
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134202709
Author: Richard Wolfson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 10E
Determine the work you would have to do to move a block of mass m from point 1 to point 2 at constant speed over the two paths shown in Fig. 7.15. The coefficient of friction has the constant value μ over the surface. Note: The diagram lies in a horizontal plane.
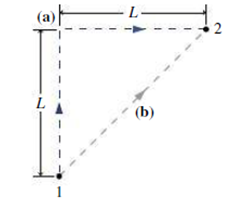
FIGURE 7.15 Exercises 10 and 11
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find the total bind
Mev.
binding energy for
13
Carbon, 6C (atomic mass = 13.0033554)
What is the
27
energy
absorbed in this endothermic Auclear reaction
2] Al + 'n → 27 Mg + ! H? (The atom mass of "Al is 26.981539u.
and that of 11 Mg is 26.984341u)
MeV
What is the energy released in this nuclear reaction 1 F + "', H-1 O+ He?
19
19
16
(The atomic mass of 1F is 18.998403 u, and that of 20 is 15.9949154)
MeV.
Chapter 7 Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Ch. 7.1 - Suppose it takes the same amount of work to push a...Ch. 7.2 - Gravitational force actually decreases with...Ch. 7.3 - A bowling ball is tied to the end of a long rope...Ch. 7.4 - For which of the following systems is (1)...Ch. 7.5 - A bowling ball is tied to the end of a long rope...Ch. 7.6 - The figure shows the potential energy associated...Ch. 7 - Figure 7.14 shows force vectors at different...Ch. 7 - Is the conservation-of-mechanical-energy principle...Ch. 7 - Why cant we define a potential energy associated...Ch. 7 - Can potential energy be negative? Can kinetic...
Ch. 7 - If the potential energy is zero at a given point,...Ch. 7 - If the difference in potential energy between two...Ch. 7 - If the difference in potential energy between two...Ch. 7 - A tightrope walker follows an essentially...Ch. 7 - If conservation of energy is a law of nature, why...Ch. 7 - Determine the work you would have to do to move a...Ch. 7 - Now lake Fig. 7.15 lo lie in a vertical plane, and...Ch. 7 - Rework Example 7.1, now taking the zero of...Ch. 7 - Find the potential energy associated with a 70-kg...Ch. 7 - You fly from Bostons Logan Airport, at sea level,...Ch. 7 - The potential energy associated with a 60-kg hiker...Ch. 7 - How much energy can be stored in a spring with k =...Ch. 7 - How far would you have to stretch a spring with k...Ch. 7 - A biophysicist grabs the ends of a DNA strand with...Ch. 7 - A skier starts down a frictionless 32 slope. After...Ch. 7 - A 10,000-kg Navy jet lands on an aircraft carrier...Ch. 7 - A 120-g arrow is shot vertically from a bow whose...Ch. 7 - In a railroad yard, a 35,000-kg boxcar moving at...Ch. 7 - You work for a toy company, and youre designing a...Ch. 7 - A 54-kg ice skater pushes off the wall of the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 25ECh. 7 - A particle slides along the frictionless track...Ch. 7 - A particle slides back and forth on a frictionless...Ch. 7 - A particle is trapped in a potential well...Ch. 7 - The reservoir at Northfield Mountain Pumped...Ch. 7 - The force in Fig. 7.14a is given by Fa=FoJ, where...Ch. 7 - A 1.50-kg brick measures 20.0 cm 8.00 cm 5.50...Ch. 7 - A carbon monoxide molecule can be modeled as a...Ch. 7 - A more accurate expression for the force law of...Ch. 7 - For small stretches, the Achilles tendon can be...Ch. 7 - The force exerted by an unusual spring when its...Ch. 7 - The force on a particle is given by F=Al/x2, where...Ch. 7 - A particle moves along the x-axis under the...Ch. 7 - As a highway engineer, youre asked to design a...Ch. 7 - A spring of constant k, compressed a distance x,...Ch. 7 - A child is on a swing whose 3.2-m-long chains make...Ch. 7 - With x x0 = h and a = g, Equation 2.11 gives the...Ch. 7 - The nuchal ligament is a cord-like structure that...Ch. 7 - A 200-g block slides back and forth on a...Ch. 7 - Automotive standards call for bumpers that sustain...Ch. 7 - A block slides on the frictionless loop-the-loop...Ch. 7 - The maximum speed of the pendulum bob in a...Ch. 7 - A mass m is dropped from height h above the top of...Ch. 7 - A particle with total energy 3.5 J is trapped in a...Ch. 7 - (a) Derive an expression for the potential energy...Ch. 7 - In ionic solids such as NaCl (salt), the potential...Ch. 7 - Repeat Exercise 19 for the case when the...Ch. 7 - As an energy-efficiency consultant, youre asked to...Ch. 7 - A spring of constant k = 340 N/m is used to launch...Ch. 7 - A bug slides back and forth in a bowl 15 cm deep,...Ch. 7 - A 190-g block is launched by compressing a spring...Ch. 7 - A block slides down a frictionless incline that...Ch. 7 - An 840-kg roller-coaster car is launched from a...Ch. 7 - A particle slides back and forth in a frictionless...Ch. 7 - A child sleds down a frictionless hill whose...Ch. 7 - A bug lands on top of the frictionless, spherical...Ch. 7 - A particle of mass m is subject to a force...Ch. 7 - A block of weight 4.5 N is launched up a 30...Ch. 7 - Your engineering department is asked to evaluate...Ch. 7 - Your roommate is writing a science fiction novel...Ch. 7 - You have a summer job at your universitys zoology...Ch. 7 - Biomechanical engineers developing artificial...Ch. 7 - Blocks with different masses are pushed against a...Ch. 7 - Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the Sun....Ch. 7 - Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the Sun....Ch. 7 - Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the Sun....Ch. 7 - Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the Sun....
