
Concept explainers
Comprehensive problem; ABC manufacturing, two products. Hazlett, Inc., operates at capacity and makes plastic combs and hairbrushes. Although the combs and brushes are a matching set, they are sold individually and so the sales mix is not 1:1. Hazlett’s management is planning its annual budget for fiscal year 2018. Here is information for 2018:
Input Prices
| Direct materials | |
| Plastic | $0.30 per ounce |
| Bristles | $0.75 per bunch |
| Direct manufacturing labor | $ 18 per direct manufacturing labor-hour |
Input Quantities per Unit of Output
| Combs | Brushes | |
| Direct materials | ||
| Plastic | 5 ounces | 8 ounces |
| Bristles | — | 16 bunches |
| Direct manufacturing labor | 0.05 hours | 0.2 hours |
| Machine-hours (MH) | 0.025 MH | 0.1 MH |
Inventory Information, Direct Materials
| Plastic | Bristles | |
| Beginning inventory | 1,600 ounces | 1,820 bunches |
| Target ending inventory | 1,766 ounces | 2,272 bunches |
| Cost of beginning inventory | $456 | $1,419 |
Hazlett accounts for direct materials using a FIFO cost flow.
Sales and Inventory Information, Finished Goods
| Combs | Brushes | |
| Expected sales in units | 12,000 | 14,000 |
| Selling price | $ 9 | $ 30 |
| Target ending inventory in units | 1,200 | 1,400 |
| Beginning inventory in units | 600 | 1,200 |
| Beginning inventory in dollars | $ 2,700 | $27,180 |
Hazlett uses a FIFO cost-flow assumption for finished-goods inventory.
Combs are manufactured in batches of 200, and brushes are manufactured in batches of 100. It takes 20 minutes to set up for a batch of combs and 1 hour to set up for a batch of brushes.
Hazlett uses activity-based costing and has classified all
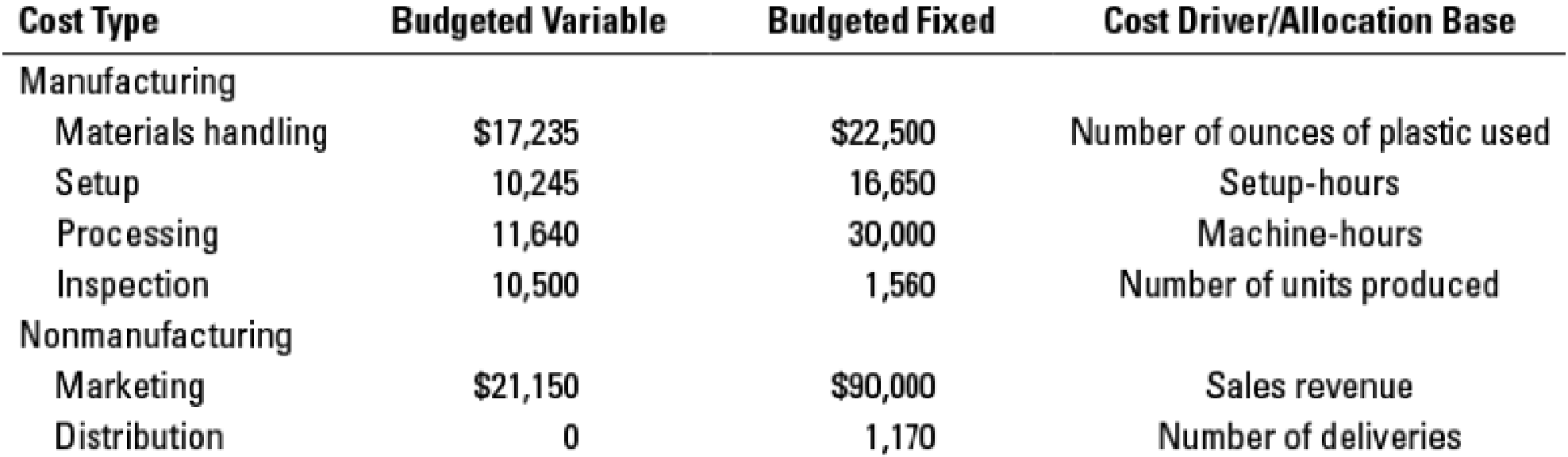
Delivery trucks transport units sold in delivery sizes of 1,000 combs or 1,000 brushes.
Do the following for the year 2018:
- 1. Prepare the revenues budget.
- 2. Use the revenues budget to:
- a. Find the budgeted allocation rate for marketing costs.
- b. Find the budgeted number of deliveries and allocation rate for distribution costs.
- 3. Prepare the production budget in units.
- 4. Use the production budget to:
- a. Find the budgeted number of setups and setup-hours and the allocation rate for setup costs.
- b. Find the budgeted total machine-hours and the allocation rate for
processing costs. - c. Find the budgeted total units produced and the allocation rate for inspection costs.
- 5. Prepare the direct material usage budget and the direct material purchases budget in both units and dollars; round to whole dollars.
- 6. Use the direct material usage budget to find the budgeted allocation rate for materials-handling costs.
- 7. Prepare the direct
manufacturing labor cost budget. - 8. Prepare the manufacturing overhead cost budget for materials handling, setup, processing, and inspection costs.
- 9. Prepare the budgeted unit cost of ending finished-goods inventory and ending inventories budget.
- 10. Prepare the cost of goods sold budget.
- 11. Prepare the nonmanufacturing overhead costs budget for marketing and distribution.
- 12. Prepare a
budgeted income statement (ignore income taxes). - 13. How does preparing the budget help Hazlett's management team better manage the company?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
REVEL for Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis -- Access Card (16th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
- financial accountingarrow_forwardWhat is the opereting cash flow at this lavel of output? General accountingarrow_forwardPioneer Manufacturing has fixed costs of $60,000 and variable costs of $40 per unit. If they sell each unit for $100, how many units must be sold to earn a target profit of $40,000? (Round your answer)arrow_forward
- Under full costingarrow_forwardAnnapolis Company completes job #601 which has a standard of 500 labor hours at a standard rate of $19.00 per hour. The job was completed in 600 hours and the average actual labor rate was $19.70 per hour. What is the labor efficiency (quantity) variance?arrow_forward3 POINTSarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

