
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134051796
Author: Walker
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 40PCE
Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in Figure 6-54. The smooth inclined surface makes an angle of 35° with the horizontal, and the block on the incline has a mass of 5.7 kg. The mass of the hanging block is m = 3.2 kg. Find (a) the direction and (b) the magnitude of the hanging block’s acceleration.
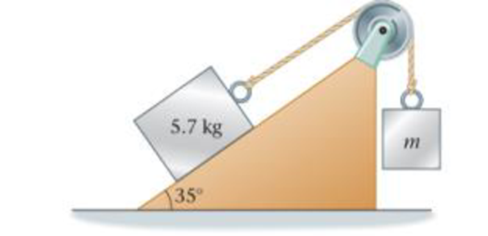
Figure 6-54
Problem 40
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2-96. Four forces are applied at a point in a body as
shown in Fig. P2-96. Determine the magnitude and direc-
tion (angles 6, 6ụ, and 0) of the resultant R of the four
forces.
F 4 kN
30°
F2 = 6 kN
F = 5 kN
40
40
y
F3 = 3 kN
5. The body on the 30° incline is acted upon by force P inclined at 20° with the horizontal. If P is resolved into
components parallel and perpendicular to incline and the value of parallel component is 1800N, compute the
value of the perpendicular component of P.
P
20
30
Figure P-009
F
Fil
X
Figure 5-38
There are two horizontal forces on the 3.0 kg box in the overhead view of Fig. 5-38 but only one (of magnitude
F1 = 15 N) is shown. The box moves along the x axis. Find the second force in unit-vector notation if the
acceleration of the box ax is 18 m/s².
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 6.1 - A block rests on a rough, horizontal surface, as...Ch. 6.2 - When a mass is attached to a certain spring, the...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose the tension in the clothesline in Quick...Ch. 6.4 - Three boxes are connected by ropes and pulled...Ch. 6.5 - A system consists of an object with mass m and...Ch. 6 - A clothesline always sags a little, even if...Ch. 6 - In the Jurassic Park sequel, The Lost World, a man...Ch. 6 - When a traffic accident is investigated, it is...Ch. 6 - In a car with rear-wheel drive, the maximum...Ch. 6 - A train typically requires a much greater distance...
Ch. 6 - Give some everyday examples of situations in which...Ch. 6 - At the local farm, you buy a flat of strawberries...Ch. 6 - It is possible to spin a bucket of water in a...Ch. 6 - Water sprays off a rapidly turning bicycle wheel....Ch. 6 - Can an object be in translational equilibrium if...Ch. 6 - Prob. 11CQCh. 6 - The gravitational attraction of the Earth is only...Ch. 6 - A popular carnival ride has passengers stand with...Ch. 6 - Referring to Question 13, after the cylinder...Ch. 6 - Your car is stuck on an icy side street. Some...Ch. 6 - The parking brake on a car causes the rear wheels...Ch. 6 - BIO The foot of your average gecko is covered with...Ch. 6 - Discuss the physics involved in the spin cycle of...Ch. 6 - The gas pedal and the brake pedal are capable of...Ch. 6 - In the movie 2001: A Space Odyssey, a rotating...Ch. 6 - When rounding a corner on a bicycle or a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain You push two identical bricks...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Two drivers traveling side-by-side...Ch. 6 - A 1.8-kg block slides on a horizontal surface with...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide with an...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - The three identical boxes shown in Figure 6-33...Ch. 6 - To move a large crate across a rough floor, you...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 37-kg crate is placed on an...Ch. 6 - Coffee To Go A person places a cup of coffee on...Ch. 6 - A mug rests on an inclined surface, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Force Times Distance At the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 13PCECh. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - Pulling up on a rope you lift a 7.27-kg bucket of...Ch. 6 - When a 9.09-kg mass is placed on top of a vertical...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A backpack full of books...Ch. 6 - Two springs, with force constants k1= 150N/m and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Illinois Jones is being pulled...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A spring with a force constant...Ch. 6 - A spring is suspended vertically from the ceiling...Ch. 6 - Mechanical Advantage The pulley system shown in...Ch. 6 - Pulling the string on a bow back with a force of...Ch. 6 - In Figure 6-42 we see two blocks connected by a...Ch. 6 - BIO Traction After a skiing accident, your leg is...