
ORGANIC CHEM W/BIOLOGICAL TOP. ACCESS
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781264382545
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG CUSTOM
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 31P
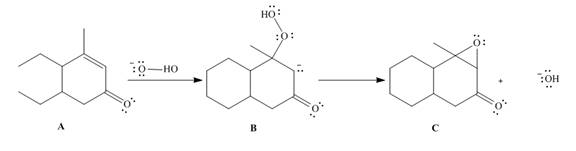
(a) Add curved arrows for each step to show how A is converted to the epoxy
(b) Classify the conversion of A to C as a substitution, elimination, or addition. (c) Draw one additional resonance structure for B.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(EXM 2, PRBLM 3) Here is this problem, can you explain it to me and show how its done. Thank you I need to see the work for like prbl solving.
can someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all bonds, intermediates and side products
Comment on the general features of the 1H-NMR spectrum of isoamyl ester provided below
What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis?
1. PPh3
3
2. n-BuLi
• Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like.
• Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is.
• Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine.
Click and drag to start drawing a structure.
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM W/BIOLOGICAL TOP. ACCESS
Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 6.3 - Problem 6.3 By taking into account...Ch. 6.3 - Problem 6.4 Use curved arrows to show the movement...Ch. 6.3 - Problem 6.5 Follow the curved arrows and draw the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 6.4 - Problem 6.7 Use the values in Table 6.2 to...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 8PCh. 6.5 - aWhich Keq corresponds to a negative value of G,...Ch. 6.5 - Given each of the following values, is the...Ch. 6.5 - Given each of the following values, is the...
Ch. 6.5 - The equilibrium constant for the conversion of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 6.6 - For a reaction with H=40kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6.6 - For a reaction with H=20kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6.7 - Draw an energy diagram for a reaction in which the...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 17PCh. 6.7 - Prob. 18PCh. 6.8 - Problem 6.19 Consider the following energy...Ch. 6.8 - Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction,...Ch. 6.9 - Which value if any corresponds to a faster...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 22PCh. 6.9 - Problem 6.23 For each rate equation, what effect...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 24PCh. 6.10 - Identify the catalyst in each equation. a....Ch. 6 - Draw the products of homolysis or heterolysis of...Ch. 6 - Explain why the bond dissociation energy for bond...Ch. 6 - Classify each transformation as substitution,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 29PCh. 6 - 6.31 (a) Add curved arrows for each step to show...Ch. 6 - Prob. 35PCh. 6 - 6.39. a. Which value corresponds to a negative...Ch. 6 - Prob. 40PCh. 6 - For which of the following reaction is S a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 42PCh. 6 - Prob. 43PCh. 6 - 6.44 Consider the following reaction: .
Use curved...Ch. 6 - Prob. 45PCh. 6 - 6.50 The conversion of acetyl chloride to methyl...Ch. 6 - Prob. 50PCh. 6 - Prob. 53P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Whether two metal foil leaves an electroscope get opposite charge when the electroscope is charged.
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
11. In the early 1800s, French naturalist Jean Baptiste Lamarck suggested that the best explanation for the rel...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Sea turtles have disappeared from many regions, and one way of trying to save them is to reintroduce them to ar...
MARINE BIOLOGY
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Identify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: X + Y H+ two steps Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х :arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism of friedel-crafts acylation using acetyl chloride of m-Xylenearrow_forwardI need help naming these in IUPACarrow_forward
- H R Part: 1/2 :CI: is a/an electrophile Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of the product(s) for the Lewis acid-base reaction. Include lone pairs and formal charges (if applicable) on the structures. 4-7: H ö- H Skip Part Check X :C1: $ % L Fi Click and drag to start drawing a structure. MacBook Pro & ㅁ x G 0: P Add or increase positive formal cha Save For Later Submit ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardDraw the friedel-crafts acylation mechanism of m-Xylenearrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- 1. Base on this experimental results, how do you know that the product which you are turning in is methyl 3-nitrobenzoate(meta substituted product ) rather than either of the other two products? 2. What observation suggests that at least a small amount of one or both of the other two isomers are in the mother liquor?arrow_forwardExplain Huckel's rule.arrow_forwardhere is my question can u help me please!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #24; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j04zMFwDeDU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY