
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553292
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 25AP
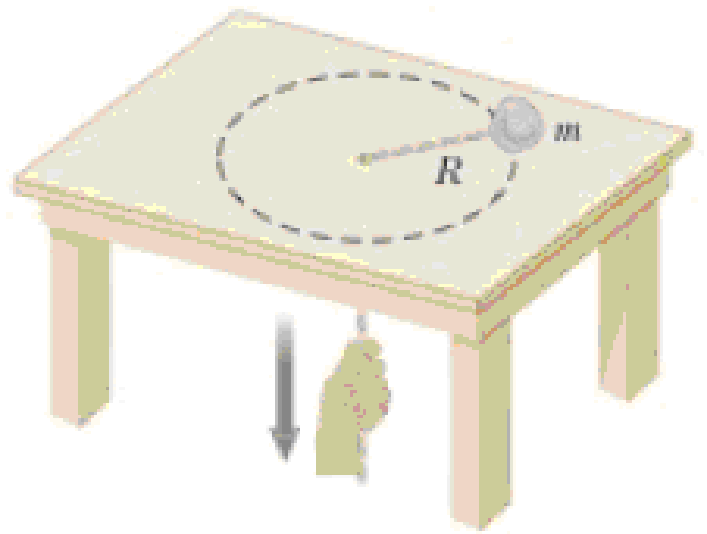
A string under a tension of 50.0 N is used to whirl a rock in a horizontal circle of radius 2.50 m at a speed of 20.4 m/s on a fricitonless surface as shown in Figure P6.25. As the string is pulled in, the speed of the rock increases. When the string on the table is 1.00 m long and the speed of the rock is 51.0 m/s, the string breaks. What is the breaking strength, in newtons, of the string?
Figure P6.25
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0?
A
30
PLEASE help with the experimental setup for this theory because i am so confused.
Part 2 - Geometry and Trigonometry
1. Line B touches the circle at a single point. Line A extends radially through the center of
the circle.
A
B
(a) Which line is tangential to the circumference of the circle?
(b) What is the angle between lines A and B.
2. In the figure below what is the angle C?
30
45
3. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0?
30°
4. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0?
A
30°
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 6.1 - You are riding on a Ferris wheel that is rotating...Ch. 6.2 - A bead slides at constant speed along a curved...Ch. 6.3 - Consider the passenger in the car making a left...Ch. 6.4 - A basketball and a 2-inch-diameter steel ball,...Ch. 6 - In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, an...Ch. 6 - Whenever two Apollo astronauts were on the surface...Ch. 6 - A car initially traveling eastward turns north by...Ch. 6 - A curve in a road forms part of a horizontal...Ch. 6 - In a cyclotron (one type of particle accelerator),...Ch. 6 - Why is the following situation impossible? The...
Ch. 6 - You are working during your summer break as an...Ch. 6 - Prob. 8PCh. 6 - Prob. 9PCh. 6 - A 40.0-kg child swings in a swing supported by two...Ch. 6 - Prob. 11PCh. 6 - One end of a cord is fixed and a small 0.500-kg...Ch. 6 - A roller coaster at the Six Flags Great America...Ch. 6 - An object of mass m = 5.00 kg, attached to a...Ch. 6 - A person stands on a scale in an elevator. As the...Ch. 6 - Review. A student, along with her backpack on the...Ch. 6 - A small container of water is placed on a...Ch. 6 - The mass of a sports car is 1 200 kg. The shape of...Ch. 6 - Review. A window washer pulls a rubber squeegee...Ch. 6 - A small piece of Styrofoam packing material is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 21PCh. 6 - Assume the resistive force acting on a speed...Ch. 6 - You can feel a force of air drag on your hand if...Ch. 6 - A car travels clockwise at constant speed around a...Ch. 6 - A string under a tension of 50.0 N is used to...Ch. 6 - Disturbed by speeding cars outside his workplace,...Ch. 6 - A car of mass m passes over a hump in a road that...Ch. 6 - A childs toy consists of a small wedge that has an...Ch. 6 - A seaplane of total mass m lands on a lake with...Ch. 6 - An object of mass m1 = 4.00 kg is tied to an...Ch. 6 - A ball of mass m = 0.275 kg swings in a vertical...Ch. 6 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 6 - The pilot of an airplane executes a loop-the-loop...Ch. 6 - A basin surrounding a drain has the shape of a...Ch. 6 - Review. While learning to drive, you arc in a 1...Ch. 6 - A truck is moving with constant acceleration a up...Ch. 6 - Prob. 37APCh. 6 - A puck of mass m1 is tied to a string and allowed...Ch. 6 - Prob. 39APCh. 6 - Members of a skydiving club were given the...Ch. 6 - A car rounds a banked curve as discussed in...Ch. 6 - Prob. 42APCh. 6 - Review. A piece of putty is initially located at...Ch. 6 - A model airplane of mass 0.750 kg flies with a...Ch. 6 - A 9.00-kg object starting from rest falls through...Ch. 6 - For t 0, an object of mass m experiences no force...Ch. 6 - A golfer tees off from a location precisely at i =...Ch. 6 - A single bead can slide with negligible friction...Ch. 6 - Prob. 49CPCh. 6 - You have a great job working at a major league...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. Rub your hands together vigorously. What happens? Discuss the energy transfers and transformations that take...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
