
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “In some cases, constitutional isomers are chiral” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The compounds which have same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms are known as constitutional isomers. Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. Chiral molecules are optically active molecules.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “In some cases, constitutional isomers are chiral” is true.
Explanation of Solution
There are many examples where constitutional isomers are chiral. In case of
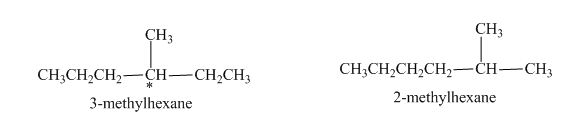
Figure 1
The statement “In some cases, constitutional isomers are chiral” is found to be true.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “In every case, a pair of enantiomers have a mirror-image relationship” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The pair of stereoisomer which is mirror images of each other is known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-congruent mirror images. If the molecules are placed on top of each other they will not give same molecule.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “In every case, a pair of enantiomers have a mirror-image relationship” is true.
Explanation of Solution
Enantiomers are defined as non-congruent mirror image. The enantiomers pair in every case will have mirror image relationship. Therefore, the statement “In every case, a pair of enantiomers have a mirror-image relationship” is true.
The statement “In every case, a pair of enantiomers have a mirror-image relationship” is found to be true.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Mirror-image molecules are in all cases enantiomers” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The pair of stereoisomer which is mirror images of each other is known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-congruent mirror images. If the molecules are placed on top of each other they will not give same molecule.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “Mirror-image molecules are in all cases enantiomers” is false.
Explanation of Solution
The molecules which contain asymmetric carbon atom are chiral molecule. Pair of chiral molecules which are non-congruent mirror image of each other are enantiomers. Achiral molecules which are mirror image of each other are not enantiomers. Therefore, the statement “Mirror-image molecules are in all cases enantiomers” is false.
The given statement “Mirror-image molecules are in all cases enantiomers” is found to be false.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “If a compound has an enantiomer, it must be chiral” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The pair of stereoisomer which is mirror images of each other is known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-congruent mirror images. If the molecules are placed on top of each other they will not give same molecule.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “If a compound has an enantiomer, it must be chiral” is true.
Explanation of Solution
The molecules which contain asymmetric carbon atom are chiral molecule. Pair of chiral molecules which are non-congruent mirror image of each other are enantiomers. Therefore, the given statement is true.
The given statement “If a compound has an enantiomer, it must be chiral” is found to be true.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Every chiral compound has a diastereomer” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomers which are non-superimposable and not mirror image are known as diastereomers. The compound must contain two or more than two stereocentre. Diastereomer are non identical stereoisomers.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “Every chiral compound has a diastereomer” is false.
Explanation of Solution
Diastereomers are compound which are non-congruent and not mirror images of each other. The compound must contain two or more than two stereocentre to form diastereomer. Chiral molecules can also have only one stereocentre. Therefore, given statement is false.
The given statement “Every chiral compound has a diastereomer” is found to be false.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “If a compound has a diastereomer, it must be chiral” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomers which are non-superimposable and not mirror image are known as diastereomer. The compound must contain two or more than two stereocentre. Diastereomer are non identical stereoisomers.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “If a compound has a diastereomer, it must be chiral” is false.
Explanation of Solution
Diastereomers are not always chiral. A meso compound is a diastereomer, but it is achiral due to internal plane of symmetry. Therefore, given statement is false. An example is shown below.
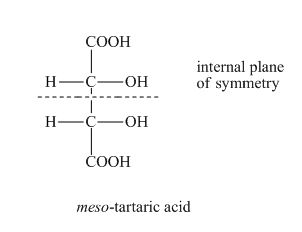
Figure 2
The statement “If a compound has a diastereomer, it must be chiral” is found to be false.
(g)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Every molecule containing one or more asymmetric carbons is chiral” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. Chiral molecules are optically active molecules. Chiral molecule can rotate the plane of polarized light.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “Every molecule containing one or more asymmetric carbons is chiral” is false.
Explanation of Solution
The meso compounds contain two asymmetric carbon centres. Meso compounds are achiral, due to the presence of internal plane of symmetry. Therefore the given statement is false.
The given statement “Every molecule containing one or more asymmetric carbons is chiral” is found to be false.
