
Concept explainers
Label the components in the following diagram of a small portion of a plasma membrane. Indicate whether regions are hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
To label: The components in the given diagram of a small portion of a plasma membrane and indicate whether the regions are hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
Introduction: All living organisms are made up of one or many cells. The organisms are classified as prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The prokaryotes are usually unicellular including the bacteria and archaea, while the eukaryotes are usually multicellular including the plants and animals. The prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than the eukaryotic cells.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 illustrates the diagram of a small portion of plasma membrane.
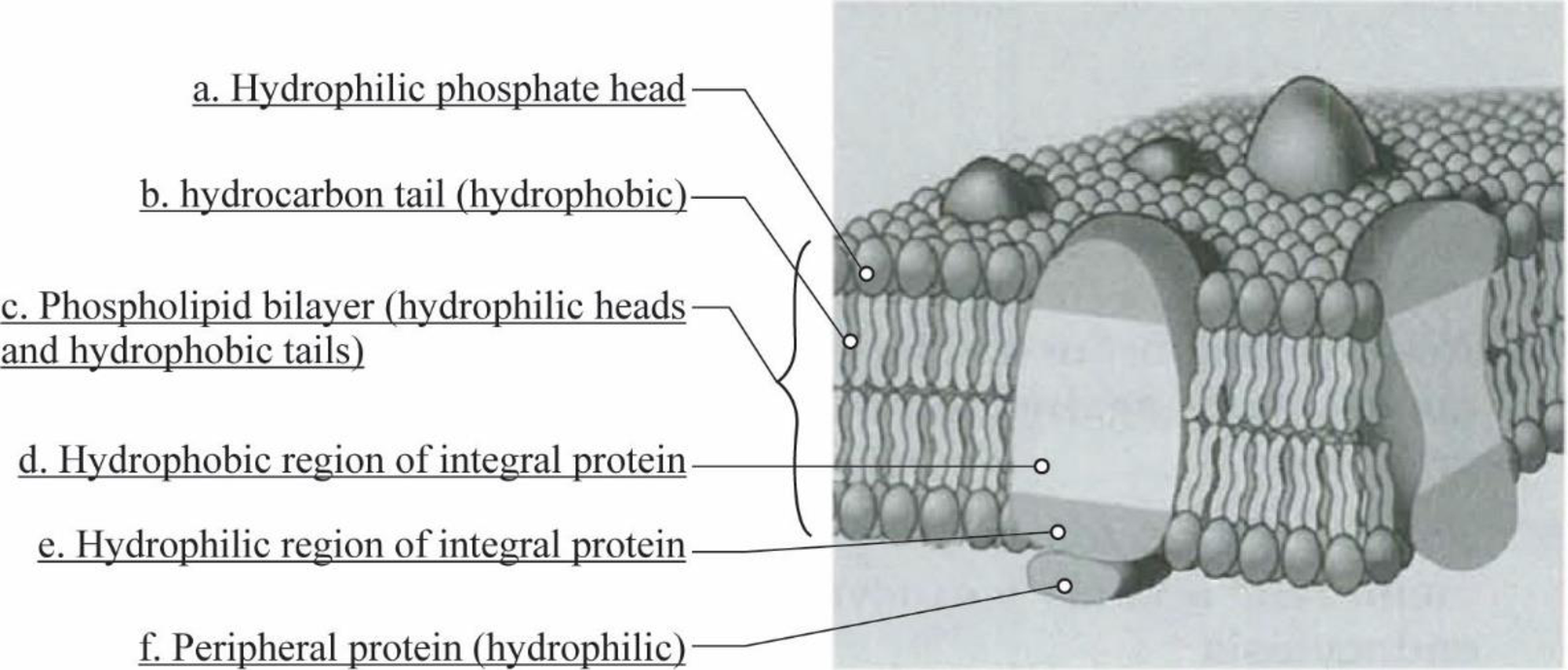
Fig.1: Plasma membrane
Explanation of Solution
Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane with lipid bilayer and protein. The lipid bilayer structure is a barrier structure. Lipid molecule consists of the polar head region called hydrophilic head, and a non-polar fatty acid chain tail called hydrophobic tail. The hydrophilic region is attracted toward aqueous condition, and the hydrophobic end is repelled away from the aqueous condition.
Membrane proteins are a part of biological membrane that primarily interacts with it to perform various functions in the cell. There are various membrane proteins that help in the transportation of molecules in and out of the cell. Based on the extend of attachment to the membrane, the membrane proteins are classified as integral proteins, peripheral proteins, and transmembrane proteins.
- Integral membrane proteins: Integral membrane proteins are a type of membrane proteins that are firmly bound to the membrane. These types of proteins are amphipathic in nature. Here, the hydrophilic head region is extended out of the cell, and its hydrophobic tail region interacts with the fatty acids present on the membrane phospholipids.
