
Concept explainers
Draw three resonance structures for the hydrogen sulfite ion (), one that obeys the octet rule for the central atom and two that expand the octet of the central atom. Calculate the formal charges on all atoms in each structure and determine which, if airy, of the resonance structures has formal charges that are inconsistent with the elements’ electronegativities.
Interpretation:
The resonance structures for hydrogen sulfite ion should be drawn where one resonance structure must obey octet rule and the other two having expanded octet. Also formal charge of all the resonance structure should be drawn and to identify the resonance structure that has an inconsistent with the electronegativities of the elements.
Concept Introduction:
- Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
- In some molecules, there is possibility of more than one Lewis structure where all the structures are equally acceptable. One of the acceptable Lewis structures of these molecules is called resonance structure. All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
- These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
- The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
- Atoms can be stable even though the number of valence electrons in the atoms in a molecule is more than 8 and is called expanded octet
To identify: the resonance structure of hydrogen sulfite ion
Answer to Problem 10PPA
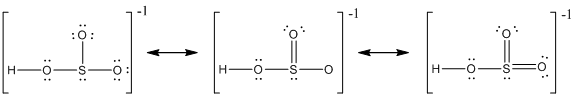
Explanation of Solution
The resonance structure of
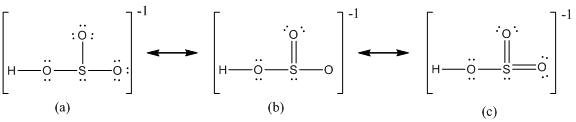
Delocalization of electrons takes place because of the presence of lone pair of electrons in the terminal atoms and the possibility of double bond. The chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure and represented by structures (a), (b) and (c). The chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons forming three possible resonance structures. In all the resonance structures the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact. Also in these structures only in the arrangement of the electrons differs not the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Here sulfur shares a double bond with one of the oxygen atom and shares two single bond with remaining two oxygen atoms. Hence in (a), the central sulfur atom is surrounded by 8 electrons therefore it obeys octet rule.
Here sulfur shares a double bond with one of the oxygen atom and shares two single bond with remaining two oxygen atoms. It also have two lone pairs on it. Hence in (b), the central sulfur atom is surrounded by 10 electrons therefore it obeys does not octet rule and is an expanded octet
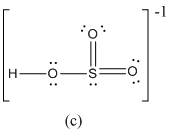
Here sulfur shares two double bond with oxygen atoms and shares a single bond with remaining one oxygen atoms. It also have two lone pairs on it. Hence in (c), the central sulfur atom is surrounded by 12 electrons therefore it obeys does not octet rule and is an expanded octet
Interpretation: the formal charge of atoms of the resonance structure of hydrogen sulfite ion should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- A formal charge (FC) is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, irrespective of relative electronegativity by thinking that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally among atoms.
- This method is used to identify the most probable Lewis structures if more than one possibility exists for a compound.
- Formal charge of an atom can be determined by the given formula.
To determine: the formal charge of atoms of the resonance structure of hydrogen sulfite ion.
Answer to Problem 10PPA
Explanation of Solution
For a
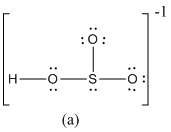
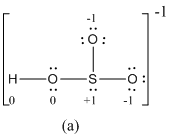
The formal charge of atoms in (a) is calculated.


- Sulfur atom
Substituting,
- Terminal oxygen atoms that has single bond with sulfur atom
Substituting,
- Oxygen atoms that has single bond with sulfur atom and hydrogen
Substituting,
- Hydrogen atom
Substituting,
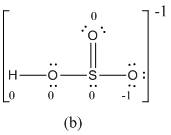
For b
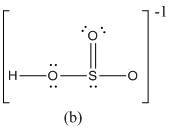
The formal charge of atoms in (b) is calculated.


- Sulfur atom
Substituting,
- Terminal oxygen atom that has single bond with sulfur atom
Substituting,
- Terminal oxygen atom that has double bond with sulfur atom
Substituting,
- Oxygen atoms that has single bond with sulfur atom and hydrogen
Substituting,
- Hydrogen atom
Substituting,
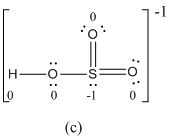
For c
The formal charge of atoms in (c) is calculated.


- Sulfur atom
Substituting,
- Terminal oxygen atoms that has double bond with sulfur atom
Substituting,
Oxygen atoms that has single bond with sulfur atom and hydrogen
Substituting,
Hydrogen atom
Substituting,
- The electronegativity of oxygen is higher than sulfur so usually more electronegative receives negative formal charge. But in the case of resonance structure (c), the less electronegative sulfur atom has -1 formal charge where oxygen gets zero formal charge. Therefore resonance structure (c) has formal charges that are inconsistent with the electronegativities of the elements.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- Reason whether it is possible to determine changes in the Galvani potential difference at the metal-solution interface.arrow_forwardObtain the standard potential at 25°C of the Cu* I Cu | Pt electrode from the standard potentials E° Cu²+/Cu = 0.341 V and E Cu²+ /Cu+ = 0.153 V.arrow_forwardIn electrochemistry, briefly describe the Galvani potential, the Volta potential, and the surface potential. Differentiate between them.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