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The system shown in Figure 6-45...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain (a) Referring to the hanging...Ch. 6 - BIO Spiderweb Forces An orb-weaver spider sits in...Ch. 6 - A 0.15-kg ball is placed in a shallow wedge with...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A picture hangs on the wall...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate You want to nail a 1.6-kg board...Ch. 6 - Prob. 34PCECh. 6 - In Example 6-13 (Connected Blocks), suppose m1 and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Suppose m1 and m2 in Example 6-14...Ch. 6 - Three boxes of masses m, 2m, and 3m are connected...Ch. 6 - Find the acceleration of the masses shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) If the hanging mass m3 in...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 3 50-kg block on a smooth...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 7.7-N force pulls horizontally...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the magnitude of the...Ch. 6 - A car drives with constant speed on an elliptical...Ch. 6 - A puck attached to a string undergoes circular...Ch. 6 - BIO Bubble Net Fishing Humpback whales sometimes...Ch. 6 - When you take your 1900-kg car out for a spin, you...Ch. 6 - BIO A Human Centrifuge To test the effects of high...Ch. 6 - A car goes around a curve on a road that is banked...Ch. 6 - Clearview Screen Large ships often have circular...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) As you ride on a Ferris...Ch. 6 - Driving in your car with a constant speed of v =...Ch. 6 - CE If you weigh yourself on a bathroom scale at...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Maneuvering a Jet Humans lose consciousness...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Gravitropism As plants grow, they tend to...Ch. 6 - BIO Human-Powered Centrifuge One of the hazards of...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 3-kg box slides across the...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide that is...Ch. 6 - Spin-Dry Dragonflies Some dragonflies splash down...Ch. 6 - The da Vinci Code Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) is...Ch. 6 - A 4 5-kg sled is pulled with constant speed across...Ch. 6 - A 0 045-kg golf ball hangs by a string from the...Ch. 6 - A physics textbook weighing 22 N rests on a desk....Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks shown in Figure 6-64...Ch. 6 - A Conical Pendulum A 0 075-kg toy airplane is tied...Ch. 6 - A tugboat tows a barge at constant speed with a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Two blocks, stacked one on top...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate In a daring rescue by helicopter...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A light spring with a fore...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks in Figure 6-69 have...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Playing a Violin The tension in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 8-kg monkey hangs from a...Ch. 6 - As your plane circles an airport, it moves in a...Ch. 6 - At a playground, a 22-kg child sits on a spinning...Ch. 6 - A 2.0-kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at...Ch. 6 - A wood block of mass m rests on a larger wood...Ch. 6 - A hockey puck of mass m is attached to a string...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A popular ride at amusement...Ch. 6 - A Conveyor Belt A box is placed on a conveyor belt...Ch. 6 - As part of a circus act, a person drives a...Ch. 6 - On the straight-line segment II in Figure 6-76 (b)...Ch. 6 - 82. Rank the straight segments I, II, and III in...Ch. 6 - In use on a typical human nose, the end-to-end...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 Suppose...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 The...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-13 Suppose that the mass on...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-15 (a) At what speed will...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
37. Balance each redox reaction occurring in acidic aqueous solution.
a. K(s) + Cr3+(aq) → Cr(s) + K+(aq)
b. Al...