(h)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Any molecule containing a stereocenter must be chiral” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. Chiral molecules are optically active molecules. Chiral molecule can rotate the plane of polarized light.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “Any molecule containing a stereocenter must be chiral” is false.
Explanation of Solution
The
The given statement “Any molecule containing a stereocenter must be chiral” is found to be false.
(i)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Any molecule with a stereocenter must have a stereoisomer” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. Chiral molecules are optically active molecules. Chiral molecule can rotate the plane of polarized light. Stereocentre can be an atom, bond, or any point in molecule at which interchange of two groups form a stereoisomer.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “Any molecule with a stereocenter must have a stereoisomer” is true.
Explanation of Solution
Stereocentre can be an atom, bond, or any point in molecule at which interchange of two groups form a stereoisomer. If a molecule contains a stereocenter, therefore it will contain an asymmetric carbon atom. This means the molecule has a stereoisomer. Therefore, the given statement is true.
The statement “Any molecule with a stereocenter must have a stereoisomer” is found to be true.
(j)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Some diastereomers have a mirror-image relationship” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomers which are non-superimposable and not mirror image are known as diastereomers. The compound must contain two or more than two stereocentre. Diastereomer are non identical stereoisomers.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The given statement “Some diastereomers have a mirror-image relationship” is false.
Explanation of Solution
Diastereomers are stereoisomers which are not identical and not mirror image of each other. Diastereomers will never have mirror image relationship. Therefore, the given statement is false.
The given statement “Some diastereomers have a mirror-image relationship” is found to be false.
(k)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Some chiral compounds are optically inactive” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. Chiral molecules are optically active molecules. Chiral molecule can rotate the plane of polarized light.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “Some chiral compounds are optically inactive” is false.
Explanation of Solution
Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. The chiral compounds are always optically active compounds. The optically inactive compounds are known as achiral compounds. Therefore, the given statement is false.
The given statement “Some chiral compounds are optically inactive” is found to be false.
(l)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Any chiral compound with a single asymmetric carbon must have a positive optical rotation if the compound has the R configuration” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Enantiomers rotate the plane of polarized light in opposite direction with equal amount. If compound rotates plane of polarized light in right hand direction, it is dextrorotatory. If compound rotates plane of polarized light in left hand direction, it is levorotatory.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “Any chiral compound with a single asymmetric carbon must have a positive optical rotation if the compound has the R configuration” is false.
Explanation of Solution
The compound having R configuration can rotate the plane of polarized light in any direction. The compound will have both dextrorotatory and levorotatory molecules. Therefore, the given statement is false.
The given statement “Any chiral compound with a single asymmetric carbon must have a positive optical rotation if the compound has the R configuration” is found to be false.
(m)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “A structure is chiral if it has no plane of symmetry” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral, if it does not contain any symmetry element. There are many symmetry elements like plane of symmetry, centre of symmetry and axis of symmetry. The absence of all the symmetry elements is essential for the structure to be chiral.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “A structure is chiral if it has no plane of symmetry” is false.
Explanation of Solution
For a structure to be chiral, it must not contain any symmetry element. Only plane of symmetry is not considered, centre of symmetry is also considered. If the molecule does not contain any symmetry element only then it will be chiral. Therefore, the given statement is false.
The given statement “A structure is chiral if it has no plane of symmetry” is found to be false.
(n)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “All chiral molecules have no plane of symmetry” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral, if it does not contain any symmetry element. There are many symmetry elements like plane of symmetry, centre of symmetry and axis of symmetry. The absence of all the symmetry elements is essential for the structure to be chiral.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “All chiral molecules have no plane of symmetry” is true.
Explanation of Solution
The chirality of molecule depends on the absence of all the symmetry elements. All chiral molecules have no plane of symmetry, no centre of symmetry and no axis of symmetry. Therefore, the given statement is true.
The given statement “All chiral molecules have no plane of symmetry” is found to be true.
(o)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “All asymmetric carbons are stereocenters” is true or false is to be predicted. If it is false then the explanation is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The compounds which have same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms are known as constitutional isomers. Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. Chiral molecules are optically active molecules.
Answer to Problem 6.34AP
The statement “All asymmetric carbons are stereocenters” is true.
