
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220103026918
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 36PCE
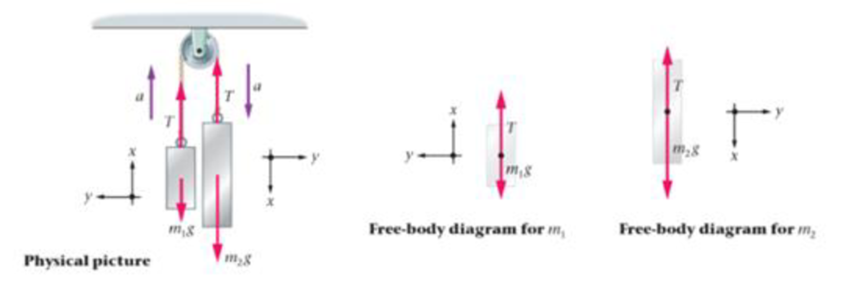
Predict/Explain Suppose m1 and m2 in Example 6-14 (Atwood’s Machine) are both increased by 1 kg. Does the acceleration of the blocks increase, decrease, or stay the same? (b) Choose the best explanation from among the following:
- I. The net force acting on the blocks is the same but the total mass that must be accelerated is greater.
- II. The difference in the masses is the same, and this is what determines the net force on the system.
- III. The force exerted on each block is greater, leading to an increased acceleration.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 6.1 - A block rests on a rough, horizontal surface, as...Ch. 6.2 - When a mass is attached to a certain spring, the...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose the tension in the clothesline in Quick...Ch. 6.4 - Three boxes are connected by ropes and pulled...Ch. 6.5 - A system consists of an object with mass m and...Ch. 6 - A clothesline always sags a little, even if...Ch. 6 - In the Jurassic Park sequel, The Lost World, a man...Ch. 6 - When a traffic accident is investigated, it is...Ch. 6 - In a car with rear-wheel drive, the maximum...Ch. 6 - A train typically requires a much greater distance...
Ch. 6 - Give some everyday examples of situations in which...Ch. 6 - At the local farm, you buy a flat of strawberries...Ch. 6 - It is possible to spin a bucket of water in a...Ch. 6 - Water sprays off a rapidly turning bicycle wheel....Ch. 6 - Can an object be in translational equilibrium if...Ch. 6 - Prob. 11CQCh. 6 - The gravitational attraction of the Earth is only...Ch. 6 - A popular carnival ride has passengers stand with...Ch. 6 - Referring to Question 13, after the cylinder...Ch. 6 - Your car is stuck on an icy side street. Some...Ch. 6 - The parking brake on a car causes the rear wheels...Ch. 6 - BIO The foot of your average gecko is covered with...Ch. 6 - Discuss the physics involved in the spin cycle of...Ch. 6 - The gas pedal and the brake pedal are capable of...Ch. 6 - In the movie 2001: A Space Odyssey, a rotating...Ch. 6 - When rounding a corner on a bicycle or a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain You push two identical bricks...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Two drivers traveling side-by-side...Ch. 6 - A 1.8-kg block slides on a horizontal surface with...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide with an...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - The three identical boxes shown in Figure 6-33...Ch. 6 - To move a large crate across a rough floor, you...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 37-kg crate is placed on an...Ch. 6 - Coffee To Go A person places a cup of coffee on...Ch. 6 - A mug rests on an inclined surface, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Force Times Distance At the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 13PCECh. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - Pulling up on a rope you lift a 7.27-kg bucket of...Ch. 6 - When a 9.09-kg mass is placed on top of a vertical...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A backpack full of books...Ch. 6 - Two springs, with force constants k1= 150N/m and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Illinois Jones is being pulled...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A spring with a force constant...Ch. 6 - A spring is suspended vertically from the ceiling...Ch. 6 - Mechanical Advantage The pulley system shown in...Ch. 6 - Pulling the string on a bow back with a force of...Ch. 6 - In Figure 6-42 we see two blocks connected by a...Ch. 6 - BIO Traction After a skiing accident, your leg is...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The system shown in Figure 6-45...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain (a) Referring to the hanging...Ch. 6 - BIO Spiderweb Forces An orb-weaver spider sits in...Ch. 6 - A 0.15-kg ball is placed in a shallow wedge with...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A picture hangs on the wall...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate You want to nail a 1.6-kg board...Ch. 6 - Prob. 34PCECh. 6 - In Example 6-13 (Connected Blocks), suppose m1 and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Suppose m1 and m2 in Example 6-14...Ch. 6 - Three boxes of masses m, 2m, and 3m are connected...Ch. 6 - Find the acceleration of the masses shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) If the hanging mass m3 in...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 3 50-kg block on a smooth...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 7.7-N force pulls horizontally...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the magnitude of the...Ch. 6 - A car drives with constant speed on an elliptical...Ch. 6 - A puck attached to a string undergoes circular...Ch. 6 - BIO Bubble Net Fishing Humpback whales sometimes...Ch. 6 - When you take your 1900-kg car out for a spin, you...Ch. 6 - BIO A Human Centrifuge To test the effects of high...Ch. 6 - A car goes around a curve on a road that is banked...Ch. 6 - Clearview Screen Large ships often have circular...