
Interpretation:
Determine the stability of the fixed point at the origin and find is there any other fixed points for the system. Depending on other parameters sketch the qualitatively different types of phase portrait.
Concept Introduction:
The parametric curves traced by solutions of a differential equation are known as trajectories.
The geometrical representation of collection of trajectories in a phase plane is called as phase portrait.
The point which satisfies the condition
Closed Orbit corresponds to periodic solution of the system i.e.
If nearby trajectories moving away from the fixed point then the point is said to be saddle point.
If the trajectories swirling around the fixed point, then it is an unstable fixed point.
If nearby trajectories moving away from the fixed point, then the point is said to be unstable fixed point.
If nearby trajectories moving towards the fixed point, then the point is said to be stable fixed point.
To check the stability of fixed point use Jacobian matrix
The point
Answer to Problem 7E
Solution:
The stability of the origin depends upon the values of the various parameters.
The other fixed points for the system are
The different qualitatively phase portrait are shown below.
Explanation of Solution
a)
The given system equations are
Fordetermining the stability of fixed point
Use the Jacobian matrix
The expression of the Jacobian matrix is
Substitute the expressions of
The above Jacobian matrix at the origin becomes,
The eigenvalues of the above Jacobian matrix are
From the above expressions of eigenvalues, the origin is unstable, if
And the origin is stable point if
Thus, the system is stable at origin the value of
(b)
To estimate the other fixed point of the system put
Putting
From the above equation, two conditions are determined.
Put
From the above equation, two conditions are determined.
Now, substituting
Thus, the one of the fixed point is
Now, substituting
Thus, the another fixed point is at
Therefore, there exists another two fixed point at
To check the stability of these points, use Jacobian matrix
Let’s check the stability of the fixed point
Substituting expression of
By substituting
The Jacobian matrix at the point
Here, the Jacobian matrixes are triangular matrix.
And
The eigenvalues of the triangular matrix are the diagonal elements.
Thus, the eigenvalues of Jacobian matrix
The stability of the fixed point
Both the eigenvalues have negative real parts. Hence the fixed point is stable.
If one of the eigenvalue has positive real part and another having negative real part, then the fixed point is saddle fixed point. If both eigenvalues have positive real part, then the fixed point is unstable.
And eigenvalues of Jacobian matrix
The stability of the fixed point
If the both the eigenvalues have negative real parts, then the fixed point is stable.
If one of the eigenvalue has positive real part and another having negative real part, then the fixed point is saddle fixed point. If both eigenvalues have positive real part, then the fixed point is unstable.
(c) The different phase portrait for the different value of the parameter constant is plotted as:
Considering a constant parameter is as follows:
The phase portrait for the above constant value is plotted as follows:
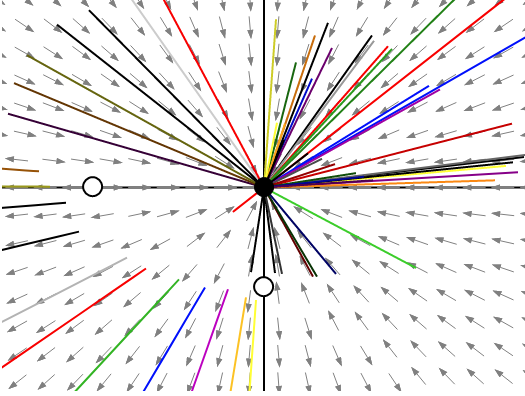
This phase portrait describes that
Considering a constant parameter is as follows:
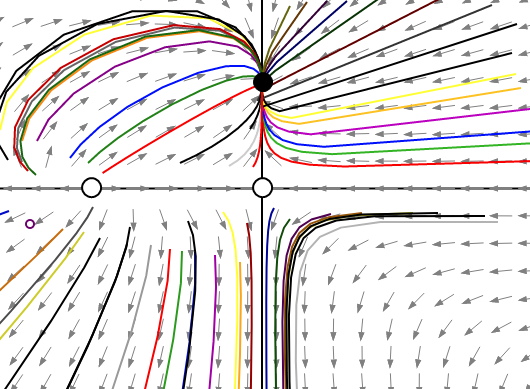
