
Concept explainers
(a).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.3.
Introduction: The epithelial tissue is formed by joining the epithelial cells in the body. The epithelial cells have important functions like protecting the tissue layers and hence they are always found on the surface of the organs and tissues. The epithelial cells also act as a barrier to control the movement of molecules in-between the glands.
(a).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
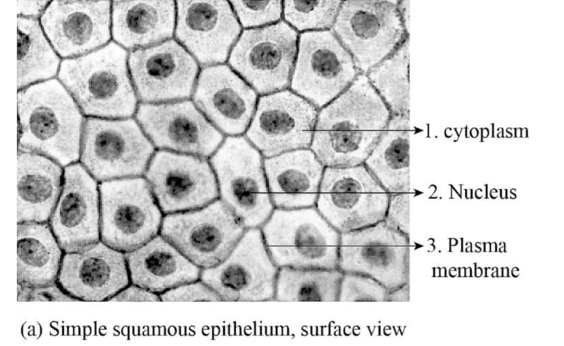
Fig.1: The figure showing simple squamous epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Simple squamous epithelial cells: The simple squamous epithelial cells are a single layer of epithelial cells that are found in the alveoli in the lungs, glomerular capsule; as endothelium in the inner lining of capillaries, as mesothelium in the peritoneal cavity and mediastinum. These epithelial cells have a specific function of gaseous exchange by diffusion, secretion, filtration, absorption. The presence of single layer allows easy passage of the gases in-between the cells.
(b).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.4.
(b).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
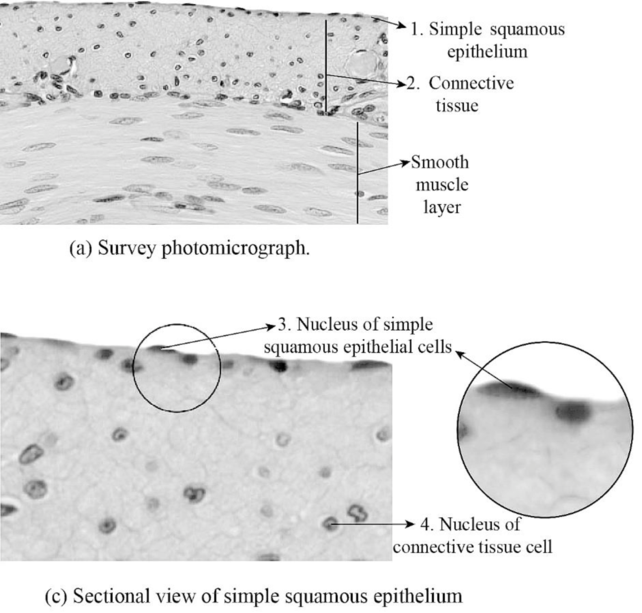
Fig.2: The figure showing sectional view of simple squamous epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
The cross section image of the simple squamous epithelial cells shows, smooth muscle are covered by the epithelial cells. The connective tissue forms the basement membrane for the epithelial cells to form a single layer of simple squamous epithelial cell over the smooth muscle.
(c).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.5.
(c).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
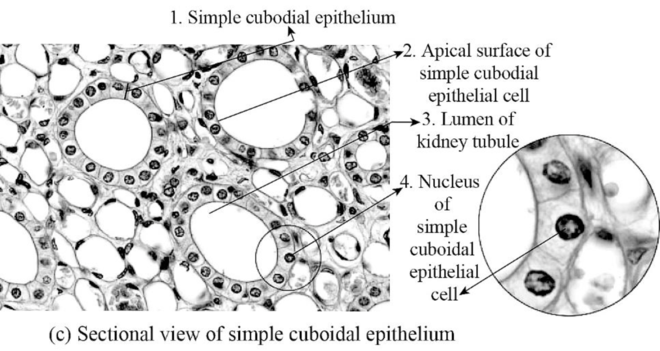
Fig.3: The figure showing simple cuboidal epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Simple cuboidal epithelial cells: The simple cuboidal epithelial cells are a single layer of epithelial cells that are found in the wall of kidney tubules and glands. These epithelial cells have a specific function of absorption and secretion. These epithelial cells absorb substance from outside of the tubules and secret those substances inside the kidney tubules.
