shows the information on a linear scale, meaning that each tick mark indicates an increase by the same amount. The plot on the right shows the same information plotted on an exponential scale, meaning that each tick mark represents another actor-of-ten increase. Before proceeding, convince yourself that the points on each plot are the same.
3. Which statements most accurately describes the relationship between the largest and smallest planets?
a. The largest planet is 6000 times as wide (in diameter) and 30 times as massive as the smallest.
b. The largest planet is 6000 times as wide (in diameter) and 6000 times as massive as the smallest.
c. The largest planet is 30 times as wide (in diameter) and 30 times as massive as the smallest.
d. The largest planet is 30 times as wide (in diameter) and 6000 times as massive as the smallest.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK COSMIC PERSPECTIVE, THE
- 20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward17. Two charges, one of charge +2.5 × 10-5 C and the other of charge +3.7 × 10-6 C, are 25.0 cm apart. The +2.5 × 10−5 C charge is to the left of the +3.7 × 10−6 C charge. a. Draw a diagram showing the point charges and label a point Y that is 20.0 cm to the left of the +3.7 × 10-6 C charge, on the line connecting the charges. (Field lines do not need to be drawn.) b. Calculate the net electric field at point Y.arrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
 Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning





