
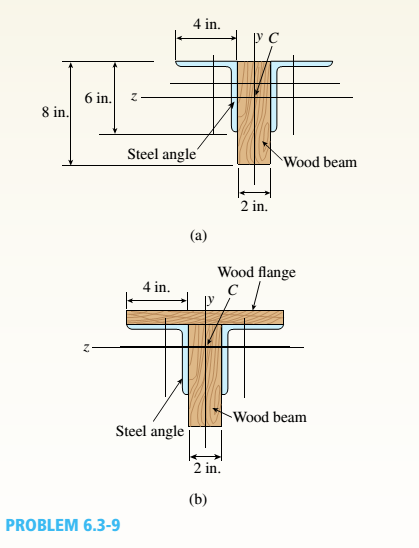
A simple beam thai is IS ft long supports a uni¬form load of intensity a. The beam is constructed of two angle sections, each L (1 × 4 × 1/2, on either side of a 2 in. x 8 in. (actual dimensions! wood beam (see the cross section shown in the figure part a]. The modulus of elasticity of the s I eel is 10 limes that of the wood,
(a) If the allowable stresses in the steel and wood are 12,000 psi and 900 psi. respectively, what is the allow atile load a t. A olc. Disregard the weight of the beam, and see Table F-5(a) of Appendix I ' for I lie dimensions and properties of the angles.
(b) Repeal partial if a I in. 10 in. wood Hange tactual dimensions) is added i see figure pallhi b).
a.
The allowed load
Answer to Problem 6.3.9P
The allowed load
Explanation of Solution
Given:
We have the following data for calculation.
Length of the beam,
Load with intensity of as q
Two angle sections used for construction of the beam,
Allowed stress of steel,
Allowed stress of wood,
Concept Used:
First, Area, centroids and moment of inertia for wood and steel sections is determined.
This step is followed by further calculation involving moment for wood and steel section and maximum moment.
Calculation:
We have
Let us first calculate for wood.
- Centroidal distance,
- Area of the wood beam,
Now, calculation for two sections of steels.
So, further calculating,
Now, performing transformation of moment if inertia below :
We are determining moment for wood.
Moment for steel sections,
Now, the maximum moment would be:
But the equation for maximum moment is:
Conclusion:
The allowed load
b.
The allowed load
Answer to Problem 6.3.9P
The allowed load
Explanation of Solution
Given:
We have the following data for calculation.
Length of the beam,
Load with intensity of as q
Two angle sections used for construction of the beam,
Allowed stress of steel,
Allowed stress of wood,
Concept Used:
First, Area, centroids and moment of inertia for wood and steel sections is determined.
This step is followed by further calculation involving moment for wood and steel section and maximum moment.
Calculation:
So, the width and height of flange would be,
Now for transformed sections,
Now performing transformation of moment if inertia as below,
We are determining moment for wood.
Moment for steel sections,
Now, the maximum moment would be,
But, the equation for maximum moment is:
Conclusion:
The allowed load is calculated by the moment equations and given information.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 2 Terms (12 Months) Printed Access Card
- Prob 5. Determine the largest load P that can be applied to the frame without causing either the average normal stress or the average shear stress at section a-a to exceed o-150 MPa and 1-60 MPa, respectively. Member CB has a square cross section of 25 mm on each side. 2 m FAC 1.5 m Facarrow_forwardDerive the component transformation equations for tensors shown below where [C] = [BA] is the DCM (direction cosine matrix) from frame A to B. ^B [T] = [C]^A [T] [C]^Tarrow_forwardCalculate for the vertical cross section moment of inertia for both Orientations 1 and 2 of a 1 x 1.5 in. horizontal hollow rectangular beam with wall thickness of t = 0.0625 in. Use the equation: I = ((bh^3)/12) - (((b-2t)(h-2t)^3)/12)arrow_forward
- Please answer 'yes' or 'no' and 'is' or 'is not' for the following:arrow_forwardConsider a large 23-cm-thick stainless steel plate (k = 15.1 W/m-K) in which heat is generated uniformly at a rate of 5 x 105 W/m³. Both sides of the plate are exposed to an environment at 30°C with a heat transfer coefficient of 60 W/m²K. The highest temperature will occur at surfaces of plate while the lowest temperature will occur at the midplane. Yes or No Yes Noarrow_forwardMy answers are incorrectarrow_forward
- Picturearrow_forwardWhat is the weight of a 5-kg substance in N, kN, kg·m/s², kgf, Ibm-ft/s², and lbf? The weight of a 5-kg substance in N is 49.05 N. The weight of a 5-kg substance in kN is KN. The weight of a 5-kg substance in kg·m/s² is 49.05 kg-m/s². The weight of a 5-kg substance in kgf is 5.0 kgf. The weight of a 5-kg substance in Ibm-ft/s² is 11.02 lbm-ft/s². The weight of a 5-kg substance in lbf is 11.023 lbf.arrow_forwardMych CD 36280 kg. 0.36 givens Tesla truck frailer 2017 Model Vven 96154kph ronge 804,5km Cr Powertrain Across PHVAC rwheel 0.006 0.88 9M² 2 2kW 0.55M ng Zg Prated Trated Pair 20 0.95 1080 kW 1760 Nm 1,2 determine the battery energy required to meet the range when fully loaded determine the approximate time for the fully-loaded truck-trailor to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph while Ignoring vehicle load forcesarrow_forward
- 12-217. The block B is sus- pended from a cable that is at- tached to the block at E, wraps around three pulleys, and is tied to the back of a truck. If the truck starts from rest when ID is zero, and moves forward with a constant acceleration of ap = 0.5 m/s², determine the speed of the block at D the instant x = 2 m. Neglect the size of the pulleys in the calcu- lation. When xƊ = 0, yc = 5 m, so that points C and D are at the Prob. 12-217 5 m yc =2M Xparrow_forwardsolve both and show matlab code auto controlsarrow_forward12-82. The roller coaster car trav- els down the helical path at con- stant speed such that the paramet- ric equations that define its posi- tion are x = c sin kt, y = c cos kt, z = h - bt, where c, h, and b are constants. Determine the mag- nitudes of its velocity and accelera- tion. Prob. 12-82 Narrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
