
For each value, are the reactants or products favored at equilibrium?
a.
b.
c.
d.
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether reactants or products are favored at equilibrium and equilibrium constant value
Concept introduction:
For a reversible reaction, equilibrium constant (
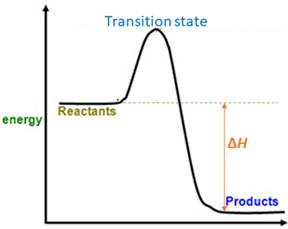
When energy is absorbed, the reaction is endothermic and the value of
Similarly, when energy is released, the reaction is exothermic and
Answer to Problem 6.63P
Products are favored.
Explanation of Solution
The magnitude of
Accordingly,
Therefore, products are favored at equilibrium.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether reactants or products are favored at equilibrium and change in enthalpy -27 kcal/mol needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
For a reversible reaction, equilibrium constant (
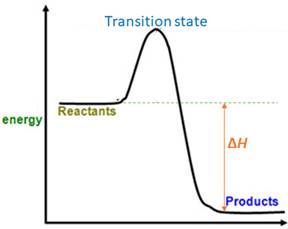
When energy is absorbed, the reaction is endothermic and the value of
Similarly, when energy is released, the reaction is exothermic and
Answer to Problem 6.63P
Products are favored.
Explanation of Solution
The value of
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether reactants or products are favored at equilibrium and equilibrium constant value
Concept introduction:
For a reversible reaction, equilibrium constant (
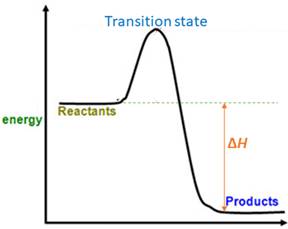
When energy is absorbed, the reaction is endothermic and the value of
Similarly, when energy is released, the reaction is exothermic and
Answer to Problem 6.63P
Reactants are favored.
Explanation of Solution
The magnitude of
Accordingly,
Therefore, reactants are favored at equilibrium.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether reactants or products are favored at equilibrium and change in enthalpy +2 kcal/mol needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
For a reversible reaction, equilibrium constant (
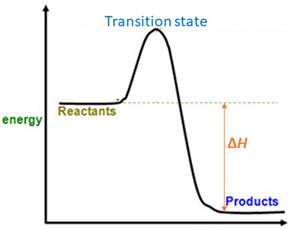
When energy is absorbed, the reaction is endothermic and the value of
Similarly, when energy is released, the reaction is exothermic and
Answer to Problem 6.63P
Reactants are favored
Explanation of Solution
The value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Organic Chemistry
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- Why are normal electrode potentials also called relative electrode potentials?arrow_forwardEasily differentiate between electrochemical potential and Galvani potential.arrow_forwardConstruct a molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide. Identify the relevant point group,include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Make sure toaccount for the difference in electronegativity between C and O. Hint: CO is substantiallyisoelectronic to N2. (PLEASE DRAW THE ENTIRE MO DIAGRAM!!!)arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning  Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