(d).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.6.
(d).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
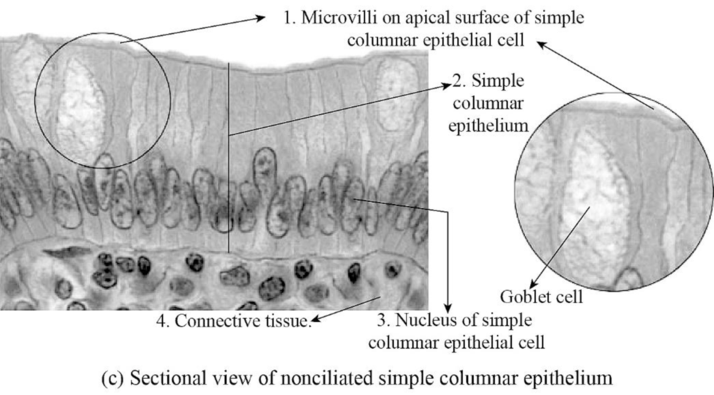
Fig.4: The figure showing simple columnar epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Simple columnar epithelial cells: The simple columnar epithelial cells are a single layer of epithelial cells that are found in the lining of the stomach and intestines. These are special types of cells that are elongated and have microvilli present on them. The columnar epithelial cells have special functions like secreting digestive juices and absorption by increasing the surface area in the small intestine.
(e).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.7.
(e).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
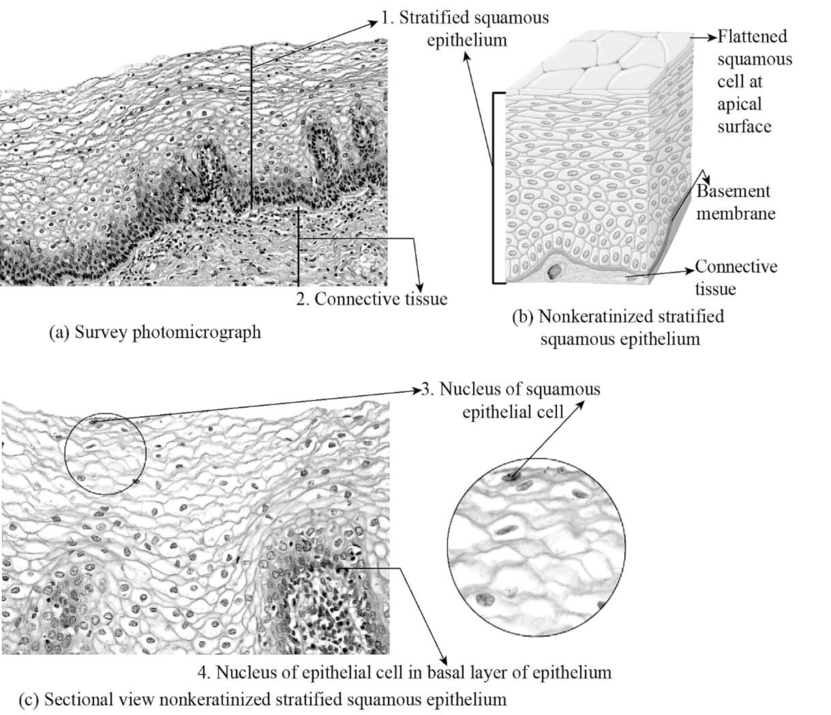
Fig.5: The figure showing stratified squamous epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Stratified squamous epithelium: The stratified squamous epithelium cells are found at areas of lips, esophagus, mouth, vagina, and anus. The stratified epithelium formed by multiple layers of epithelium cells that makes surface area to be thicker, damage resistance, forms a protective barrier against friction and abrasion, and also prevent the entry of pathogens due to their tight adherence of multi-layered cells.
(f).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.8.
