
Concept explainers
Figure 7.11 Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an "uncoupler" that makes the inner mitochondrial membrane "leaky" to protons. It was used until 1938 as a weight-loss drug. What effect would you expect DNP to have on the change in pH across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Why do you think this might be an effective weight-loss drug?
To write:
The effect of DNP on the pH across the mitochondrial membrane and the reason that it is a weight-loss drug.
Introduction:
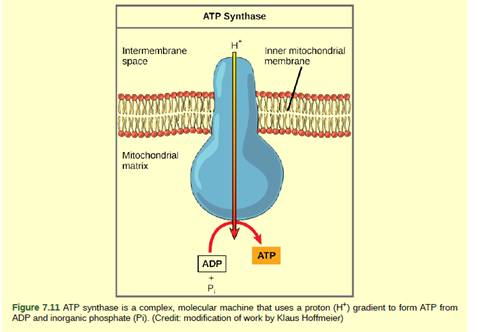
Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an uncoupler. The flow of electrons can be separated by DNP along with the pumping of the H+ ion for the purpose of production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). It means that the electron transport chain can no longer form a proton gradient, and ATP synthase can no longer make ATP.
DNP is a drug given to the patient for losing weight. After using DNA as weight loss drug, a person obtains less energy out of the eaten food. One of the worst side effects of taking DNP is overheating of the body, the energy from electron transport is lost as heat.
Explanation of Solution
DNP is an uncoupler, it disrupts the ATP synthesis by leaking protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane. As a result, the proton gradient cannot be formed across the inner mitochondrial membrane as pumping of H+ (hydrogen ion) is stopped. So, there will be a decrease in pH across the inner membrane of mitochondria.
Therefore, ATP production becoming less efficient. Hence, the energy which is normally produced during cellular respiration is being wasted as heat. In such condition, majority of the eaten food could not be used for the purpose of ATP synthesis and we lose weight.
DNP is an effective diet drug used to lose weight. It acts as an uncoupler which disrupts the H+ gradient across mitochondrial membrane reducing ATP synthesis. Since ATP cannot be formed, the energy from electron transport is lost as heat.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
BIOLOGY 2E
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- Please indentify the unknown organismarrow_forwardPlease indentify the unknown organismarrow_forward5G JA ATTC 3 3 CTIA A1G5 5 GAAT I I3 3 CTIA AA5 Fig. 5-3: The Eco restriction site (left) would be cleaved at the locations indicated by the arrows. However, a SNP in the position shown in gray (right) would prevent cleavage at this site by EcoRI One of the SNPs in B. rapa is found within the Park14 locus and can be detected by RFLP analysis. The CT polymorphism is found in the intron of the Bra013780 gene found on Chromosome 1. The Park14 allele with the "C" in the SNP has two EcoRI sites and thus is cleaved twice by EcoRI If there is a "T" in that SNP, one of the EcoRI sites is altered, so the Park14 allele with the T in the SNP has only one EcoRI site (Fig. 5-3). Park14 allele with SNP(C) Park14 allele with SNPT) 839 EcoRI 1101 EcoRI 839 EcoRI Fig. 5.4: Schematic restriction maps of the two different Park14 alleles (1316 bp long) of B. rapa. Where on these maps is the CT SNP located? 90 The primers used to amplify the DNA at the Park14 locus (see Fig. 5 and Table 3 of Slankster et…arrow_forward
- From your previous experiment, you found that this enhancer activates stripe 2 of eve expression. When you sequence this enhancer you find several binding sites for the gap gene, Giant. To test how Giant interacts with eve, you decide to remove all of the Giant binding sites from the eve enhancer. What results do you expect to see with respect to eve expression?arrow_forwardWhat experiment could you do to see if the maternal gene, bicoid, is sufficient to form anterior fates?arrow_forwardYou’re curious about the effect that gap genes have on the pair-rule gene, evenskipped (eve), so you isolate and sequence each of the eve enhancers. You’re particularly interested in one of the enhancers, which is just upstream of the eve gene. Describe an experimental technique you would use to find out where this particular eve enhancer is active.arrow_forward
- For short answer questions, write your answers on the line provided. To the right is the mRNA codon table to use as needed throughout the exam. First letter U บบบ U CA UUCPhe UUA UCU Phe UCC UUG Leu CUU UAU. G U UAC TV UGCys UAA Stop UGA Stop A UAG Stop UGG Trp Ser UCA UCG CCU] 0 CUC CUA CCC CAC CAU His CGU CGC Leu Pro CCA CAA Gin CGA Arg CUG CCG CAG CGG AUU ACU AAU T AUC lle A 1 ACC Thr AUA ACA AUG Mot ACG AGG Arg GUU GCU GUC GCC G Val Ala GAC Asp GGU GGC GUA GUG GCA GCG GAA GGA Gly Glu GAGJ GGG AACASH AGU Ser AAA1 AAG Lys GAU AGA CAL CALUCAO CAO G Third letter 1. (+7) Use the table below to answer the questions; use the codon table above to assist you. The promoter sequence of DNA is on the LEFT. You do not need to fill in the entire table. Assume we are in the middle of a gene sequence (no need to find a start codon). DNA 1 DNA 2 mRNA tRNA Polypeptide C Val G C. T A C a. On which strand of DNA is the template strand (DNA 1 or 2)?_ b. On which side of the mRNA is the 5' end (left or…arrow_forward3. (6 pts) Fill in the boxes according to the directions on the right. Structure R-C R-COOH OH R-OH i R-CO-R' R R-PO4 R-CH3 C. 0 R' R-O-P-OH 1 OH H R-C-H R-N' I- H H R-NH₂ \H Name Propertiesarrow_forward4. (6 pts) Use the molecule below to answer these questions and identify the side chains and ends. Please use tidy boxes to indicate parts and write the letter labels within that box. a. How many monomer subunits are shown? b. Box a Polar but non-ionizable side chain and label P c. Box a Basic Polar side chain and label BP d. Box the carboxyl group at the end of the polypeptide and label with letter C (C-terminus) H H OHHO H H 0 HHO H-N-CC-N-C-C N-C-C-N-GC-OH I H-C-H CH2 CH2 CH2 H3C-C+H CH2 CH2 OH CH CH₂ C=O OH CH2 NH2arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