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
You have generated three transgenic lines of maize that are resistant to the European corn borer, a significant...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
2. List the subdivisions of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
5. When the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, this patt...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS Review the description of meiosis (see Figure 10.8) and Mendels laws of segregation and indepe...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
l. Suppose you have the uniformly charged cube in FIGURE Q24.1. Can you use symmetry alone to deduce the shape ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two blocks on two inclines are attached by a string over a pulley where the two inclines meet. When the blocks are released from rest, the 25 kg block on the 67° incline slides down the incline, pulling the 32 kg block on the 24° incline up its incline. In both cases the coefficient of friction between the block and the incline is 0.13. Determine the acceleration of the blocks and the tension in the string joining them as they accelerate. 32 kg 24° 67° 25 kgarrow_forward27 Go Body A in Fig. 6-33 weighs 102 N, and body B weighs 32 N. The coefficients of friction between A and the incline are 0.56 and P = 0.25. Angle 0 is 40°. Let the positive direction of an x axis be up, the incline. In unit-vector notation. what is the acceleration of A if A is initially (a) at rest. (b) moving up the incline, and (c) moving down the incline? 0 Frictionless, massle pulley Figure 6-33 Problems 27 and 28.arrow_forward3:31 4 M M 令l docs.google.com/forms (2 O Option 3 O Option 4 A block of mass m -1 kg is found on an inclined plane that makes an angle 30° with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction and coef- ficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline are: H. = 0.6 and - 0.5. Take the positive di- rection to be up the inclined plane With the block initially at rest, the acceleration of the block is a = -9.33 a = 0.66 O Option 4 O Option 2 a = 0 a = -0,66 O Option 1 O Option 3 With the block initially moving up the inclined, the acceleration is: a = 0,66 a = -9.33 O Option 2 O Option 4 a = -0,66 a = 0arrow_forward
- Calculate the Tensions, and Accelerations of blocks 1 and 2 if m1= 5 kg and m2 = 6 kgarrow_forward3-8 Determine the magnitude and direction angle of force F4 so that the particle shown in Fig. P3-8 is in equilib- rium. F₁ = 500 N F₂ = 750 N 30° 33° 60° F3 = 1000 N Fig. P3-8 0 F4 Xarrow_forwardConsider Figure P2-10 on P. 37 of your textbook showing two forces applied to a truss. Assume the 400 N acts along the + x-axis. a) Find the magnitude of the resultant force acting at point B. b) What is the angle © between the resultant force and the + x-axis?arrow_forward
- 15-102. The 800-lb roller-coaster car starts from rest on the track having the shape of a cylindrical helix. If the normal force of the tracks on the car has a transverse component of No = 68 lb, determine the transverse component of its Ne velocity in t = 4s. Also, what is the car's velocity when it descends 8 ft? Neglect the size of the car. r=8 ft Probs. 15-101/102 8 ftarrow_forwardI:52) An adventurous archaeologist crosses between two rock cliffs by slowly going hand over hand along a rope stretched between the cliffs. He stops to rest at the middle of the rope. The rope will break if the tension in it exceeds 2.50×104 NN. Our hero’s mass is 90.0 kg. What is the smallest value the angle θ can have if the rope is not to break? Express your answer in degreesarrow_forwardThe following force vectors act on an object: i) 25 Newtons at 45 degrees north of east and ii) 50 Newtons at 30 degrees south of east. Which of the following represents the magnitude of the resultant and its angle relative to the easterly direction?~ 35.7 N 0 dg ~ 61.4 N -6.85 deg ~ 75.0 N 15 deg ~ 61.4 N 21.8 deg ~ 55.6 N -7.5 degarrow_forward
- An elevator cab that weighs 28.6 kN moves upward. What is the tension in the cable if the cab's speed is (a) increasing at a rate of 1.20 m/s? and (b) decreasing at a rate of 1.20 m/s?? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units This answer has no units • (degrees) Attempts: 0 of 3 used Submit Answer Save for Later kg m/s m/s^2 N N/m kg-m/s or N.s N/m^2 or Pa kg/m^3 m/s^3 timesarrow_forward1. An elevator shown below filled with passengers has a mass of 1650 kg. The elevator does motions (a) through (c) in succession. meg For each of the parts below draw a free body diagram of the elevator in your notebook for each of the parts (a) to (c). Draw the acceleration and velocity vectors in the boxes. For each part, are the vectors for tension in the string and weight of the elevator of equal lengths or unequal lengths. y 1. X ME m aarrow_forward65. A 100-kg streetlight is supported equally by two ropes as shown in Figure 4-43. One T 40 40 e rope pulls up and to the right, 40° above the horizon- tal; the other rope pulls up and to the left, 40° above the horizontal. Find the tension in cach rope. SSM Figure 4-43 Problem 65 000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY