
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.9, Problem 6.155P
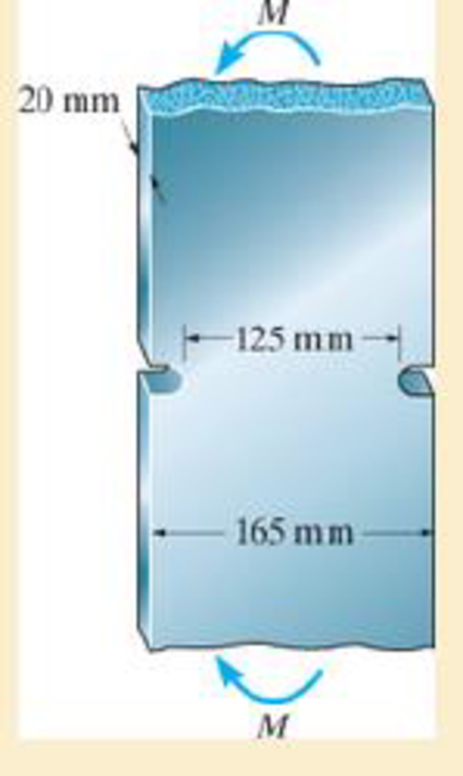
If the radius of each notch on the plate is r = 10 mm, determine the largest moment M that can be applied. The allowable bending stress is σallow = 180 MPa.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
CORRECT ANSWER WITH COMPLETE FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE.
A torque wrench is used to tighten the pipe shown.Dimensions: S1 = 400 mm; S2 = 250 mm; S3 = 100 mmModulus of Rigidity G = 78 GPa1. The diameter of the solid pipe is 20 mm. How much is themaximum force P (N) that can be applied based on theallowable shear stress of 60 MPa?2. For a hollow pipe with 50 mm outside diameter and is 6 mmthick, compute for the maximum force P (kN) that can beapplied such that the angle of twist at A does not exceed 5degrees.3. The torque applied to tighten the hollow pipe is 200 N-m.Given: Pipe outside diameter = 50 mm Pipe thickness = 6 mmSolve for the resulting maximum shear stress (MPa) in the pipe.
Correct answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote.
6: The shaft carries a total torque T0 that is uniformly distributedover its length L. Determine the angle of twist (degrees) of the shaft in termsif T0 = 1.2 kN-m, L = 2 m, G = 80 GPa, and diameter = 120 mm.
2. Calculate the force in all members of the trusses shown using the method of joints.
A
5525 lb
C
3500 lb
BY
14'-0"
D
10'- 0"
6250 lb
10'- 0"
E
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 6.2 - In each case, the beam is subjected to the...Ch. 6.2 - and then draw the shear and moment diagrams for...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, express the shear and moment...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, express the shear and moment...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, express the shear and moment...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft...
Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam,...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam,...Ch. 6.2 - Express the shear and moment in terms of x for 0 ...Ch. 6.2 - Express the internal shear and moment in the...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft....Ch. 6.2 - Express the internal shear and moment in terms of...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam,...Ch. 6.2 - If the force applied to the handle of the load...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft....Ch. 6.2 - The crane is used to support the engine, which has...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Members ABC and BD of the counter chair are...Ch. 6.2 - A reinforced concrete pier is used to support the...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam...Ch. 6.2 - The industrial robot is held in the stationary...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the placement distance a of the roller...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 6.2 - The 150-lb man sits in the center of the boat,...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - The footing supports the load transmitted by the...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - The support at A allows the beam to slide freely...Ch. 6.2 - The smooth pin is supported by two leaves A and B...Ch. 6.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the rod....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam...Ch. 6.2 - The beam is used to support a uniform load along...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the double...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the simply...Ch. 6.2 - The compound beam is fixed at A, pin connected at...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 6.2 - The compound beam is fixed at A, pin connected at...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - A short link at B is used to connect beams AB and...Ch. 6.2 - The truck is to be used to transport the concrete...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the cross...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the location of the centroid, y, and the...Ch. 6.4 - In each case, show how the bending stress acts on...Ch. 6.4 - Sketch the bending stress distribution over each...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - An A-36 steel strip has an allowable bending...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the moment M that will produce a maximum...