
Concept explainers
MATHEMATICAL For the following aspartase reaction (see Question 28) in the presence of the inhibitor hydroxymethylaspartate, determine
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
In an enzymatic reaction, the inhibitors are the molecules that bind with the enzymes and block their activity. Enzymatic inhibition can be of many types. If a substrate and an inhibitor compete with each other to bind with the enzyme and both have similar structures, then the inhibition is known as competitive. On the other hand, if an inhibitor does not compete with the substrate and both of them can bind to an enzyme at their respective specific sites, then it is known as non-competitive inhibition.
Answer to Problem 61RE
Plot the reciprocal substrate concentration on the x-axis and two reaction velocities (both in the presence and absence of inhibitors) on the y-axis.
Before drawing the plot, the data needs to be modified so that it can be aligned in the Lineweaver–Burk plot. The modification of the data is as follows:
The Lineweaver–Burk plot from above data is:
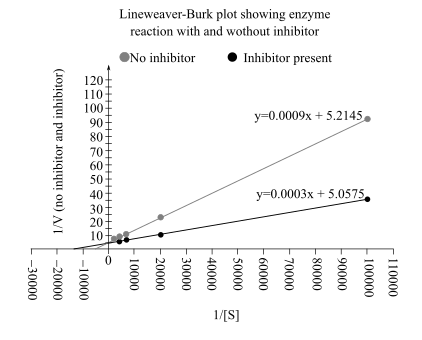
From this plot
In an uninhibited reaction, the
Therefore, the value of
Therefore, the value of
By comparing the Lineweaver–Burk plot of both reactions, it can be said that the inhibition is competitive in nature
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In competitive inhibition, the substrate and the inhibitor have a similar structure. Hence, like the substrate, the inhibitor has also got nearly same affinity toward the active site of an enzyme and is able to bind with the enzyme. As a result, the enzyme’s affinity towards the substrate changes (it inhibits the substrate to bind with the enzyme). In other words, the
Also, in Lineweaver–Burk plot the
The reaction (without inhibitor) has a low value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Owlv2,1 Term Printed Access Card For Campbell/farrell/mcdougal's Biochemistry, 9th
- a) What are the differences between the Direct & Indirect Immunofluorescence Assays? (0.5 mark) b) What are the advantages of the Indirect Immunofluorescence Assays? (0.5 mark) c) A Super-Resolution Imaging Technique was developed in 2018 using imidazole, a His-tag ligand conjugated with a fluorophore to report the presence of a recombinant His-tag protein target, (Sci Rep, 2018, 8:5507). How does this technique improve the image quality? (2 marks)arrow_forwarda) What are the differences between the Direct & Indirect Immunofluorescence Assays? b) What are the advantages of the Indirect Immunofluorescence Assays? c) A Super-Resolution Imaging Technique was developed in 2018 using imidazole, a His-tag ligand conjugated with a fluorophore to report the presence of a recombinant His-tag protein target, (Sci Rep, 2018, 8:5507). How does this technique improve the image quality?arrow_forwardCalculate the number of ATP produced from oxidation of 1 molecule of glucosearrow_forward
- Example 1: 1. Suppose an enzyme (MW = 5,000 g/mole) has a concentration of 0.05 mg/L. If the kcat is 1 x 10 s, what is the theoretical maximum reaction velocity for the enzyme? A) 1050 µM/s. B) 100 µM/s. C) 150 μM/s. D) 105 μM/s.arrow_forwardIn 1956, E. P. Kennedy and S. B. Weiss published their study of membrane lipid phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) synthesis in rat liver. Their hypothesis was that phosphocholine joined with some cellular component to yield lecithin. In an earlier experiment, incubating 32 P-labeled phosphocholine at physiological temperature (37 °C) with broken cells from rat liver yielded labeled lecithin. This became their assay for the enzymes involved in lecithin synthesis. Determine the optimal pH for this enzyme and characterize the enzyme activity at different pH values. -O-P-O-CH2-CH₁₂-N(CH3)3 Phosphocholine H₂C-O-C-R HC-O-C-R2 + + + Cell fraction + ? HC-O-P-O-CH₁₂-CH₂-N(CH), O Phosphatidylcholine The researchers then centrifuged the broken cell preparation to separate the membranes from the soluble proteins. They tested three preparations: whole extract, membranes, and soluble proteins. Table 1 summarizes the results. Table 1: Cell fraction requirement for incorporation of 32p-phosphocholine into…arrow_forwardResearchers isolated an unknown substance, X, from rabbit muscle. They determined its structure from the following observations and experiments. (a) Qualitative analysis showed that X was composed entirely of C, H, and O. A weighed sample of X was completely oxidized and the H2O and CO2 produced were measured. This quantitative analysis revealed that X contained 40.00% C, 6.71% H, and 53.29% O by weight. (b) The molecular mass of X, as determined by mass spectrometry, was 90.00 atomic mass units (u). (c) Infrared spectroscopy showed that X contained one double bond. (d) X dissolved readily in water, and the solution demonstrated optical activity when tested in a polarimeter. (e) The aqueous solution of X is acidic. What is the empirical formula of X?arrow_forward
- Show work. don't give Ai generated solution....give correct solutionarrow_forwardBiochemistry What is the process of "transamination" in either the muscles or the liver, that involves keto acid or glutamic acid? Please explain how the steps work. Thank you!arrow_forwardBiochemistry Please help. Thank you What is the importance of glutamic acid in the metabolism of nitrogen from amino acids? (we know therole; it’s used to remove the nitrogen from amino acids so that the remaining carbon skeleton can bebroken down by the “usual” pathways, but what is the important, unique role that only glutamicacid/glutamate can do?)arrow_forward
- Biochemistry Please help. Thank you When carbamyl phosphate is joined to L-ornathine, where does the energy for the reaction come from?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you What is the function of glutamate dehydrogenase?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you How and why does a high protein diet affect the enzymes of the urea cycle?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
