
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118743164
Author: Jacquelyn G. Black, Laura J. Black
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 22SQ
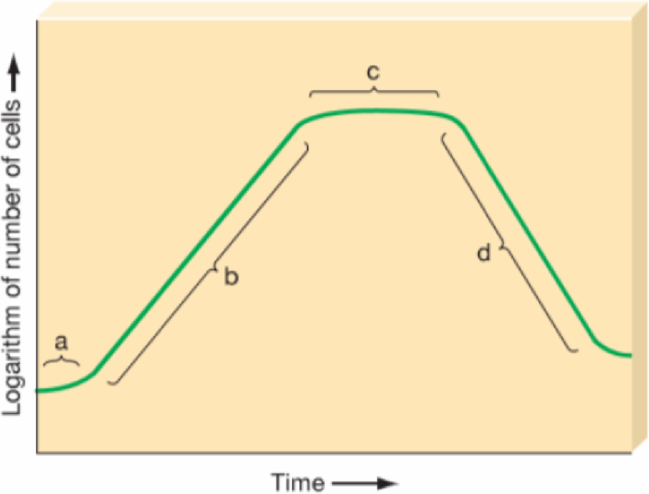
Identify the position of each of the following on the accompanying graph:
_____Organisms divide at their most rapid rate
_____New cells are produced at same rate as old cells die
_____Lag phase
_____Log phase
_____Many cells undergo involution and death
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Identify which kingdom the organism belongs to and give the common name
I live on your skin. If given the chance, I will cause serious infections. I grow in colonies that look like bunches of grapes, but I’m a single-celled organism. I have DNA, but not in a nucleus. I’m a _____________
I live in super salty environments where no other creature can live. I’m single-celled. My DNA is not in a nucleus. I’m a ____________________.
I’m found in the sea. I’m multicellular and can be 100 feet or more in length. I’m greenish and turn sunlight into food. While I have leaf-like and root-like body segments, I’m never found living on land. I’m a ____________________.
I’m large, green, and leafy. I make seeds that animals like to eat. My chloroplasts make my food. I’m a ____________________.
I live on land, but have to stay in moist places. I have a cuticle that protects me from drying out. I’m photosynthetic. I’m a ____________________.
I look like white fuzz with black dots…
Label the Amoeba and Identify whether it is eukaryote or prokaryote and Indicate the type of cellular reproduction process the cell undergo
Six Kingdoms of Life Chart Practice
Name:
Kingdom
Type of Cells
Number of Cells
How it Obtains
Reproduction
Food
Asexual by
binary fission,
budding or
fragmentation.
Some autotrophs
Archaebacteria
Prokaryotic
Unicellular
and some
heterotrophs.
Some autotrophs
Eubacteria
Prokaryotic
Unicellular
and some
Asexual
heterotrophs.
Some autotrophs
Some unicellular
Protista
Eukaryotic
and some
and some
Mostly asexual
multicellular
heterotrophs.
Some unicellular
Some asexual
Fungi
Eukaryotic
and some
Heterotrophs
and some
multicellular
sexual
Some asexual
Plantae
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Autotrophs
and some
sexual
Animalia
eukaryotic
Multicellular
Heterotrophs
Sexual
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells do have a nucleus.
Autotroph means it can make its own food. Heterotroph means it must
obtain nutrients from another organism.
Asexual reproduction involves only one parent, and the offspring are
genetically identical to that parent. Sexual reproduction involves two parents,…
Chapter 6 Solutions
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
Ch. 6 - What are the differences between the lag phase and...Ch. 6 - How does logarithmic rate of increase differ from...Ch. 6 - Prob. 1.3SCCh. 6 - Why does a direct microscopic count of bacteria...Ch. 6 - What does the ending -phile mean? Distinguish...Ch. 6 - What enzymes do most obligate anaerobes lack? How...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2.3SCCh. 6 - Prob. 3.1SCCh. 6 - Distinguish between the various kinds of media:...Ch. 6 - What is the purpose of a stock culture? Why is it...
