
(a) Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
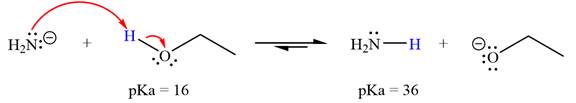
Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the acetate ion
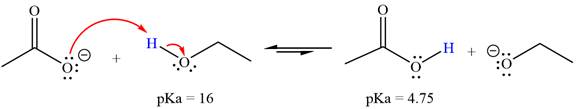
Acetic acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving chloride ion
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of chloride ion
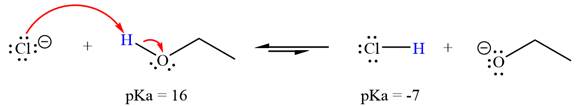
Hydrochloric acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving phenoxide ion (
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of phenoxide ion (
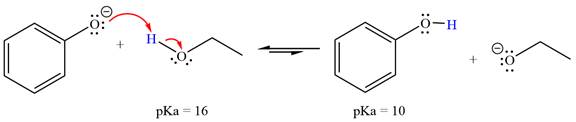
Phenol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of cyanide ion
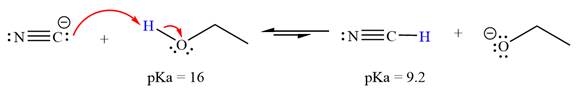
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(f)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of propyl group
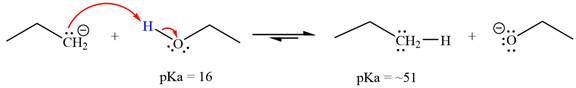
Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