This phase portrait describes that stable point is on the
Considering a constant parameter is as follows:
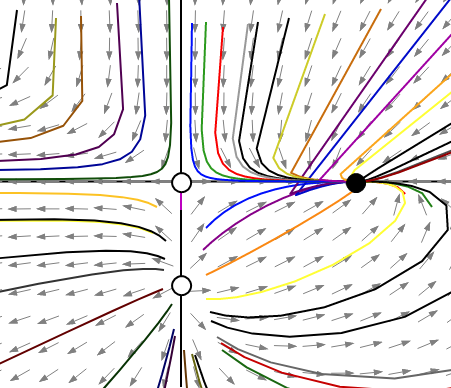
The phase portrait describes that the stable point is on
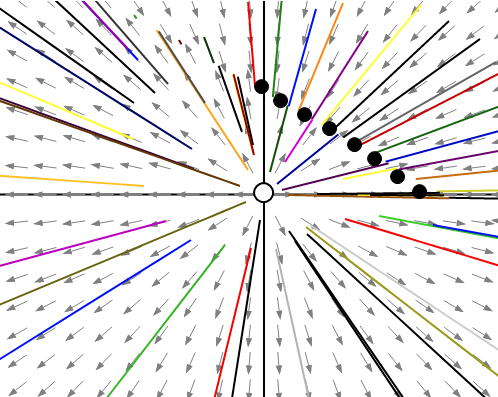
This phase portrait describes that there are infinite number of fixed points in the first quadrant of the graph and an unstable point at origin.
There are four different qualitatively phase portrait can be sketched for the system and there is no possibility of other phase portrait because the nullclines are axes and parallel lines.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
- Q Calculate the Fourier series for f(x) = x on the interval -16≤x≤ Tarrow_forwardFind all positive integers n such that n.2n +1 is a square.arrow_forwardA straight-line H is tangent to the function g(x)=-6x-3+ 8 and passes through the point (- 4,7). Determine, the gradient of the straight-line Choose.... y-intercept of the straight-line Choose... + which of the following is the answers -1.125 -6.72 1.125 7.28 0.07 - 7.28 6.72arrow_forward
- You are required to match the correct response to each statement provided. Another term/word that can be used synonymously to Choose... gradient. A term/phrase that is associated with Arithmetic Progression. Common difference → An identity matrix can be referred to as a Choose... ÷ What is the inequality sign that represents "at most"? VIarrow_forwardAffect of sports on students linked with physical problemsarrow_forward26.1. Locate and determine the order of zeros of the following functions: (a). e2z – e*, (b). z2sinhz, (c). z*cos2z, (d). z3 cosz2.arrow_forward
- 31.5. Let be the circle |+1| = 2 traversed twice in the clockwise direction. Evaluate dz (22 + 2)²arrow_forwardUsing FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative; 1. The distance x of a runner from a fixed point is measured (in meters) at an interval of half a second. The data obtained is: t 0 x 0 0.5 3.65 1.0 1.5 2.0 6.80 9.90 12.15 Use CDF to approximate the runner's velocity at times t = 0.5s and t = 1.5s 2. Using FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative of f(x)=x Inx for an input of 2 assuming a step size of 1. Calculate using Analytical Solution and Absolute Relative Error: = True Value - Approximate Value| x100 True Value 3. Given the data below where f(x) sin (3x), estimate f(1.5) using Langrage Interpolation. x 1 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 f(x) 0.14 -0.69 -0.99 -0.55 0.31 4. The vertical distance covered by a rocket from t=8 to t=30 seconds is given by: 30 x = Loo (2000ln 140000 140000 - 2100 9.8t) dt Using the Trapezoidal Rule, n=2, find the distance covered. 5. Use Simpson's 1/3 and 3/8 Rule to approximate for sin x dx. Compare the results for n=4 and n=8arrow_forward1. A Blue Whale's resting heart rate has period that happens to be approximately equal to 2π. A typical ECG of a whale's heartbeat over one period may be approximated by the function, f(x) = 0.005x4 2 0.005x³-0.364x² + 1.27x on the interval [0, 27]. Find an nth-order Fourier approximation to the Blue Whale's heartbeat, where n ≥ 3 is different from that used in any other posts on this topic, to generate a periodic function that can be used to model its heartbeat, and graph your result. Be sure to include your chosen value of n in your Subject Heading.arrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