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the maximum tensile and compressive...Ch. 6.4 - The beam is constructed from four pieces of wood,...Ch. 6.4 - The beam is constructed from four pieces of wood,...Ch. 6.4 - The beam is made from three boards nailed together...Ch. 6.4 - The beam is made from three boards nailed together...Ch. 6.4 - If the built-up beam is subjected to an internal...Ch. 6.4 - If the built-up beam is subjected to an internal...Ch. 6.4 - The beam is subjected to a moment of M = 40 kN m....Ch. 6.4 - The steel shaft has a diameter of 2 in. It is...Ch. 6.4 - The beam is made of steel that has an allowable...Ch. 6.4 - A shaft is made of a polymer having an elliptical...Ch. 6.4 - Solve Prob. 6-65 if the moment M = 50 N m is...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.67PCh. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by smooth journal bearings...Ch. 6.4 - The axle of the freight car is subjected to a...Ch. 6.4 - The strut on the utility pole supports the cable...Ch. 6.4 - The boat has a weight of 2300 lb and a center of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the absolute maximum bending stress in...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 6.4 - The pin is used to connect the three links...Ch. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 6.4 - A timber beam has a cross section which is...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to an internal moment of...Ch. 6.4 - If the allowable tensile and compressive stress...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to an internal moment of...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a moment of M = 100 kN...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is made of material having an...Ch. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 6.4 - If the intensity of the load w = 15 kN/m,...Ch. 6.4 - If the allowable bending stress is allow = 150...Ch. 6.4 - The beam is subjected to the triangular...Ch. 6.4 - The beam has a rectangular cross section with b =...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.88PCh. 6.4 - If the compound beam in Prob. 642 has a square...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam in Prob. 628 has a rectangular cross...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the absolute maximum bending stress in...Ch. 6.4 - Determine, to the nearest millimeter, the smallest...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the absolute maximum bending stress in...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the absolute maximum bending stress in...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the smallest diameter of the shaft to...Ch. 6.4 - A log that is 2 ft in diameter is to be cut into a...Ch. 6.4 - A log that is 2 ft in diameter is to be cut into a...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam in Prob.63 has a rectangular cross...Ch. 6.4 - The simply supported truss is subjected to the...Ch. 6.4 - If d = 450 mm, determine the absolute maximum...Ch. 6.4 - If the allowable bending stress is allow = 6 MPa,...Ch. 6.4 - The beam has a rectangular cross section as shown....Ch. 6.4 - The beam has the rectangular cross section shown....Ch. 6.5 - Determine the bending stress at corners A and B....Ch. 6.5 - Determine the maximum bending stress in the beams...Ch. 6.5 - The member has a square cross section and is...Ch. 6.5 - The member has a square cross section and is...Ch. 6.5 - Consider the general case of a prismatic beam...Ch. 6.5 - Determine the bending stress at point A of the...Ch. 6.5 - Determine the bending stress at point A of the...Ch. 6.5 - The steel shaft is subjected to the two loads. If...Ch. 6.5 - The 65-mm-diameter steel shaft is subjected to the...Ch. 6.5 - For the section, lz = 31.7(10-5) m4, lY =...Ch. 6.5 - For the section, lz, = 31.7(10-5) m4, lY =...Ch. 6.5 - The box beam is subjected to a moment of M = 15...Ch. 6.5 - Determine the maximum magnitude of the bending...Ch. 6.5 - The shaft is subjected to the vertical and...Ch. 6.5 - For the section, Iy' = 31.7(10-6) m4, Iz' =...Ch. 6.5 - For the section, Iy' = 31.7(10-6) m4, Iz' =...Ch. 6.5 - If the applied distributed loading of w = 4 kN/m...Ch. 6.5 - Determine the maximum allowable intensity w of the...Ch. 6.9 - The composite beam is made of steel (A) bonded to...Ch. 6.9 - The composite beam is made of steel (A) bonded to...Ch. 6.9 - Segment A of the composite beam is