What were the major microbiological interests of Martinus Beijerinck and Sergei Winogradsky? It can be said tha...
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
2. Why is it that the range of resting blood pressures of humans is best represented by a bell-shaped curve co...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
How does the removal of hydrogen atoms from nutrient molecules result in a loss of energy from the nutrient mol...
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Details solution No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem correctly please.Thank you!!arrow_forwardWill you please walk me through the calculations in more detail for solving this problem? I am a bit rusty on calculus and confused about the specific steps of the derivation: https://www.bartleby.com/solution-answer/chapter-3-problem-15e-modern-physics-2nd-edition/9780805303087/7cf8c31d-9476-46d5-a5a9-b897b16fe6fcarrow_forward
- please help with the abstract. Abstract - This document outlines the format of the lab report and describes the Excel assignment. The abstract should be a short paragraph that very briefly includes the experiment objective, method, result and conclusion. After skimming the abstract, the reader should be able to decide whether they want to keep reading your work. Both the format of the report and the error analysis are to be followed. Note that abstract is not just the introduction and conclusion combined, but rather the whole experiment in short including the results. I have attacted the theory.arrow_forwardUsing the Experimental Acceleration due to Gravity values from each data table, Data Tables 1, 2, and 3; determine the Standard Deviation, σ, mean, μ, variance, σ2 and the 95% Margin of Error (Confidence Level) Data: Ex. Acc. 1: 12.29 m/s^2. Ex. Acc. 2: 10.86 m/s^2, Ex. Acc. 3: 9.05 m/s^2arrow_forwardIn the Super Smash Bros. games the character Yoshi’s has a “ground pound” down special move where he launches himself downward to attack an enemy beneath him. A) If Yoshi flings himself downwards at 9.76 miles per hour to hit an enemy 10.5 m below him, how fast is Yoshi traveling when he hits the enemy? 1 mile = 1609 m B) How much time does it take Yoshi to hit the enemy beneath him?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward1.62 On a training flight, a Figure P1.62 student pilot flies from Lincoln, Nebraska, to Clarinda, Iowa, next to St. Joseph, Missouri, and then to Manhattan, Kansas (Fig. P1.62). The directions are shown relative to north: 0° is north, 90° is east, 180° is south, and 270° is west. Use the method of components to find (a) the distance she has to fly from Manhattan to get back to Lincoln, and (b) the direction (relative to north) she must fly to get there. Illustrate your solutions with a vector diagram. IOWA 147 km Lincoln 85° Clarinda 106 km 167° St. Joseph NEBRASKA Manhattan 166 km 235° S KANSAS MISSOURIarrow_forwardPlz no chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical work done (GCSE Physics); Author: Dr de Bruin's Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OapgRhYDMvw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY