
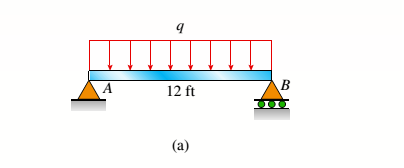
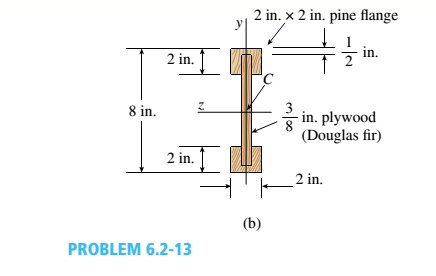
A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span supports a distributed load of intensity q = 90 lb/ft over its length (see figure part a). The beam is constructed with a web of Douglas-fir plywood and flanges of pine glued to the web, as shown in the figure part b. The plywood is 3/8 in. thick: the flanges are 2 in, × 2 in, (actual size). The modulus of elasticity for the plywood is 1,600,000 psi and for the pine is 1,200,000 psL
- Calculate the maximum bending stresses in the pine flanges and in the plywood web.
a.
The bending stress that is maximum in the plywood web and pine flanges
Answer to Problem 6.2.13P
Bending Stress Maximum for plywood
Bending Stress Maximum for pine
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure
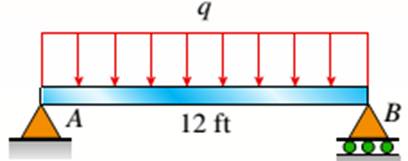
The I beam that is wooden has the span of 12 ft over its length supporting a distributed intensity load q=90lb/ft. The beam is made of Douglas fir plywood web and pine flanges with the plywood having a thickness of 3/8 in and that of flanges 2in.*2in. The elasticity modulus of the plywood is 1,600,000psi and for pine it is 1,200,000psi.
Concept Used:
Bending Stress Maximum for plywood,
Where,
Calculation:
Bending moment maximum is given as
Substituting the values we have,
Plywood moment of inertia is given as,
Pine moment of inertia is given as,
Bending Stress Maximum for plywood,
Bending Stress Maximum for pine,
Conclusion:
Thus, the bending stress that is maximum in the plywood web and pine flanges is given by equating the maximum bending movement
b.
The qmax with 1600psi maximum stress in flanges and for web being 1200psi.
Answer to Problem 6.2.13P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure:
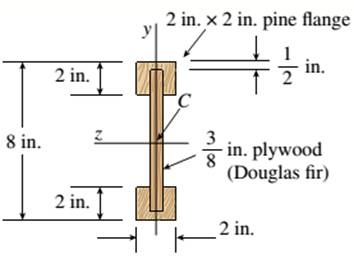
The I beam that is wooden has the span of 12 ft over its length supporting a distributed intensity load q=90lb/ft. The beam is made of Douglas fir plywood web and pine flanges with the plywood having a thickness of 3/8 in and that of flanges 2in.*2in. The elasticity modulus of the plywood is 1,600,000psi and for pine it is 1,200,000psi.
Concept Used:
Web maximum stress,
Where,
Calculation:
Maximum stress Maximum for Web,
Substituting the values we have,
Maximum stress Maximum for flange,
Substituting the values we have,
Bending moment that is maximum,
Maximum uniform load distributed is given as,
Conclusion:
Thus, the qmax with 1600psi maximum stress in flanges and for web being 1200psi is given by the equation of maximum load.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 2 Terms (12 Months) Printed Access Card
- In cold isostatic pressing, the mold is most typically made of which one of the following: thermosetting polymer tool steel sheet metal textile rubberarrow_forwardThe coefficient of friction between the part and the tool in cold working tends to be: lower higher no different relative to its value in hot workingarrow_forwardThe force F={25i−45j+15k}F={25i−45j+15k} lblb acts at the end A of the pipe assembly shown in (Figure 1). Determine the magnitude of the component F1 which acts along the member AB. Determine the magnitude of the component F2 which acts perpendicular to the AB.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
