
Concept explainers
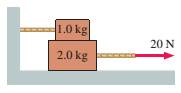
The 1.0 kg block in FIGURE EX7.24 is tied to the wall with a rope. It sits on top of the 2.0 kg block. The lower block is pulled to the right with a tension force of 20 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction at both the lower and upper surfaces of the 2.0 kg block is
a. What is the tension in the rope attached to the wall?
b. What is the acceleration of the 2.0 kg block?
FIGURE EX7.24
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 7 Solutions
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- A collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forwardA number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q(upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forwardFor each part make sure to include sign to represent direction, with up being positive and down being negative. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 30.5 m/s. A) How high does it rise? y= B) How long does it take to reach its highest point? t= C) How long does it take the ball return to its starting point after it reaches its highest point? t= D) What is its velocity when it returns to the level from which it started? v=arrow_forward
- Four point charges of equal magnitude Q = 55 nC are placed on the corners of a rectangle of sides D1 = 27 cm and D2 = 11cm. The charges on the left side of the rectangle are positive while the charges on the right side of the rectangle are negative. Use a coordinate system where the positive y-direction is up and the positive x-direction is to the right. A. Which of the following represents a free-body diagram for the charge on the lower left hand corner of the rectangle? B. Calculate the horizontal component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fx = __________________________________________NC. Calculate the vertical component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fy = __________________________________________ND. Calculate the magnitude of the…arrow_forwardPoint charges q1=50.0μC and q2=-35μC are placed d1=1.0m apart, as shown. A. A third charge, q3=25μC, is positioned somewhere along the line that passes through the first two charges, and the net force on q3 is zero. Which statement best describes the position of this third charge?1) Charge q3 is to the right of charge q2. 2) Charge q3 is between charges q1 and q2. 3) Charge q3 is to the left of charge q1. B. What is the distance, in meters, between charges q1 and q3? (Your response to the previous step may be used to simplify your solution.)Give numeric value.d2 = __________________________________________mC. Select option that correctly describes the change in the net force on charge q3 if the magnitude of its charge is increased.1) The magnitude of the net force on charge q3 would still be zero. 2) The effect depends upon the numeric value of charge q3. 3) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q2. 4) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q1. D. Select option that…arrow_forwardThe magnitude of the force between a pair of point charges is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation distance. Four distinct charge-pair arrangements are presented. All charges are multiples of a common positive charge, q. All charge separations are multiples of a common length, L. Rank the four arrangements from smallest to greatest magnitude of the electric force.arrow_forward
- A number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q (upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forwardA collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forwardIn Dark Souls 3 you can kill the Ancient Wyvern by dropping on its head from above it. Let’s say you jump off the ledge with an initial velocity of 3.86 mph and spend 1.72 s in the air before hitting the wyvern’s head. Assume the gravity is the same as that of Earth and upwards is the positive direction. Also, 1 mile = 1609 m. A) How high up is the the ledge you jumped from as measured from the wyvern’s head? B) What is your velocity when you hit the wyvern?arrow_forward
- A conducting sphere is mounted on an insulating stand, and initially it is electrically neutral. A student wishes to induce a charge distribution similar to what is shown here. The student may connect the sphere to ground or leave it electrically isolated. The student may also place a charged insulated rod near to the sphere without touching it. Q. The diagrams below indicate different choices for whether or not to include a ground connection as well as the sign of the charge on and the placement of an insulating rod. Choose a diagram that would produce the desired charge distribution. (If there are multiple correct answers, you need to select only one of them.)arrow_forwardA person is making pancakes and tries to flip one in the pan. The person is holding the pan a distance y0 = 1.10 m above the ground when they launch the pancake. The pancake just barely touches the ceiling, which is at a height y = 2.47 m above the ground. A) What must be the initial velocity of the pancake to reach that height? B) This person, shocked that they almost hit the ceiling, does not catch it on the way down and the pancake hits the floor. Assuming up as the positive direction, what is the velocity of the pancake when it hits the floor, ruining breakfast and this person’s day?arrow_forwardOne of Spider-Man’s less talked about powers is that he can jump really high. In the comics Spider-Man can jump upwards 3 stories. A) If Spider-Man leaves the ground at 14.3 m/s, how high can he get? y= B) If Spider-Man jumps directly upwards with the initial velocity used above and then returns to the ground, what total amount of time does he spend airborn? t=arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