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
WHAT IF? What would the human life cycle be like if we had alternation of generations? Assume that the multice...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
A source of electromagnetic radiation produces infrared light. Which of the following could be the wavelength ...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Some organizations are starting to envision a sustainable societyone in which each generation inherits sufficie...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
When you rub your cold hands together, the friction between them results in heat that warms your hands. Why doe...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
The distances you obtained in Question 3 are for only one side of the ridge. Assuming that a ridge spreads equa...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the energy released in this B+ nuclear reaction خالد 2½ Al w/ Mg + ie? (The atomic mass of 11 Al is 23.9999394 and that > of 12 Mg is 23.985041 u) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released / absorbed in this nuclear reaction 14 N+ & He → » O + ! N? (The atomic mass of 14 N is 14.003074u. 17N+ and that of 10 is 16.9991324). MeVarrow_forwardCan someone help me answer this question thanks.arrow_forward
- Can someone help me with this question thanks.arrow_forward4B. Four electrons are located on the corners of a square, one on each corner, with the sides of the square being 25 cm long. a) Draw a sketch of the scenario and use your sketch to b) Determine the total force (magnitude and direction) on one of the electrons from the other three?arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 3. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed vo from the floor of a room of height h. It hits the ceiling and then returns to the floor, from which it rebounds, managing just to hit the ceiling a second time. Assume that the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor, e, is equal to that between the ball and the ceiling. Compute e.arrow_forward
- Portfolio Problem 4. Consider two identical springs, each with natural length and spring constant k, attached to a horizontal frame at distance 2l apart. Their free ends are attached to the same particle of mass m, which is hanging under gravity. Let z denote the vertical displacement of the particle from the hori- zontal frame, so that z < 0 when the particle is below the frame, as shown in the figure. The particle has zero horizontal velocity, so that the motion is one dimensional along z. 000000 0 eeeeee (a) Show that the total force acting on the particle is X F-mg k-2kz 1 (1. l k. (b) Find the potential energy U(x, y, z) of the system such that U x = : 0. = O when (c) The particle is pulled down until the springs are each of length 3l, and then released. Find the velocity of the particle when it crosses z = 0.arrow_forwardIn the figure below, a semicircular conductor of radius R = 0.260 m is rotated about the axis AC at a constant rate of 130 rev/min. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.22 T fills the entire region below the axis and is directed out of the page. R Pout (a) Calculate the maximum value of the emf induced between the ends of the conductor. 1.77 v (b) What is the value of the average induced emf for each complete rotation? 0 v (c) How would your answers to parts (a) and (b) change if the magnetic field were allowed to extend a distance R above the axis of rotation? (Select all that apply.) The value in part (a) would increase. The value in part (a) would remain the same. The value in part (a) would decrease. The value in part (b) would increase. The value in part (b) would remain the same. The value in part (b) would decrease. × (d) Sketch the emf versus time when the field is as drawn in the figure. Choose File No file chosen This answer has not been graded yet. (e) Sketch the emf…arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 2. A particle of mass m slides in a straight line (say along i) on a surface, with initial position x ©0 and initial velocity Vo > 0 at t = 0. The = particle is subject to a constant force F = -mai, with a > 0. While sliding on the surface, the particle is also subject to a friction force v Ff = -m fo = −m fov, with fo > 0, i.e., the friction force has constant magnitude mfo and is always opposed to the motion. We also assume fo 0, and solve it to find v(t) and x(t). How long does it take for the particle to come to a stop? How far does it travel? (b) After coming to a stop, the particle starts sliding backwards with negative velocity. Write the equation of motion in this case, and solve it to find the time at which the particle returns to the original position, x = 0. Show that the final speed at x 0 is smaller than Vo. = Express all your answers in terms of a, fo and Vo.arrow_forward
- = Portfolio Problem 1. A particle of mass m is dropped (i.e., falls down with zero initial velocity) at time t 0 from height h. If the particle is subject to gravitational acceleration only, i.e., a = −gk, determine its speed as it hits the ground by solving explicitly the expressions for its velocity and position. Next, verify your result using dimensional analysis, assuming that the general relation is of the form v = khag³m, where k is a dimensionless constant.arrow_forwardReview Conceptual Example 2 before attempting this problem. Two slits are 0.158 mm apart. A mixture of red light (wavelength = 693 nm) and yellow-green light (wavelength = 567 nm) falls on the slits. A flat observation screen is located 2.42 m away. What is the distance on the screen between the third-order red fringe and the third-order yellow- green fringe? m = 3 m = 3 m= 0 m = 3 m = 3 Fringes on observation screenarrow_forwardIn the figure below, a semicircular conductor of radius R = 0.260 m is rotated about the axis AC at a constant rate of 130 rev/min. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.22 T fills the entire region below the axis and is directed out of the page. In this illustration, a wire extends straight to the right from point A, then curves up and around in a semicircle of radius R. On the right side of the semicircle, the wire continues straight to the right to point C. The wire lies in the plane of the page, in a region of no magnetic field. Directly below the axis A C is a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page, vector Bout. If viewed from the right, the wire can rotate counterclockwise, so that the semicircular part can rotate into the region of magnetic field. (a) Calculate the maximum value of the emf induced between the ends of the conductor. V(b) What is the value of the average induced emf for each complete rotation? Consider carefully whether the correct answer is…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical work done (GCSE Physics); Author: Dr de Bruin's Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OapgRhYDMvw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY