
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
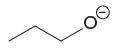
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of species is

The second species has negative charge whereas the first species is uncharged. A negatively charged species is less stable than the uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic than the uncharged species. Therefore, the stronger base in given pair of species is

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(b)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
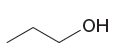
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of species is

The first species is neutral, and the second is positively charged. The neutral species can easily abstract protons as it has two lone pairs whereas the second species has no lone pair to abstract a proton. Therefore, the stronger base in the given pair of species is

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(c)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of species is

In the first species, the negative charge is on the
![]()
The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(d)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
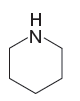
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of species is
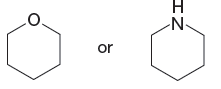
The first species has an oxygen atom and second species has an N atom. The nitrogen atom is less electronegative than oxygen and can easily donate a lone pair. Therefore, the stronger base in the given pair of species is

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(e)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
Explanation of Solution
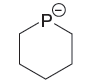
The given pair of species is
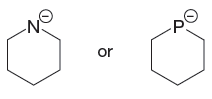
The first species has a negatively charged nitrogen atom whereas the second species has a negatively charged P atom. The phosphorus atom is less electronegative than nitrogen. The species having a negative charge on less electronegative atom is more basic. Therefore, the stronger base in the given pair of species is

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(f)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
Explanation of Solution
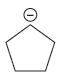
The given pair of species is
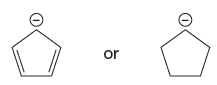
The first species is more stable due to resonance; it shows the delocalization of the negative charge and makes the species more acidic, whereas, the second species does not show the resonance effect, making it more basic than the first species. Therefore, the stronger base in the given pair of species is

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(g)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
Explanation of Solution
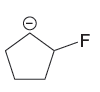
The given pair of species is
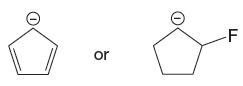
The first species is more stable due to resonance; it shows the delocalization of the negative charge and makes the species more acidic, whereas the second species does not show resonance effect, making it more basic than the first species. Therefore, the stronger base in the given pair of species is

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(h)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
Explanation of Solution
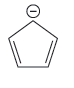
The given pair of species is
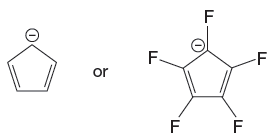
Both the species have the resonance effect but presence of five electronegative F atoms in the second species makes it more stable and therefore more acidic than the first species. Therefore, the stronger base in the given pair of species is

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
(i)
Interpretation:
The stronger base from the given pair of species is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is the species that accepts a proton by donating its lone pair of electrons. A negatively charged species is less stable than uncharged species; hence the negatively charged species is more basic. The negative charge on the less electronegative atom makes it a stronger base. Resonance can stabilize a negatively charged species and make it a weaker base. Electron donating group, which is less electronegative than hydrogen, stabilizes the positive charge but destabilizes a nearby negative charge and makes the species more basic. The neutral species may easily abstract protons due to the lone pair and may become more basic than the positively charged species. A positive charge is energetically favored on the atom with the lower effective electronegativity, i.e.,
Answer to Problem 6.64P
The stronger base in the given pair of species is
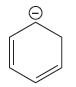
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of species is

The negative charge on the first species is in complete conjugation, making it more stable and increasing the acidity. The negative charge on the second species shows conjugation, but there is no

The stronger base from the given pair of species is predicted on the basis of factors affecting charge stability.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forwardΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward:0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forward
- Draw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- answer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forward
- answer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardC app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Drawingarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CHзBr Drawingarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


