
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 3VCQ
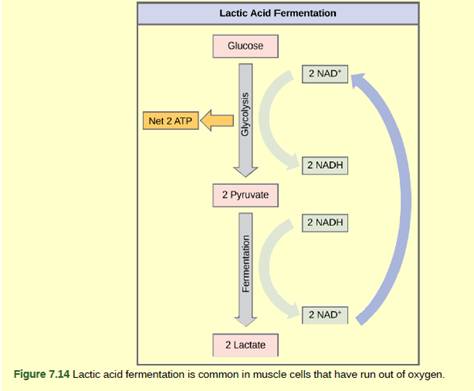
(Figure 7.14) Tremetol, a metabolic poison found in the white snake root plant, prevents the
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
I have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.
13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a
viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then
calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by
both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages.
3 colonies
56
cells
10 μL
10 μL
100 μL
500 με
m
OS
A
B
D
5.0 mL
990 με
990 με
900 με
500 μL
EN
2
100 με
100 μL
118
colonies
12
colonies
Describe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Biology 2e
Ch. 7 - Figure 7.11 Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an "uncoupler"...Ch. 7 - Figure 7.12 Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase,...Ch. 7 - (Figure 7.14) Tremetol, a metabolic poison found...Ch. 7 - The energy currency used by cells is ATP ADP AMP...Ch. 7 - A reducing chemical reaction. reduces the compound...Ch. 7 - During the second half of glycolysis, what occurs?...Ch. 7 - What is removed from pyruvate during its...Ch. 7 - What do the electrons added to NAD+ do? They...Ch. 7 - GTP or ATP is produced during the conversion of...Ch. 7 - How many NADU molecules are produced on each turn...
Ch. 7 - What compound receives elections from NADH? FMN...Ch. 7 - Chemiosmosis involves. the movement of electrons...Ch. 7 - Which of the following fermentation methods can...Ch. 7 - A major connection for sugars in glycolysis is...Ch. 7 - Beta-oxidation is. the breakdown of sugars the...Ch. 7 - The effect of high levels of ADP is to__inv __...Ch. 7 - The control of which enzyme exerts the most...Ch. 7 - Why is it beneficial for cells to use ATP rather...Ch. 7 - Nearly all organisms on Earth carry out some form...Ch. 7 - Because they lose their mitochondria during...Ch. 7 - What is the primary difference between a circular...Ch. 7 - How do the roles of ubiquinone and cytochrome c...Ch. 7 - What accounts for the different number of ATP...Ch. 7 - What is the primary difference between...Ch. 7 - Would you describe metabolic pathways as...Ch. 7 - How does citrate from the citric acid cycle affect...Ch. 7 - Why might negative feedback mechanisms be more...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Endospore formation is called (a) _____. It is initiated by (b) _____. Formation of a new cell from an endospor...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Which type of cartilage is most plentiful in the adult body?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected propor-tions of the follo...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
79. Complete and balance each acid-base reaction.
a.
b.
c.
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Match the following examples of mutagens. Column A Column B ___a. A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in pl...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward
- what measures can a mother to take to improve the produce of her to milk to her newborn baby ?arrow_forward1. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Eastern white pine tree green (but only the ancestral line NOT shared with other organisms) 2. Oncle the last common ancestor of the Colorado blue spruce tree and Eastern white pine tree. 3. Put a box around the last common ancestor of the sugar maple tree and the dogwood tree. 4. Put a triangle around the last common ancestor of the red pine tree and the american holly bush. 5. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Ponderosa pine tree red (including all shared ancestors). 6. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the American elm tree blue (including all shared ancestors). 7 Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Sabal palm tree purple (including all shared ancestors) 8. Using a yellow highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all pine trees. 9. Using a orange highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all gymnosperms 10. Can you tell…arrow_forwardYou have been hired as a public relations specialist to give invertebrates a good name. After all, they are much more than just creepy crawly bugs! Your first task though is to convince yourself that is true. The best way to do that is to start close to home. Find something in your house that is a product obtained directly from an invertebrate or only due to an invertebrate’s actions. Describe the product, its function and utility, as well as any human manufactured alternatives. Be sure to highlight the advantages of obtaining this directly from nature. Keep in mind, a product can be something you use, wear, eat, or enjoy for its visual appeal.arrow_forward
- Use the following tree diagram to answer Questions #8-10. 8) Which of the following two animals are the most closely related based on the tree to the left? a) Pig and camel b) Hippo and pig c) Deer and cow 9) CIRCLE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a hippo and a cow is. 10) Put a SQUARE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a pig and a peccary is.arrow_forwardExplain: Healthy Cell Function Overview→ Briefly describe how a healthy cell usually works: metabolism (ATP production), pH balance, glycogen storage, ion transport, enzymes, etc. Gene Mutation and Genetics Part→ Focus on the autosomal recessive mutation and explain: How gene mutation affects the cell. How autosomal inheritance works. Compare the normal and mutated gene sequences simply. → Talk about possible consequences of a faulty hydrolytic enzyme.arrow_forwardCan you fill out those termsarrow_forward
- Explain down bellow what happens to the cell: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forwardAn 1100 pound equine patient was given 20 mg/kg sucralfate 3 times a day, 2.8 mg/kg famotidine twice a day, and 10mg/kg doxycycline twice a day. Sucralfate comes as a 1 gm tablet, famotidine as 20 mg tablets, and doxycycline as 100mg tablets. All are in bottles of 100 tablets.How many total mg are needed for the patient and how many tablets of each would be needed to provide each dose?How many bottles of each would be needed to have available if this patient were to be on this drug regimen for 5 days?arrow_forwardThe patient needs a solution of 2.5% dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s solution to run at 75 ml/hr for at least the next 12hours. LRS comes in fluid bags of 500 ml, 1 Liter, 3 Liters and 5 Liters. How can a 2.5% solution be made by adding50% dextrose to the LRS?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College



Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How do Plants Handle Stress?; Author: Alex Dainis;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TYsnveEHqec;License: Standard Youtube License