
a.
Write a system of linear inequalities.
a.
Answer to Problem 17PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Cholesterol in human blood is necessary, but too much can lead to health problems. There are three main types of cholesterol: HDL (high-density lipoproteins), LDL (low-density lipoproteins), and VLDL (very low-density lipoproteins). HDL is considered “good” cholesterol; LDL and VLDL are considered “bad” cholesterol. A standard fasting cholesterol blood test measures total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. These numbers are used to estimate LDL and VLDL, which are difficult to measure directly. It is recommended that your combined LDL/VLDL cholesterol level be less than
Write a system of linear inequalities for the recommended cholesterol levels. Let represent the HDL cholesterol level, and let represent the combined LDL VLDL cholesterol level.
Calculation:
If
LDL level should be less than
Hence ,the system of inequalities can be:
b.
Graph the system of inequalities.
b.
Answer to Problem 17PS
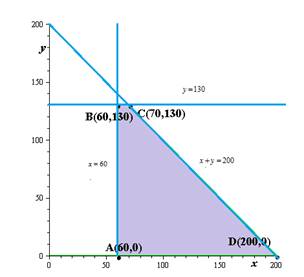
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Cholesterol in human blood is necessary, but too much can lead to health problems. There are three main types of cholesterol: HDL (high-density lipoproteins), LDL (low-density lipoproteins), and VLDL (very low-density lipoproteins). HDL is considered “good” cholesterol; LDL and VLDL are considered “bad” cholesterol. A standard fasting cholesterol blood test measures total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. These numbers are used to estimate LDL and VLDL, which are difficult to measure directly. It is recommended that your combined LDL/VLDL cholesterol level be less than
Graph the system of inequalities from part (a).Label any vertices of the solution region.
Calculation:
We need to sketch the graph and label the vertices.
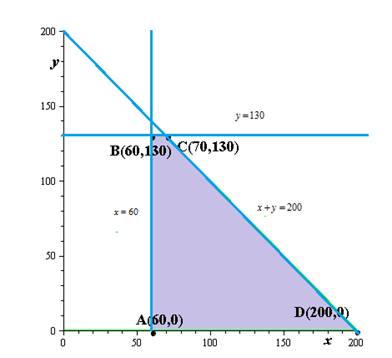
Hence, the result.
c.
Are the cholesterol levels within recommendations?
c.
Answer to Problem 17PS
The given level is not well within the limit .
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Cholesterol in human blood is necessary, but too much can lead to health problems. There are three main types of cholesterol: HDL (high-density lipoproteins), LDL (low-density lipoproteins), and VLDL (very low-density lipoproteins). HDL is considered “good” cholesterol; LDL and VLDL are considered “bad” cholesterol. A standard fasting cholesterol blood test measures total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. These numbers are used to estimate LDL and VLDL, which are difficult to measure directly. It is recommended that your combined LDL/VLDL cholesterol level be less than
Are the following cholesterol levels within recommendations? Explain your reasoning.
LDL/VLDL:
HDL:
Total:
Calculation:
We need to check the following levels come under the recommendation limit or not.
LDL/VLDL:
HDL:
Total:
Hence, the given level is not well within the limit since the total cholesterol is greater than
d.
Give an example of cholesterol levels.
d.
Answer to Problem 17PS
HDL −
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Cholesterol in human blood is necessary, but too much can lead to health problems. There are three main types of cholesterol: HDL (high-density lipoproteins), LDL (low-density lipoproteins), and VLDL (very low-density lipoproteins). HDL is considered “good” cholesterol; LDL and VLDL are considered “bad” cholesterol. A standard fasting cholesterol blood test measures total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. These numbers are used to estimate LDL and VLDL, which are difficult to measure directly. It is recommended that your combined LDL/VLDL cholesterol level be less than
Give an example of cholesterol levels in which the LDL VLDL cholesterol level is too high but the HDL cholesterol level is acceptable.
Calculation:
We need to find a cholesterol level where LDL level is too high and HDL level and total cholesterol are in acceptable limits.
In order to make LDL in high level, make HDL level with some low acceptable level.
Let us take HDL level as
Hence, another one can be HDL −
e.
Find a point in the solution region.
e.
Answer to Problem 17PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Cholesterol in human blood is necessary, but too much can lead to health problems. There are three main types of cholesterol: HDL (high-density lipoproteins), LDL (low-density lipoproteins), and VLDL (very low-density lipoproteins). HDL is considered “good” cholesterol; LDL and VLDL are considered “bad” cholesterol. A standard fasting cholesterol blood test measures total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. These numbers are used to estimate LDL and VLDL, which are difficult to measure directly. It is recommended that your combined LDL/VLDL cholesterol level be less than
Another recommendation is that the ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol be less than 4 (that is, less than
Calculation:
We have to find LDL and HDL level in such a way that the ratio of total cholesterol to HDL is less than
Let us take some arbitrary point in the feasible solution set from the graph .
The point
The HDL should be at least and the feasible region starts from the
Hence, the point
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- #2arrow_forward2. We want to find the inverse of f(x) = (x+3)² a. On the graph at right, sketch f(x). (Hint: use what you know about transformations!) (2 points) b. What domain should we choose to get only the part of f (x) that is one- to-one and non-decreasing? Give your answer in inequality notation. (2 points) - c. Now use algebra to find f¯¹ (x). (2 points) -4- 3- 2 1 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 -1- -2- --3- -4 -N- 2 3 4arrow_forward1. Suppose f(x) = 2 4 == x+3 and g(x) = ½-½. Find and fully simplify ƒ(g(x)). Be sure to show all x your work, write neatly so your work is easy to follow, and connect your expressions with equals signs. (4 points)arrow_forward
- Find the one sided limit Tim f(x) where f(x)= (2x-1 X>1+ *arrow_forwardFind the limit lim X-700 4 13x-15 3x4+x³-12arrow_forwardFind the slope of the line secant to the curve F(x) = 13-x³ (from x=1 to x=2]arrow_forwardFind the ONe sided limit lim 2x X-2 1-xarrow_forwardFor each function, identify all points of discontinuity and label them as removable, jump, or infinite. A) f(x) = x-4 (X+15)(x-4) B) f(x) = (x²-1 x ≤2 14-2x 2arrow_forwardFind the one sided limit 2 lim Flx) where f(x) = (x²-4_xarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningSolve ANY Optimization Problem in 5 Steps w/ Examples. What are they and How do you solve them?; Author: Ace Tutors;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BfOSKc_sncg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYTypes of solution in LPP|Basic|Multiple solution|Unbounded|Infeasible|GTU|Special case of LP problem; Author: Mechanical Engineering Management;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F-D2WICq8Sk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYOptimization Problems in Calculus; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q1U6AmIa_uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYIntroduction to Optimization; Author: Math with Dr. Claire;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YLzgYm2tN8E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningSolve ANY Optimization Problem in 5 Steps w/ Examples. What are they and How do you solve them?; Author: Ace Tutors;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BfOSKc_sncg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYTypes of solution in LPP|Basic|Multiple solution|Unbounded|Infeasible|GTU|Special case of LP problem; Author: Mechanical Engineering Management;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F-D2WICq8Sk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYOptimization Problems in Calculus; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q1U6AmIa_uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYIntroduction to Optimization; Author: Math with Dr. Claire;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YLzgYm2tN8E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY