
Interpretation:
From the given experimental data both in absence and presence of its inhibitor a Lineweaver–Burk plot is to be drawn and values of
Concept introduction:
An inhibitor may be defined as a molecule that binds with the enzymes and decreases the activity of enzyme toward the substrate and this decrease in enzyme activity is called enzymatic inhibition.
Enzymatic inhibition can be of many types. When substrate and inhibitor of an enzyme compete with each other to bind with the enzyme and both of them are structurally same it is known as competitive inhibition. On the other hand, when inhibitors don’t compete with the substrate and both of them can bind to the enzyme at their specific site present on the substrate it is known as noncompetitive inhibition.
To determine the rate of the reaction, experimental data must be put into Lineweaver Burk plot where the x-axis represents the values of
Answer to Problem 60RE
Plot the reciprocal of substrate concentration along the x-axis and the reciprocal of velocities (both in the presence and absence of inhibitors) along the y-axis.
Before drawing the plot, the data needs to be modified so that it can be put into Lineweaver–Burk plot. The modification of the data is
The Lineweaver–Burk plot from above data is as follows:
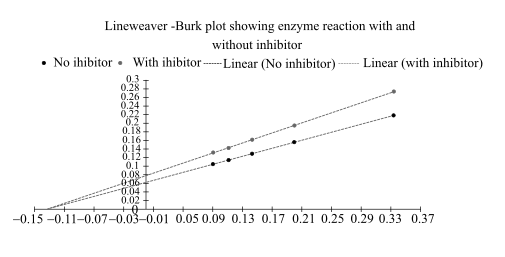
From this plot,
Or,
The value
So, the value of
The
The value of
By comparing these two plots it can be said that it is a type of noncompetitive inhibition.
Explanation of Solution
In the case of competitive inhibition, the substrate and inhibitor compete with each other to bind with the active site of the enzyme. By increasing substrate concentration, the effect of competitive inhibition can be discarded. In high substrate concentration
In the case of non-competitive inhibition, inhibitors bind with the allosteric site of the enzyme and enzyme itself can bind with both substrate and inhibitors. It is possible because it has two different sites for both inhibitor and substrate. When the inhibitor binds with an enzyme it blocks its activity even if the substrate is also bound to the enzyme. These inhibitors do not change the substrate affinity of the enzyme so the
In this Lineweaver Burk plot,
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Owlv2,1 Term Printed Access Card For Campbell/farrell/mcdougal's Biochemistry, 9th
- Draw the reaction between sphingosine and arachidonic acid. Draw out the full structures.arrow_forwardDraw both cis and trans oleic acid. Explain why cis-oleic acid has a melting point of 13.4°C and trans-oleic acid has a melting point of 44.5°C.arrow_forwardDraw the full structure of the mixed triacylglycerol formed by the reaction of glycerol and the fatty acids arachidic, lauric and trans-palmitoleic. Draw the line structure.arrow_forward
- Draw out the structure for lycopene and label each isoprene unit. "Where is lycopene found in nature and what health benefits does it provide?arrow_forwardWhat does it mean to be an essential fatty acid? What are the essential fatty acids?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast primary and secondary active transport mechanisms in terms of energy utilisation and efficiency. Provide examples of each and discuss their physiological significance in maintaining ionic balance and nutrient uptake. Rubric Understanding the key concepts (clearly and accurately explains primary and secondary active transport mechanisms, showing a deep understanding of their roles) Energy utilisation analysis ( thoroughly compares energy utilisation in primary and secondary transport with specific and relevant examples Efficiency discussion Use of examples (provides relevant and accurate examples (e.g sodium potassium pump, SGLT1) with clear links to physiological significance. Clarity and structure (presents ideas logically and cohesively with clear organisation and smooth transition between sections)arrow_forward
- 9. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence, starting with ethyl acetoacetate? 요요. 1. NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH 1. NaOH, H₂O 2. H3O+ 3. A OCH2CH3 2. ethyl acetoacetate ii A 3. H3O+ OH B C D Earrow_forward7. Only one of the following ketones cannot be made via an acetoacetic ester synthesis. Which one is it? Ph کہ A B C D Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? HO A OH 1. NaOEt, EtOH 1. LiAlH4 EtO OEt 2. H3O+ 2. H3O+ OH B OH OH C -OH HO -OH OH D E .CO₂Etarrow_forward
- what is a protein that contains a b-sheet and how does the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of the protein.arrow_forwarddraw and annotate a b-sheet and lable the hydrogen bonding. what is an example that contains the b-sheet and how the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of your example protein.arrow_forwardFour distinct classes of interactions (inter and intramolecular forces) contribute to a protein's tertiary and quaternary structures. Name the interaction then describe the amino acids that can form this type of interaction. Draw and annotate a diagram of the interaction between two amino acids.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