made from...Ch. 6.9 - Segment A of the composite beam is made from...Ch. 6.9 - The white spruce beam is reinforced with A-992...Ch. 6.9 - The wooden section of the beam is reinforced with...Ch. 6.9 - The wooden section of the beam is reinforced with...Ch. 6.9 - The Douglas Fir beam is reinforced with A-992...Ch. 6.9 - The steel channel is used to reinforce the wood...Ch. 6.9 - A wood beam is reinforced with steel straps at its...Ch. 6.9 - A bimetallic strip is made from pieces of 2014-T6...Ch. 6.9 - Determine the maximum uniform distributed load w0...Ch. 6.9 - The composite beam is made of A-36 steel (A)...Ch. 6.9 - The composite beam is made of A-36 steel (A)...Ch. 6.9 - If the beam is subjected to a moment of M = 45 kN...Ch. 6.9 - The Douglas Fir beam is reinforced with A-36 steel...Ch. 6.9 - For the curved beam in Fig. 640a, show that when...Ch. 6.9 - The curved member is subjected to the moment of M...Ch. 6.9 - The curved member is made from material having an...Ch. 6.9 - The curved beam is subjected to a moment of M = 40...Ch. 6.9 - The curved beam is made from material having an...Ch. 6.9 - If P = 3 kN, determine the bending stress at...Ch. 6.9 - If the maximum bending stress at section a-a is...Ch. 6.9 - The elbow of the pipe has an outer radius of 0.75...Ch. 6.9 - If the bar is subjected to a couple as shown,...Ch. 6.9 - The curved bar used on a machine has a rectangular...Ch. 6.9 - The steel rod has a circular cross section. If it...Ch. 6.9 - If it is subjected to a moment of M = 5 kN m,...Ch. 6.9 - The member has a circular cross section. If the...Ch. 6.9 - The curved bar used on a machine has a rectangular...Ch. 6.9 - The bar is subjected to a moment of M = 100 N, m....Ch. 6.9 - The allowable bending stress for the bar is allow...Ch. 6.9 - The bar has a thickness of 1 in. and the allowable...Ch. 6.9 - The bar has a thickness of 1 in. and is subjected...Ch. 6.9 - The bar has a thickness of 0.5 in. and the...Ch. 6.9 - If the radius of each notch on the plate is r = 10...Ch. 6.9 - The stepped bar has a thickness of 10 mm....Ch. 6.9 - The bar has a thickness of 0.5 in. and is...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor for the wide-flange...Ch. 6.10 - The wide-flange member is made from an elastic...Ch. 6.10 - The rod has a circular cross section. If it is...Ch. 6.10 - The rod has a circular cross section. If it is...Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of an elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the plastic moment Mp that can be...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor for the beam. Prob....Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor for the beam. Prob....Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of an elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 6.10 - Prob. 6.168PCh. 6.10 - Prob. 6.169PCh. 6.10 - Prob. 6.170PCh. 6.10 - The rod has a circular cross section. If it is...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor of the cross section....Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor for the member having...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor of the cross section....Ch. 6.10 - The box beam is made of an elastic perfectly...Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of an elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 6.10 - The plexiglass bar has a stress-strain curve that...Ch. 6.10 - The stress-strain diagram for a titanium alloy can...Ch. 6.10 - A beam is made from polypropylene plastic and has...Ch. 6.10 - The bar is made of an aluminum alloy having a...Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of phenolic, a structural...Ch. 6 - Using appropriate measurements and data, explain...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor for the wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The compound beam consists of two segments that...Ch. 6 - The composite beam consists of a wood core and two...Ch. 6 - If it resists a moment of M = 125 N m, determine...Ch. 6 - Determine the maximum bending stress in the handle...Ch. 6 - The curved beam is subjected to a bending moment...Ch. 6 - Determine the shear and moment in the beam as...Ch. 6 - A wooden beam has a square cross section as shown...Ch. 6 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft...Ch. 6 - The strut has a square cross section a by a and is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Correct answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. 