
Concept explainers
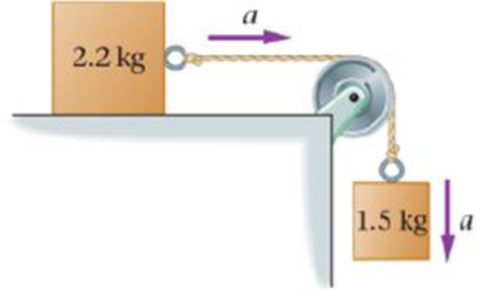
Predict/Calculate The blocks in Figure 6-69 have an acceleration of magnitude a = 1.1 m/s2. (a) Is the tension in the string greater than, less than, or equal to (1.5 kg) × 9.81 m/s2)? Explain. (b) What is the tension in the string connecting the blocks? (c) What is the magnitude of the
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- A block of ice (m = 15.0 kg) with an attached rope is at rest on a frictionless surface. You pull the block with a horizontal force of 95.0 N for 1.54 s. a. Determine the magnitude of each force acting on the block of ice while you are pulling. b. With what speed is the ice moving after you are finished pulling? Repeat Problem 71, but this time you pull on the block at an angle of 20.0.arrow_forwardA sled and rider have a total mass of 56.8 kg. They are on a snowy hill accelerating at 0.7g. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the snow is 0.18. What is the angle of the hills slope measured upward from the horizontal? You may find a spreadsheet program helpful in answering this question.arrow_forwardWhy is the following situation impossible? Your 3.80-kg physics book is placed next to you on the horizontal seat of your car. The coefficient of static friction between the book and the seat is 0.650, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.550. You are traveling forward at 72.0 km/h and brake to a stop with constant acceleration over a distance of 30.0 m. Your physics book remains on the seat rather than sliding forward onto the floor.arrow_forward
- Give reasons for the answers to each of the following questions: (a) Clan a normal force be horizontal? (b) Can a normal force be directed vertically downward? (c) Consider a tennis ball in contact with a stationary floor and with nothing else. Can the normal force be different in magnitude from the gravitational force exerted on the ball? (d) Can the force exerted by the floor on the hall be different in magnitude from the force the ball exerts on the floor?arrow_forwardWe know from studying friction forces that static friction increases with increasing normal force between the surfaces, which becomes important for vehicles traveling on icy or snowy roads that have coefficients of static friction much smaller than those of dry pavement. In particular, the greater the normal force on the drive wheels (those coupled to the engine), the better the traction. The horizontal position of the center of mass of a typical compact automobile is located 1.1 m toward the rear as measured from the front wheel axle. The wheelbase (distance from the front wheel axle to the rear wheel axle) is 2.7 m. Assume the car is stationary on level ground and has a weight of 12,000 N. Determine the total normal force on the two front tires and on the two rear tires. Which do you suppose are the drive wheels in this case?arrow_forwardCalculate the normal force on a 15.0 kg block in the following circumstances: (a) The block is resting on a level surface. (b) The block is resting on a surface tilted up at a 30.0 angle with respect to the horizontal. (c) The block is resting on the floor of an elevator that is accelerating upwards at 3.00 m./s2. (d) The block is on a level surface and a force of 125 N is exerted on it at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal. (Sec Section 1.5.)arrow_forward
- Why is the following situation impossible? A 1.30-kg toaster is not plugged in. The coefficient of static friction between the toaster and a horizontal countertop is 0.350. To make the toaster start moving, you carelessly pull on its electric cord. Unfortunately, the cord has become frayed from your previous similar actions and will break if the tension in the cord exceeds 4.00 N. By pulling on the cord at a particular angle, you successfully start the toaster moving without breaking the cord.arrow_forwardA child of mass m swings in a swing supported by two chains, each of length R. If the tension in each chain at the lowest point is T, find (a) the childs speed at the lowest point and (b) the force exerted by the seat on the child at the lowest point. (Ignore the mass of the seat.)arrow_forwardTo determine the coefficients of friction between rubber and various surfaces, a student uses a rubber eraser and an incline. In one experiment, the eraser begins to slip down the incline when the angle of inclination is 36.0 and then moves down the incline with constant speed when the angle is reduced to 30.0. From these data, determine the coefficients of static and kinetic friction for this experiment.arrow_forward
- A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a wall by a force P that makes an angle of = 50.0 with the horizontal as shown in Figure P5.12. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.250. (a) Determine the possible values for the magnitude of P that allow the block to remain stationary. (b) Describe what happens if P has a larger value and what happens if it is smaller. (c) Repeat parts (a) and (b), assuming the force makes an angle of = 13.0 with the horizontal. Figure P5.12arrow_forward3arrow_forwardFigure 3 shows a 150 kg block on a ramp. If the force applied to the block initially at rest is 800 N and the coefficient of static friction is 0.20, determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





