
Concept explainers
To model:
A carbon atom.
Introduction:
Carbon is a substance with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent which makes four electrons accessible to form covalent bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The following picture shows arrangement of subatomic particles in a carbon atom.
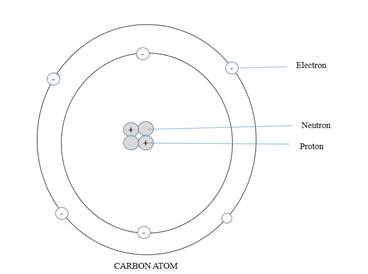
In compounds, carbon atoms always share four pairs of electrons in four covalent bonds. This means that one carbon atom can form single bonds with up to four other atoms. This unique property of carbon is known as catenation.
Carbon atoms can also form multiple bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Biology Science Notebook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
- H3C H Br-Br C=C H₂O H3C-CH2 CH3 (large excess)arrow_forwardmarvin dunham, a 68 year old male, is admitted to the hospital with a deep laceration to the forehead. dr. wallace applies a pressure dressing to his head to control the bleeding. what is the pcs codearrow_forwardExplain the impact William B. Travis has made.arrow_forward
- If PCR was performed on the fragment of DNA shown below using "5'-TAGG-3" and "3'-TCTA-5'" as the primers, how many base pairs long would the PCR product be? To help with this, remember the antiparallel structure of DNA and that primers are complementary and antiparallel to the target sequence that they bind to. Hint: Check out the 5' and 3' labels....they are important! 3’- T A T C C G A C A A T C G A T C G A T T G C C T T C T A A -5’ 5’- A T A G G C T G T T A G C T A G C T A A C G G A A G A T T – 3’arrow_forwardWhen setting up a PCR reaction to act as a negative control for the surface protein A gene... Which primers will you add to the reaction mix? mecA primers, spa primers, mecA primers and spa primers, no primers What will you add in place of template? sterile water, MRSA DNA, Patient DNA, S. aureus DNAarrow_forwardDraft a science fair project for a 11 year old based on the human body, specifically the liverarrow_forward
- You generate a transgenic mouse line with a lox-stop-lox sequence upstream of a dominant-negative Notch fused to GFP. Upon crossing this mouse with another mouse line expressing ectoderm-specific Cre, what would you expect for the phenotype of neuronal differentiation in the resulting embryos?arrow_forwardHair follicle formation is thought to result from a reaction-diffusion mechanism with Wnt and its antagonist Dkk1. How is Dkk1 regulated by Wnt? Describe specific cis-regulatory elements and the net effect on Dkk1 expression.arrow_forwardLimetown S1E4 Transcript: E n 2025SP-BIO-111-PSNT1: Natu X Natural Selection in insects X + newconnect.mheducation.com/student/todo CA NATURAL SELECTION NATURAL SELECTION IN INSECTS (HARDY-WEINBERG LAW) INTRODUCTION LABORATORY SIMULATION A Lab Data Is this the correct allele frequency? Is this the correct genotype frequency? Is this the correct phenotype frequency? Total 1000 Phenotype Frequency Typica Carbonaria Allele Frequency 9 P 635 823 968 1118 1435 Color Initial Frequency Light 0.25 Dark 0.75 Frequency Gs 0.02 Allele Initial Allele Frequency Gs Allele Frequency d 0.50 0 D 0.50 0 Genotype Frequency Moths Genotype Color Moths Released Initial Frequency Frequency G5 Number of Moths Gs NC - Xarrow_forward
- Which of the following is not a sequence-specific DNA binding protein? 1. the catabolite-activated protein 2. the trp repressor protein 3. the flowering locus C protein 4. the flowering locus D protein 5. GAL4 6. all of the above are sequence-specific DNA binding proteinsarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not a DNA binding protein? 1. the lac repressor protein 2. the catabolite activated protein 3. the trp repressor protein 4. the flowering locus C protein 5. the flowering locus D protein 6. GAL4 7. all of the above are DNA binding proteinsarrow_forwardWhat symbolic and cultural behaviors are evident in the archaeological record and associated with Neandertals and anatomically modern humans in Europe beginning around 35,000 yBP (during the Upper Paleolithic)?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





