
Concept explainers
Analyzing and Interpreting the Effects of the LIFO/FIFO Choice on Inventory Turnover Ratio
Simple Plan Enterprises uses a periodic inventory system. Its records showed the following:
Inventory, December 31, using FIFO → 38 Units @$14 = $532
Inventory, December 31, using UFO → 38 Units @ $10 = $380
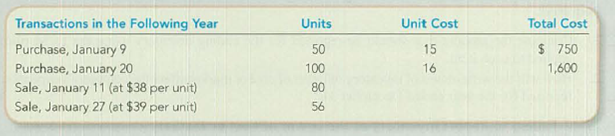
Required:
- 1. Compute the number and cost of goods available for sale, the cost of ending inventory, and the cost of goods sold under FIFO and LIFO.
- 2. Compute the inventory turnover ratio under the FIFO and LIFO inventory costing methods (show computations).
- 3. Based on your answer to requirement 2, explain whether analysts should consider the inventory costing method when comparing companies’ inventory turnover ratios.
Requirement 1:
To Compute: The number of units and cost of goods available for sale and cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under FIFO and LIFO.
Explanation of Solution
Determine cost of goods available for sale _FIFO.
| Date | Particulars | Units ($) | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a × b) | ||
| December 31 | Beginning inventory | 38 | 14 | 532 |
| January 9 | Purchased | 50 | 15 | 750 |
| January 20 | Purchased | 100 | 16 | 1,600 |
| Total | 188 | $2,882 |
Table (1)
Therefore, the cost of goods sold available for sale under FIFO for 188 units of inventory is $2,882.
Determine cost of goods available for sale _LIFO.
| Date | Particulars | Units ($) | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a × b) | ||
| December 31 | Beginning inventory | 38 | 10 | 380 |
| January 9 | Purchased | 50 | 15 | 750 |
| January 20 | Purchased | 100 | 16 | 1,600 |
| Total | 188 | $2,730 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the cost of goods sold available for sale under LIFO for 188 units of inventory is $2,882.
Calculate the number of units in ending inventory:
Therefore, the number of units in ending inventory is 52 units.
In First-in-First-Out method, the cost of initial purchased items is sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists the recent purchased items.
Determine the amount of cost of goods sold.
| Date | Particulars | Units | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a × b) | ||
| December 31 | Beginning inventory | 38 | 14 | 532 |
| January 9 | Purchased | 50 | 15 | 750 |
| January 20 | Purchased | 48 | 16 | 768 |
| Cost of goods sold | 136 | $2,050 |
Table (3)
Determine ending inventory under FIFO method.
| Date | Particulars | Units | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a × b) | ||
| Ending inventory | 52 | 16 | 832 | |
| Ending inventory | $832 |
Table (4)
Hence, the cost of goods sold under FIFO is $2,050 and the value of ending inventory is $832.
In Last-in-First-Out method, the cost of last purchased items is sold first. The value of the closing stock consists the initial purchased items.
Determine the amount of cost of goods sold.
| Date | Particulars | Units | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a × b) | ||
| January 20 | Purchased | 100 | 16 | 1,600 |
| January 9 | Purchased | 36 | 15 | 540 |
| Cost of goods sold | 136 | $2,140 |
Table (5)
Determine ending inventory under LIFO method.
| Date | Particulars | Units | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a × b) | ||
| December 31 | Beginning inventory | 38 | 10 | 380 |
| January 9 | Purchased | 14 | 15 | 210 |
| Ending inventory | $590 |
Table (6)
Hence, the cost of goods sold under LIFO is $2,140 and the value of ending inventory is $590.
Requirement 2:
To Compute: The inventory turnover ratio under FIFO and LIFO inventory costing method.
Answer to Problem 14E
| Inventory Costing Method | Inventory Turnover Ratio |
| FIFO | 3.01 |
| LIFO | 4.41 |
Explanation of Solution
Inventory Turnover: The comparison between the average number of time of sales and the average level of inventory during a period is called as Inventory Turnover. In other words, it is the ratio between the Cost of Goods Sold and Average Inventory.
Calculate the inventory turnover ratio under FIFO:
Step 1: Calculate the average inventory.
Step 2: Calculate the inventory turnover ratio.
Calculate the inventory turnover ratio under LIFO:
Step 1: Calculate the average inventory.
Step 2: Calculate the inventory turnover ratio.
Requirement 3:
To Explain: Whether analysts consider the inventory costing method when comparing companies inventory turnover ratios.
Explanation of Solution
- The inventory costing method present a major difference in the inventory turnover ratio.
- If analysts compare the inventory turnover ratio across companies, they must take this into account before deciding whether one company has better inventory management than another.
- If they are comparing the same company over time, it is not as important provided the company is consistent in the method it uses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
GEN COMBO LL FUNDAMENTALS OF FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING; CONNECT ACCESS CARD
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





