
Review of Selected Concepts Related to Nomenclature
Write the chemical formula of each of the following. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
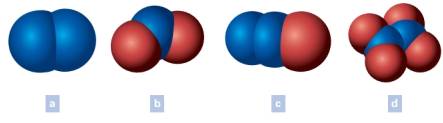
(a)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (a) is written as N2
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. The number of each kind of atom which makes up the particle generally called as the composition, is denoted by the chemical formula. Commonly, elements can be madeup of molecules having single atom, two atoms or complex multi-atoms. Coversely, when the substance itself is an element it should have all atoms of the same element. In the above example (a), the two lobes are having the same blue color which is for the element nitrogen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 2
Chemical formula = N2
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (a) is written.
(b)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (b) is written as NO2
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. In the above example (b), the two lobes are having the same color which is for the element oxygen and one lobe is having the color for nitrogen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 1
Total number of lobes of oxygen (O) = 2
Chemical formula = NO2
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (b) is written.
(c)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (c) is written as N2O
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. In the above example (c), the two lobes are having the same color which is for the element nitrogen and one lobe is having the color for oxygen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 2
Total number of lobes of oxygen (O) = 1
Chemical formula = N2O
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (c) is written.
(d)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (d) is written as N2O4
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. In the above example (d), the two lobes are having the same color which is for the element nitrogen and other four lobes are having the color for oxygen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 2
Total number of lobes of oxygen (O) = 4
Chemical formula = N2O4
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (d) is written.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach, 6th + OWLv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Please label this COZY spectraarrow_forwardPlease label this HNMRarrow_forwardConsider the following gas chromatographs of Compound A, Compound B, and a mixture of Compounds A and B. Inject A B mixture Area= 9 Area = 5 Area = 3 Area Inject . མི། Inject J2 What is the percentage of Compound B in the the mixture?arrow_forward
- Rank these according to stability. CH3 H3C CH3 1 CH3 H3C 1 most stable, 3 least stable O 1 most stable, 2 least stable 2 most stable, 1 least stable O2 most stable, 3 least stable O3 most stable, 2 least stable O3 most stable, 1 least stable CH3 2 CH3 CH3 H₂C CH3 3 CH3 CHarrow_forwardConsider this IR and NMR: INFRARED SPECTRUM TRANSMITTANCE 0.8- 0.6 0.4 0.2 3000 10 9 8 00 HSP-00-541 7 CO 6 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) сл 5 ppm 4 M Which compound gave rise to these spectra? N 1000 1 0arrow_forwardConsider this reaction (molecular weights are under each compound): HC=CH + 2 HCI --> C2H4Cl 2 MW = 26 36.5 99 If 4.4 g of HC=CH are reacted with 110 mL of a 2.3 M HCI solution, and 6.0 g of product are actually produced, what is the percent yield?arrow_forward
- What is the name of the major product of this reaction? OH CH3 H₂SO4, heat 1-methylcyclohexene O2-methyl-1-cyclohexene O 3-mthylcyclohexene 1-methyl-2-cyclohexenearrow_forwardWe added a brown solution of Br2 to one of our products, and the brown color disappeared. This indicated that our product wasarrow_forwardRank the following according to reactivity toward nitration: a) benzene b) bromobenzene c) nitrobenzene d) phenol Od) greatest, c) least Od) greatest, b) least Od) greatest, a) least a) greatest, b) least a) greatest, c) least Oa) greatest, d) least Ob) greatest, a) least O b) greatest, c) least Ob) greatest, d) least O c) greatest, a) least O c) greatest, b) least O c) greatest, d) leastarrow_forward
- O-Nitrophenol was distilled over with the steam in our experiment while the other isomer did not. This is due to: O intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the ortho isomer O intermolecular hydrogen bonding in the the ortho isomer O the ortho isomer has a lower density O the ortho isomer has a lower molecular weightarrow_forwardK 44% Problem 68 of 15 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :6: :: :CI: CI CI: :0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows H H Cl CI: CI CI: Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows H :CI: Alarrow_forwardI I H :0: Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. 0:0 :0: CI ΑΙ :CI: :CI: :0: CI Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows cl. :0: Cl © ハ CI:: CI H CO Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows 10: AI ::arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





