
Concept explainers
Dama Company produces women’s blouses and uses the FIFO method to account for its
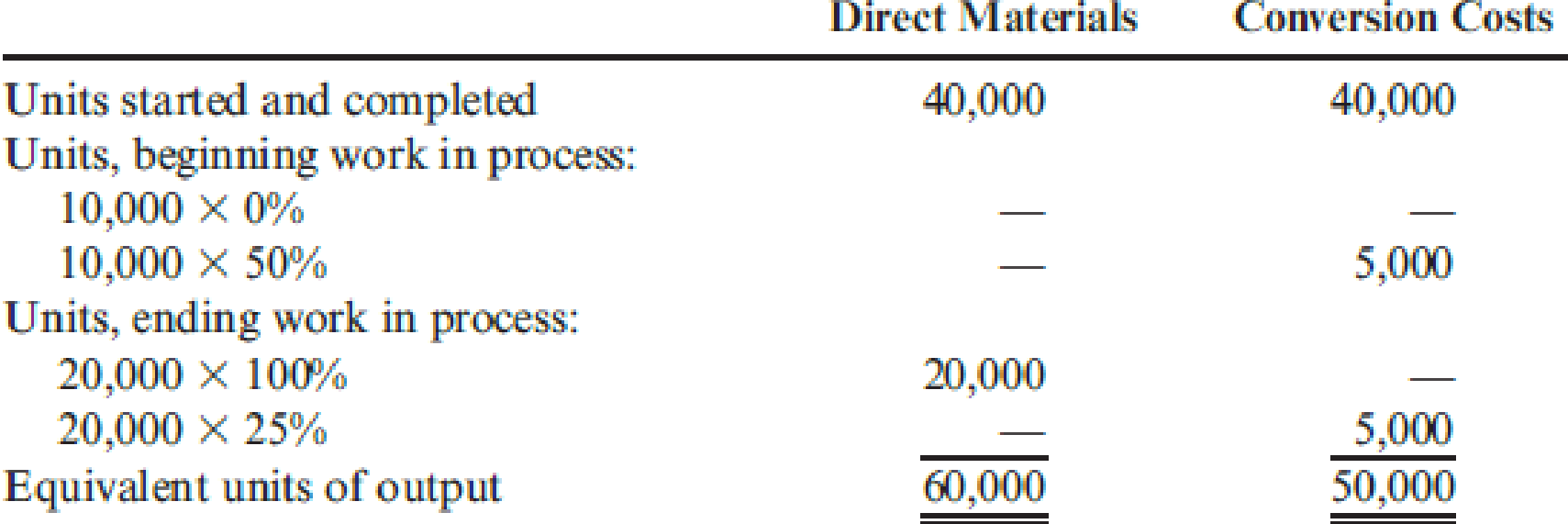
Costs in beginning work in process were direct materials, $20,000; conversion costs, $80,000. Manufacturing costs incurred during April were direct materials, $240,000; conversion costs, $320,000.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a physical flow schedule for April.
- 2. Compute the cost per equivalent unit for April.
- 3. Determine the cost of ending work in process and the cost of goods transferred out.
- 4. Prepare the journal entry that transfers the costs from Cutting to Sewing.
1.
Prepare the schedule of physical flow.
Explanation of Solution
Process Costing: It is a method of cost accounting used by an enterprise with processes categorised by continuous production. The cost for manufacturing those products are assigned to the manufacturing department before the averaged over units are being produced.
Prepare the schedule of physical flow.
| Particulars | Units |
| Units to account for: | |
| Units, beginning work in process | 10,000 |
| Units started | 60,000 |
| Total units to account for | 70,000 |
| Units accounted for: | |
| Units started completed | 40,000 |
| Units, beginning work in process | 10,000 |
| Units, ending work in process | 20,000 |
| Total units accounted for | 70,000 |
(Table 1)
2.
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit for the month April.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit for the month April.
Working note 1: Calculate the unit material cost.
Working note 2: Calculate the unit conversion cost.
3.
Ascertain the value of cost of EWIP and the cost of goods transferred out.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the value of cost of EWIPs.
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Ending work in process: | |
| Direct materials (3) | 80,000 |
| Conversion cost (4) | 32,000 |
| Total cost of ending work in process | 112,000 |
(Table 2)
Ascertain the cost of goods transferred out.
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Cost of goods transferred out: | |
| Units started and completed (5) | 416,000 |
| Units, beginning work in process: | |
| Prior-period cost | 100,000 |
| Current costs to finish (6) | 32,000 |
| Total cost of goods transferred out | 548,000 |
(Table 3)
Working note 3: Calculate the units of direct materials during ending work in process.
Working note 4: Calculate the units of conversion cost during ending work in process.
Working note 5: Calculate the value of the units that were started and completed.
Working note 6: Calculate the current cost to finish.
4.
Journalize the given transaction.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transaction.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process (Sewing) | 548,000 | ||
| Work in process (Cutting) | 548,000 | ||
| (To record transfer of cost from cutting to sewing) |
(Table 4)
- Work in (sewing) is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the work in process account by $548,000.
- Work in process (cutting) is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the work in process account by $548,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Cornerstones of Cost Management, Loose-Leaf Version, 4th + CengageNOWv2, 1 term Printed Access Card
- The accounting equation states: a. Assets + Liabilities = Stockholders' Equity b. Assets Liabilities - Stockholders' Equity c. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity d. Assets + Stockholders' Equity = Liabilities e. None of the abovearrow_forwardhy teacher please solve this questionsarrow_forwardTutor need provide answerarrow_forward
- A woman earned wages of $56,800, received $1,400 in interest from a savings account, and contributed $3,200 to a tax-deferred retirement plan. She was entitled to a personal exemption of $3,100 and had deductions totaling $5,070. Find her gross income, adjusted gross income, and taxable income.arrow_forwardPlease provide answerarrow_forwardWhat are the total fixed costs for this general accounting question?arrow_forward
- At the beginning of the year, a company estimates the following manufacturing costs for the next period: direct labor, $860,000; direct materials, $527,000; and factory overhead, $245,000. 1. Compute its predetermined overhead rate as a percent of direct labor. 2. Compute its overhead cost as a percent of direct materials. Need Answerarrow_forwardSolve this question is solution accountingarrow_forwardOpereting income will increase by ??arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