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) As you ride on a Ferris...Ch. 6 - Driving in your car with a constant speed of v =...Ch. 6 - CE If you weigh yourself on a bathroom scale at...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Maneuvering a Jet Humans lose consciousness...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Gravitropism As plants grow, they tend to...Ch. 6 - BIO Human-Powered Centrifuge One of the hazards of...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 3-kg box slides across the...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide that is...Ch. 6 - Spin-Dry Dragonflies Some dragonflies splash down...Ch. 6 - The da Vinci Code Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) is...Ch. 6 - A 4 5-kg sled is pulled with constant speed across...Ch. 6 - A 0 045-kg golf ball hangs by a string from the...Ch. 6 - A physics textbook weighing 22 N rests on a desk....Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks shown in Figure 6-64...Ch. 6 - A Conical Pendulum A 0 075-kg toy airplane is tied...Ch. 6 - A tugboat tows a barge at constant speed with a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Two blocks, stacked one on top...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate In a daring rescue by helicopter...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A light spring with a fore...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks in Figure 6-69 have...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Playing a Violin The tension in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 8-kg monkey hangs from a...Ch. 6 - As your plane circles an airport, it moves in a...Ch. 6 - At a playground, a 22-kg child sits on a spinning...Ch. 6 - A 2.0-kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at...Ch. 6 - A wood block of mass m rests on a larger wood...Ch. 6 - A hockey puck of mass m is attached to a string...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A popular ride at amusement...Ch. 6 - A Conveyor Belt A box is placed on a conveyor belt...Ch. 6 - As part of a circus act, a person drives a...Ch. 6 - On the straight-line segment II in Figure 6-76 (b)...Ch. 6 - 82. Rank the straight segments I, II, and III in...Ch. 6 - In use on a typical human nose, the end-to-end...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 Suppose...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 The...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-13 Suppose that the mass on...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-15 (a) At what speed will...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
When you rub your cold hands together, the friction between them results in heat that warms your hands. Why doe...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
WRITE ABOUT A THEME: INTERACTIONS In Batesian mimicry, a palatable species gains protection by mimicking an unp...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
25. The 100 kg block in FIGURE EX7.25 takes 6.0 s to reach the floor after being released from rest. What is th...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Evaporating sweat cools the body because evaporation is endothermic and absorbs 2.44 kJ per gram of water evapo...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms? a. algal oil b. ethanol c. hydrogen d. met...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
- A small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius cc and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What is the direction of the electric field for b<r<c? Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for c<r<d. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for r>d.arrow_forwardTICE D Conservation of Momentum 1. A 63.0 kg astronaut is on a spacewalk when the tether line to the shuttle breaks. The astronaut is able to throw a spare 10.0 kg oxygen tank in a direction away from the shuttle with a speed of 12.0 m/s, propelling the astronaut back to the shuttle. Assuming that the astronaut starts from rest with respect to the shuttle, find the astronaut's final speed with respect to the shuttle after the tank is thrown. 2. An 85.0 kg fisherman jumps from a dock into a 135.0 kg rowboat at rest on the west side of the dock. If the velocity of the fisherman is 4.30 m/s to the west as he leaves the dock, what is the final velocity of the fisher- man and the boat? 3. Each croquet ball in a set has a mass of 0.50 kg. The green ball, traveling at 12.0 m/s, strikes the blue ball, which is at rest. Assuming that the balls slide on a frictionless surface and all collisions are head-on, find the final speed of the blue ball in each of the following situations: a. The green…arrow_forwardThe 5.15 A current through a 1.50 H inductor is dissipated by a 2.15 Q resistor in a circuit like that in the figure below with the switch in position 2. 0.632/ C A L (a) 0.368/ 0+ 0 = L/R 2T 3r 4 (b) (a) What is the initial energy (in J) in the inductor? 0 t = L/R 2t (c) Эт 4t 19.89 ] (b) How long will it take (in s) the current to decline to 5.00% of its initial value? 2.09 S (c) Calculate the average power (in W) dissipated, and compare it with the initial power dissipated by the resistor. 28.5 1.96 x W X (ratio of initial power to average power)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY