
To find: the area of regular pentagon for the given situation.
Answer to Problem 45E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The regular pentagon is inscribed in a circle.
Diameter of circle = 7.3cm
Calculation:
The diagram for the given condition will be as follows:
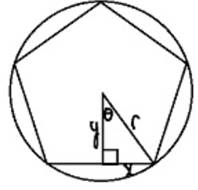
Let the base, height and hypotenuse of the triangle be x , y and r respectively. The hypotenuse and radius of circle are equal.
The radius of circle will be evaluated as follows:
Thus the radius of the circle is 3.65 cm.
Look at the figure carefully; if you create two triangles as shown in the figure for each side, then the total number of triangles in the entire circle will be 10. Thus the value of
The base
The height
Thus the base and height of the triangle is 2.15 cm and 2.95 cm respectively.
The area of triangle is evaluated as follows:
Thus the area of triangle is
Chapter 6 Solutions
Advanced Mathematical Concepts: Precalculus with Applications, Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Find the length of the following curve. 3 1 2 N x= 3 -y from y 6 to y=9arrow_forward3 4/3 3213 + 8 for 1 ≤x≤8. Find the length of the curve y=xarrow_forwardGiven that the outward flux of a vector field through the sphere of radius r centered at the origin is 5(1 cos(2r)) sin(r), and D is the value of the divergence of the vector field at the origin, the value of sin (2D) is -0.998 0.616 0.963 0.486 0.835 -0.070 -0.668 -0.129arrow_forward
- 10 The hypotenuse of a right triangle has one end at the origin and one end on the curve y = Express the area of the triangle as a function of x. A(x) =arrow_forwardIn Problems 17-26, solve the initial value problem. 17. dy = (1+ y²) tan x, y(0) = √√3arrow_forwardcould you explain this as well as disproving each wrong optionarrow_forward
- could you please show the computation of this by wiresarrow_forward4 Consider f(x) periodic function with period 2, coinciding with (x) = -x on the interval [,0) and being the null function on the interval [0,7). The Fourier series of f: (A) does not converge in quadratic norm to f(x) on [−π,π] (B) is pointwise convergent to f(x) for every x = R П (C) is in the form - 4 ∞ +Σ ak cos(kx) + bk sin(kx), ak ‡0, bk ‡0 k=1 (D) is in the form ak cos(kx) + bk sin(kx), ak 0, bk 0 k=1arrow_forwardSolve the equation.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