8: The steel rod fits loosely inside the aluminum sleeve. Both components are attached to a rigid wall at A andjoined together by a pin at B. Because of a slight misalignmentof the pre-drilled holes, the torque T0 = 750 N-m was appliedto the steel rod before the pin could be inserted into theholes. Determine the torque (N-m) in each component afterT0 was removed. Use G = 80 GPa for steel and G = 28 GPa foraluminumarrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. 9: The two steel shafts, each with one end builtinto a rigid support, have flanges attached to their freeends. The flanges are to be bolted together. However,initially there is a 6⁰ mismatch in the location of the boltholes as shown in the figure. Determine the maximumshear stress(ksi) in each shaft after the flanges have beenbolted together. The shear modulus of elasticity for steelis 12 x 106 psi. Neglect deformations of the bolts and theflanges.arrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. The tapered, wrought iron shaft carriesthe torque T = 2000 lb-in at its free end. Determine theangle of twist (degrees) of the shaft. Use G = 10 x 106psi for wrought ironarrow_forward
- Correct answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. The compound shaft, consisting of steel and aluminumsegments, carries the two torques shown in the figure. Determine themaximum permissible value of T subject to the following designconditions: τst ≤ 83 MPa, τal ≤ 55 MPa, and θ ≤ 6⁰ (θ is the angle ofrotation of the free end). Use G =83 GPa for steel and G = 28 GPa foraluminum.arrow_forwardThe solid compound shaft, made of threedifferent materials, carries the two torques shown. Theshear moduli are 28 GPa for aluminum, 83 GPa for steel,and 35 GPa for bronze.1. Calculate the maximum shear stress (MPa) in eachmaterial.2. Find the angle of rotation (degrees) of the free endof the shaft.arrow_forwardCorrect answer only please. I will upvote. The velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forward
- I want the steps of operation of the circuit, clearly in detail. Please. LV1arrow_forwardComplet the solution: Vavg Ti Te Ts Qhexp Nuexp htheo Re Nutheo Error (m/s) (°C) (°C) (°C) (W) 2.11 18.8 21.3 45.8 2.61 18.5 20.8 46.3 Heat transfer Given data: a= 10 cm. L= 10 cm. b= 20 cm. H=40cm. ⚫ a = 10, cm: This could represent the width of the duct. ⚫b=20, cm: This might be the height of the duct. ⚫L = 10, cm: This usually stands for the length of the duct in the direction of flow. ⚫H=40, cm: This could indicate the height of some component or another duct-related dimension, but the exact meaning depends on the experiment's context.arrow_forwardplease explain each step and include drawings on the phase diagram. thanksarrow_forward
- Write clearly which points correspond to concentration of solute in front of alpha, concentration of solute in front of beta, amount of solid in the liquid in front of alpha/beta, lowest possible energy (tangent), as well as any other important information. Thank youarrow_forwardQ3: A 4-stroke 6 litres engine is fuelled with methane (CH4) at an air-fuel ratio = 0.8. It operates at 2000 rpm with a volumetric efficiency of 80%. The exhaust (product) leaves the engine at 800 K, and the heat lost to the coolant is 3.4×105 kJ/kmol. What is the engine's output power? Assume both air and fuel (methane) inlet to the engine at 298 K. Take for methane, the molecular weight is M = 16 kg/kmol, and the heat of combustion is 50.01 MJ/kg. The ambient conditions (p = 101 kPa, T = 25 °C). (24 points)arrow_forwardTemperature (°C) 100 4. Consider the solidification of a binary Pb-10%Sn alloy. Assume that during solidification, there is complete mixing in the liquid and no diffusion in the solid. Use the phase diagram below to answer the following question. (a) Draw (on the phase diagram) the compositions of the liquid and the solid at the interface as a function of temperature during solidification. (b) Illustrate on the phase diagram how one would calculate the volume fraction solidified at a given temperature. (c) (d) Indicate the temperature at which solidification is complete. Do you expect ẞ to be present in the as-cast microstructure? Explain 300 327°C 200 a (Pb) 20 20 a + L 18.3 183°C α + β 40 60 Composition (wt% Sn) Liquid 600 500 232°C B+L 400 B 61.9 97.8 300 808 100 (Sn) 200 100 Temperature (°F)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License