- Transmembrane proteins: Transmembrane proteins extend completely through the membrane. These types of proteins majorly function on both sides of the layer (intracellular and extracellular) and help to transport molecules across it.
- Peripheral membrane proteins: Peripheral membrane proteins are located on the inner and outer surfaces of the plasma membrane, and are not embedded in the lipid bilayer as the other membrane proteins. They bound to the exposed regions of the integral proteins through non-covalent interactions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
- There is a patient with breast cancer, after staining the breast tissue with H&E, state the molecular subtype of the tumour extracted. Results of H&E staining are down belowarrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Instant Absorption Questions Calculate these : a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardUse the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for a propanoic acid solution (CH₂CH₂CO₂H, pK₁ = 4.874) to calculate the quotient [A-]/[HA] at three different pH values. pH = 4.479 [A-] [HA] [A-] pH = 4.874 [HA] = pH = 5.220 [A-] = [HA]arrow_forward
- In order to establish the expiration date of perishable food, growth curve data must be collected. Once the microbial load is so high that it poses a hazard to human health, the food item is no longer considered safe (expired). Generally a load of x50,000 bacteria/gram is considered unsafe. Your task is to determine the microbial growth curves for MicroYo, a new brand of yogurt. The growth is determined by sampling the yogurt and growing the bacterial isolates in broth culture which is then serially diluted by a total of x10,000 and inoculated onto standard petri plates of nutrient agar. The following colony counts are measured: Time (days) MicroYo colony count# 1 1 4 1 12 2 16 20 4 7 What day should you recommend expiring the yogurt (the last possible date before the microbial load is unsafe). 12 4 20 16arrow_forward9. Chicken combs in chickens is an example where you see interactions between genes. See potential genotypes and phenotypes below. Which genotype, when mated to a rose comb chicken, will produce progeny that are 50% walnut comb and 50% pea comb? walnut (RRPP) walnut (RrPP) pea (rrPP) walnut (RRPP) walnut (RrPp) pea (rrPp) rose rose single (RRPP) (Rrpp) (rrpp)arrow_forwardDescribe a compound light microscope and its importance in microbiology (2) examples of at least two microbes viewed under a compound light microscope and their general characteristics (note: the microbes you choose do not need to be the ones outlined in the above tutorial video) and (3) at least one source you used for the information included in your infographic.arrow_forward
- Price of visit Number of visits $700 0 $600 [1 $500 2 $400 3 $300 4 00000 The Table blow gives the demand curve for doctor visits for Elena. If the price of a doctor's visit is $600, and Elena does not have health insurance, she will visit the doctor times. If Elena obtains 50% coinsurance (the company pays 50% of the medical bill, Elena pays 50%), then Elena will visit the doctor times. 1; 2 0; 3 0; 2 1;4 2; 1arrow_forwardP 200 150- 100 50 w/instrance/ w/insurance 2 100 Demand Assume that the white curve (labeled "Demand") represents an individual's true demand for this particular health care service. The coinsurance associated with insurance option 1 (in blue) is likely _. 0000 100% 25% 50% 0%arrow_forwardUse the figure below. Bob and Nancy have the same income and total utility.. willingness to pay for an insurance premium will be lower than because they are. risk- averse. Total utility Current utility Bob's utility Nancy's utility 0000 Bob; Nancy; less Nancy; Bob; less Nancy; Bob; more Bob; Nancy; more Current Income incomearrow_forward
- Consider the figure below. Suppose the true price of a health care service is P1. Suppose further that the individual has obtained insurance that has a fixed copayment for this particular service. The copayment is represented by price P2. represents the quantity of the service the individual would consume without insurance. quantity of the service the individual would consume with the insurance. Health Care Service represents the P. P₂ a Q1;Q2 Q2; Q3 Q1; Q3 Q3; Q1 Q2; Q1 फ f Q ८ g d h Q3\D 7Q 00000arrow_forwardThe table shows the utility Jordan receives at various income levels, but they do not know what their income will be next year. There is a 15% chance their income will be $25,000, a 20% chance their income will be $35,000, and a 65% chance their income will be $45,000. We know that Jordan is Income $25,000 Utility 2,800 30,000 3,200 35,000 3,500 40,000 3,700 45,000 3,800 ☐ none of the above 0 000 risk taker (lover) because their marginal utility of income is increasing risk neutral because their marginal utility of income is constant risk averse because their marginal utility of income is decreasing risk neutral because their marginal utility of income is decreasingarrow_forwardOOOO a d+e d a+b+c Consider the figure below. Suppose the true price of a health care service is P1. Suppose further that the individual has obtained insurance that has a fixed copayment for this particular service. The copayment is represented by price P2. The social loss from moral hazard if the individual has copayment P2 is represented graphically by the area(s): Health Care Service P. a No 4 ८ e g Q2 Q3 Darrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