Explanation of Solution
The stereo center can be a point, atom, bond in a molecule which makes the molecule asymmetric. All asymmetric carbons are stereocentres. Therefore, given statement is true.
The given statement “All asymmetric carbons are stereocenters” is found to be true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- (2 pts) What do you expect to happen in a Na2O crystal if a Cl− ion replaces one of the O2−ions in the lattice?arrow_forward(2 pts) WSe2 is an ionic compound semiconductor that can be made to be p-type or n-type.What must happen to the chemical composition for it to be p-type? What must happen tothe chemical composition for it to be n-type?arrow_forward8. (2 pts) Silicon semiconductors have a bandgap of 1.11 eV. What is the longest photon wavelength that can promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band in a silicon-based photovoltaic solar cell? Show all work. E = hv = hc/λ h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js c = 3.00 x 108 m/s 1 eV 1.602 x 10-19 Jarrow_forward
- A solution containing 100.0 mL of 0.155 M EDTA buffered to pH 10.00 was titrated with 100.0 mL of 0.0152 M Hg(ClO4)2 in a cell: calomel electrode (saturated)//titration solution/Hg(l) Given the formation constant of Hg(EDTA)2-, logKf= 21.5, and alphaY4-=0.30, find out the cell voltage E. Hg2+(aq) + 2e- = Hg(l) E0= 0.852 V E' (calomel electrode, saturated KCl) = 0.241 Varrow_forwardFrom the following reduction potentials I2 (s) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V I2 (aq) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.620 V I3- (aq) + 2e- = 3I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V a) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (aq) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). b) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (s) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). c) Calculate the solubility of I2 (s) in water.arrow_forward2. (3 pts) Consider the unit cell for the spinel compound, CrFe204. How many total particles are in the unit cell? Also, show how the number of particles and their positions are consistent with the CrFe204 stoichiometry - this may or may not be reflected by the particle colors in the diagram. (HINT: In the diagram, the blue particle is in an interior position while each red particle is either in a corner or face position.)arrow_forward
- From the following potentials, calculate the activity of Cl- in saturated KCl. E0 (calomel electrode)= 0.268 V E (calomel electrode, saturated KCl)= 0.241 Varrow_forwardCalculate the voltage of each of the following cells. a) Fe(s)/Fe2+ (1.55 x 10-2 M)//Cu2+ (6.55 x 10-3 M)/Cu(s) b) Pt, H2 (0.255 bar)/HCl (4.55 x 10-4 M), AgCl (sat'd)/Ag Fe2+ +2e- = Fe E0= -0.44 V Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu E0= 0.337 V Ag+ + e- = Ag E0= 0.799 V AgCl(s) + e- = Ag(s) + Cl- E0= 0.222 V 2H+ + 2e- = H2 E0= 0.000 Varrow_forwardA solution contains 0.097 M Ce3+, 1.55x10-3 M Ce4+, 1.55x10-3 M Mn2+, 0.097 M MnO4-, and 1.00 M HClO4 (F= 9.649 x 104 C/mol). a) Write a balanced net reaction that can occur between species in this solution. b) Calculate deltaG0 and K for the reaction. c) Calculate E and deltaG for the conditions given. Ce4+ + e- = Ce3+ E0= 1.70 V MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- = Mn2+ + 4H2O E0= 1.507 Varrow_forward
- 1. Provide a step-by-step mechanism for formation of ALL STEREOISOMERS in the following reaction. Na HCO3 (Sodium bicarbonate, baking soda) is not soluble in CH2Cl2. The powder is a weak base used to neutralize strong acid (pKa < 0) produced by the reaction. Redraw the product to show the configuration(s) that form at C-2 and C-4. Br2 OH CH2Cl2 Na* HCO3 Br HO OH + Na Br +arrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O2/HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI + enant OH Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardGermanium (Ge) is a semiconductor with a bandgap of 2.2 eV. How could you dope Ge to make it a p-type semiconductor with a larger bandgap? Group of answer choices It is impossible to dope Ge and have this result in a larger bandgap. Dope the Ge with silicon (Si) Dope the Ge with gallium (Ga) Dope the Ge with phosphorus (P)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