Ch. 6 - Prob. 1CCSCh. 6 - Exactly 100 bacteria with a generation time of 30...Ch. 6 - In the above example, do you think that the number...Ch. 6 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 6 - Prob. 1SQCh. 6 - Match the following growth phase terms to their...Ch. 6 - Which of the following is the best definition of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 4SQCh. 6 - The most probable number (MPN) technique is a...Ch. 6 - Match the terms with their definitions:Ch. 6 - Prob. 7SQCh. 6 - Why do foods containing a high concentration of...Ch. 6 - Some bacteria have complex nutritional...Ch. 6 - Prob. 10SQCh. 6 - Which type of cell will shift to aerobic...Ch. 6 - Which of the following statements about endospores...Ch. 6 - Prob. 13SQCh. 6 - Blood agar is often used to observe changes in the...Ch. 6 - A bacterial medium that contains 20 grams of beef...Ch. 6 - MacConkey agar contains the dye, crystal violet,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 17SQCh. 6 - What are the purposes of carrying out the streak...Ch. 6 - Prob. 19SQCh. 6 - During quorum sensing, bacteria sense their...Ch. 6 - Prob. 21SQCh. 6 - Identify the position of each of the following on...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Distinguish between capsid and capsomere.
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
17. Anthropologists are interested in locating areas in Africa where fossils 4-8 million years old might be fou...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
Which culture produces the most lactic acid? Use the following choices to answer questions. a. E. coli growing ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
3. Which of the following is a major functional characteristic of all organisms? (a) movement, (b) growth (c) m...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy & Physiology) Standalone Book
When two spiny mouse species coexist, Acomys cahirinus is nocturnal, whereas A. russatus is active during the d...
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An infectious disease research group is studying a microbe that can cause infections and gastrointestinal disease in humans, and which can also survive and reproduce in hamsters. A dormant cyst form of the microbe infects human hosts through fecal-oral transmission if they come in contact with hamster droppings and don’t wash their hands before eating. The organism exhibits active, motile morphological forms at other stages of its life cycle. Sexual reproduction (fusion of haploid gametes) occurs in the hamsters; only asexual reproduction occurs in humans. It has a nucleus, but does NOT have a cell wall. This microbe could be which of the following? Protozoan Fungus Bacterium Virusarrow_forwardThe organism represented below is multicellular, heterotrophic, and completely aquatic. - Offspring resulting from only the process of mitotic cell division Which other characteristics could be used to descri this organism? A) reproduces in a water habitat and is a producer B) carries out photosynthesis and needs oxygen C) deposits cellular wastes on land and decompos dead organisms D) reproduces asexually and is a consumerarrow_forwardWhich process is shown in the plant cell below? O--00 O cell growth O cell reproduction O metamorphosis O photosynthesis 8arrow_forward
- For each type of organism, place a check mark in the box to indicate whether the cellular characteristic or function is present.arrow_forwardTaxonomy refers to the science of classification of living organisms. The five Kingdom Classification system was widely used from 1920 to 1980. eukaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic multicellular multicellular multicellular absorb photosynthesize nonmotile ingest motile nonmotile sexual sexual sexual Animals Fungi Plants eukaryotic unicellular or multicellular absorb, ingest, or photosynthesize sexual and asexual Protists 00 prokaryotic absorb and photosynthesize motile or nonmotile Robert Harding Whittaker (1920 - 1980) Monera asexual Explain why this classification system was abandoned in favor of the 3-domain system.arrow_forwardDescribe the cyanobacteria in terms of: nature of nucleus cell wall composition cytoplasmic organelles flagella photosynthetic pigments carbohydrate reserve reproduction g.1 unicellular/colonial forms _ g.2 filamentous formsarrow_forward
- which of the following sentences are NOT correct about mitochondria: is found in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is not found in some cells such as liver cells is generate most the cell's supply ATP O is a double membrane-bound organelle which of the following are NOT correct about prokaryotic organisms is reproduction by binary fission is have linear DNA is have flagella made of tubulin is have nuclear bodyarrow_forwardPut a checkmark (1) on the group where each of the following structures are present. Cellular Structures Plantae Animalia FungiProtista Monera 1. Nucleus 2. Nucleoid 3. Nucleolus 4. Ribosomes 5. Golgi Body 6. Endoplasmic reticulum 7. Plasma membrane 8. Centriole 9. Cell wall 10. Chloroplast 11. Mitochondria 12. Cytoplasm 13. Cytoskeleton 14.Pigments 15. DNAarrow_forwardBinary fission Oogenesis (formation of eggs) Mitosis Meiosisarrow_forward
- Characterize the plant-like protists (algae) based on the following parameters.arrow_forwardat would happen if an organism lost the ability to carry out cell division? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a) Cells can recover on its own if they are damaged. b) Damaged cells will not be replaced by new cell and organism may not function well. c) Organism will continue to function normally d) Adult organism does not depend on cell divisionarrow_forwardCharacterize the animal-like protists (protozoa) based on the following parameters.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Endosymbiotic Theory; Author: Amoeba Sisters;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FGnS-Xk0ZqU;License: Standard Youtube License