
Concept explainers
Draw the products of homolysis or heterolysis of each indicated bond. Use electronegativity
differences to decide on the location of charges in the heterolysis reaction. Classify each
carbon reactive intermediate as a radical, carbocation, or carbanion.
a.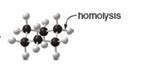 b.
b. 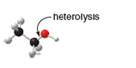
(a)
Interpretation: The products of homolysis or heterolysis of the indicated bond is to be drawn by using the electronegativity differences. Each carbon reactive intermediate is to be classified as a radical, carbocation, or carbanion.
Concept introduction: In organic chemistry, the formation of carbocation or carbanion occurs due to the heterolysis or homolysis process. Carbocations possess six electrons around them, whereas carbanions possess the lone pair of electrons. Carbocation behaves as electrophile due to lack of electrons and incomplete octet.
Answer to Problem 26P
In the given indicated bond, homolysis takes place that results in the formation of the radicals.
The first product is,
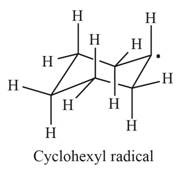
The second product is,

Explanation of Solution
The heterolysis does not take place in the given compound due to the less electronegativity difference between atoms.
The product of homolysis is shown below.
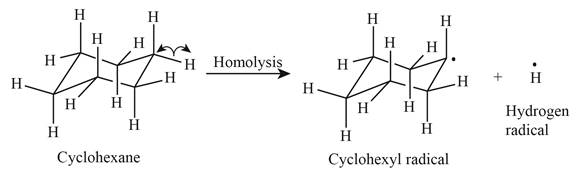
Figure 1
In the above reaction, cyclohexane forms cyclohexyl radical and hydrogen radical by homolysis. Homolysis is opposite to the heterolysis. It forms radical with unpaired electron because the electrons are not attracted toward one element in the homolysis.
In the given indicated bond, homolysis takes place that results in the formation of the radical. The product of homolysis is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The products of homolysis or heterolysis of the indicated bond is to be drawn by using the electronegativity differences. Each carbon reactive intermediate is to be classified as a radical, carbocation, or carbanion.
Concept introduction: In organic chemistry, the formation of carbocation or carbanion occurs due to the heterolysis or homolysis process. Carbocations possess six electrons around them, whereas carbanions possess the lone pair of electrons. Carbocation behaves as electrophile due to lack of electrons and incomplete octet.
Carbanion behaves as a nucleophile in the chemical reaction due to the presence of excess electrons. Heterolysis is the process in which unequal sharing of electrons results in the breaking of the bond.
Answer to Problem 26P
In the given indicated bond, heterolysis takes place that results in the formation of the carbocation.
The first product is,
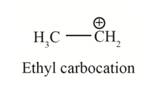
The second product is,
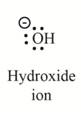
Explanation of Solution
Heterolysis in the compound takes place due to the more electronegativity difference. The product of heterolysis is shown below.
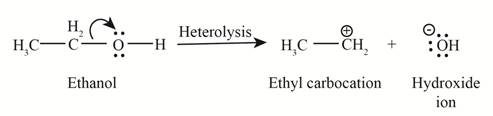
Figure 2
In the above reaction, ethanol forms ethyl carbocation and hydroxide ion by heterolysis. The heterolysis in the chemical reaction leads to the formation of ionic species because electrons are attracted toward more electronegative atom. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. Therefore, heterolysis and the formation of carbocation take place in the reaction.
In the given indicated bond, heterolysis takes place that results in the formation of the carbocation. The product of heterolysis is shown in Figure 2.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-STUDY GDE./SOL.MAN.
- n Feb 3 A T + 4. (2 pts) Draw the structure of the major component of the Limonene isolated. Explain how you confirmed the structure. 5. (2 pts) Draw the fragment corresponding to the base peak in the Mass spectrum of Limonene. 6. (1 pts) Predict the 1H NMR spectral data of R-Limonene. Proton NMR: 5.3 pon multiplet (H Ringarrow_forwardPart VI. Ca H 10 O is the molecular formula of compound Tom and gives the in the table below. Give a possible structure for compound Tom. 13C Signals summarized C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 13C shift (ppm) 23.5 27.0 33.0 35.8 127 162 205 DEPT-90 + DEPT-135 + +arrow_forward2. Using the following data to calculate the value of AvapH o of water at 298K. AvapH o of water at 373K is 40.7 kJ/mol; molar heat capacity of liquid water at constant pressure is 75.2J mol-1 K-1 and molar heat capacity of water vapor at constant pressure is 33.6 J mol-1 K-1.arrow_forward
- Part VII. Below are the 'HNMR 13 3 C-NMR, COSY 2D- NMR, and HSQC 20-NMR (Similar with HETCOR but axes are reversed) spectra of an organic compound with molecular formula C6H13 O. Assign chemical shift values to the H and c atoms of the compound. Find the structure. Show complete solutions. Predicted 1H NMR Spectrum ли 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.0 0.9 0.8 f1 (ppm)arrow_forward3. Draw the expanded structural formula, the condensed structural formula, and the skeletal structural formula for 2-pentene. expanded structure: Condensed structure: Skeletal formula: 4. Draw the expanded structural formula, the condensed structural formula, and the skeletal structural formula for 2-methyl-3-heptene. expanded structure: Condensed structure: Skeletal formula: following structurearrow_forwardPart IV. Propose a plausible Structure w/ the following descriptions: a) A 5-carbon hydrocarbon w/ a single peak in its proton decoupled the DEPT-135 Spectrum shows a negative peak C-NMR spectrum where b) what cyclohexane dione isomer gives the largest no. Of 13C NMR signals? c) C5H120 (5-carbon alcohol) w/ most deshielded carbon absent in any of its DEPT Spectivaarrow_forward
- 13C NMR is good for: a) determining the molecular weight of the compound b) identifying certain functional groups. c) determining the carbon skeleton, for example methyl vs ethyl vs propyl groups d) determining how many different kinds of carbon are in the moleculearrow_forward6 D 2. (1 pt) Limonene can be isolated by performing steam distillation of orange peel. Could you have performed this experiment using hexane instead of water? Explain. 3. (2 pts) Using GCMS results, analyze and discuss the purity of the Limonene obtained from the steam distillation of orange peel.arrow_forwardPart III. Arrange the following carbons (in blue) in order of increasing chemical shift. HO B NH 2 A CIarrow_forward
- 6. Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals as carbonyl, aryl, or alkyl. 100 ō (ppm) 50 0 7. 200 150 Assign all of the protons on the spectrum below. 8. A B 4 E C 3 ō (ppm) 2 1 0 Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals to the corresponding protons. OH 6 OH 3 2 1 0 4 ō (ppm)arrow_forwardIn the Thermo Fisher application note about wine analysis (Lesson 3), the following chromatogram was collected of nine components of wine. If peak 3 has a retention time of 3.15 minutes and a peak width of 0.070 minutes, and peak 4 has a retention time of 3.24 minutes and a peak width of 0.075 minutes, what is the resolution factor between the two peaks? [Hint: it will help to review Lesson 2 for this question.] MAU 300 200 T 34 5 100- 1 2 CO 6 7 8 9 0 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2 Minutes 3.22 0.62 1.04 O 1.24arrow_forwardThe diagram shows two metals, A and B, which melt at 1000°C and 1400°C. State the weight percentage of the primary constituent (grains of C) that would be obtained by solidifying a 20% alloy of B. 1000°C a+L L+C 900°С 12 α a+C 45 1200 C L+y 140096 C+Y a+ß 800°C 700°C C+B 96 92 a+B 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 A % peso B Barrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