(f).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
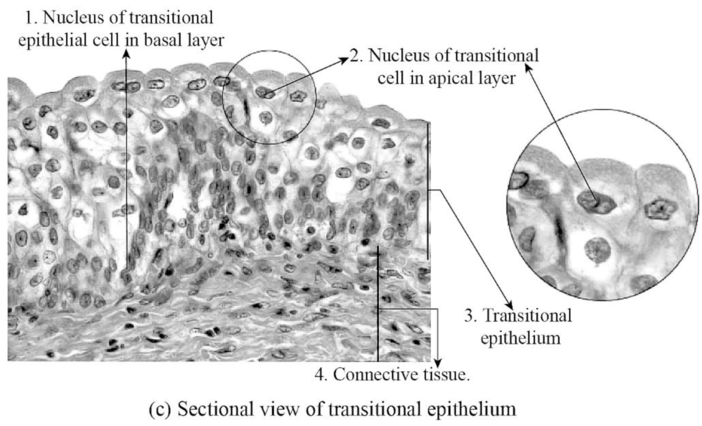
Fig.6: The figure showing transitional epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Transitional epithelium cell: The transitional epithelial cells are one of the types of epithelial cells that has a special function like changing the structure of the cell. The transitional epithelial cells are found in the lining of the urinary bladder, urethra, and ureters. The function of the transitional epithelial cells is to form a protective barrier on the surface of the urinary bladder and also reduces tension.
(g).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.9.
Introduction: The epithelial cell is formed by joining cells that together form layers of epithelial cells in the body. The epithelial cells have important functions like protecting the tissue layers and hence they are always found on the surface of the organs and tissues.
(g).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
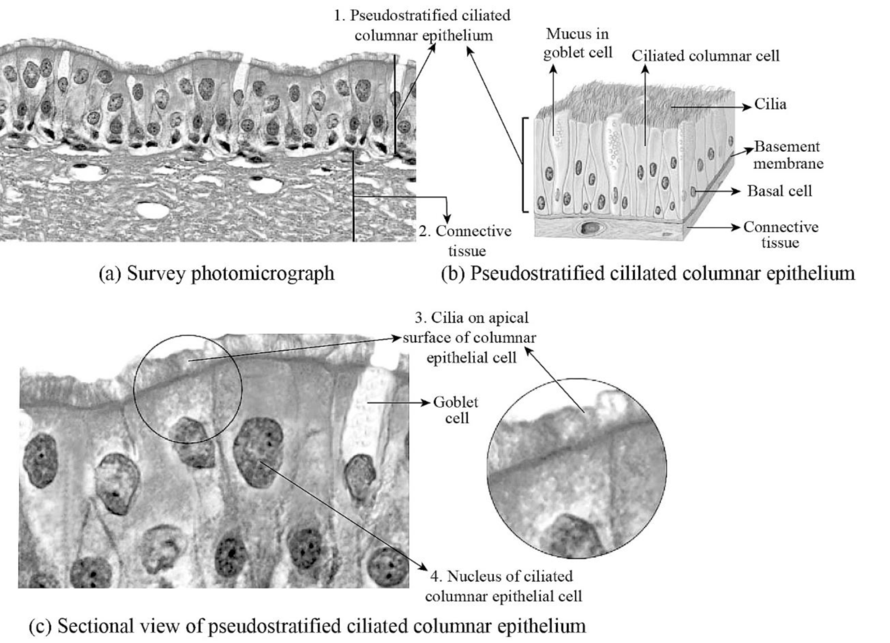
Fig.7: The figure showing pseudostratified epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Pseudostratified epithelium cell: The stratified epithelium formed by multiple layers of epithelium cells that makes surface area to be thicker, damage resistance, forms a protective barrier against friction and abrasion, and also prevent the entry of pathogens. The pseudostratified epithelial cells also look like multilayer epithelium but it is a single-layered thick cell. The pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells found in the nasal cavity lining. The pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells protect the nasal cavity by secretion of mucus to trap the pathogens and dust.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
- Using quail and chick embryos, quail-specific antibody and fluorescent tissue-specific antibodies, design an experiment where you investigate the tissues the cranial neural crest can give rise to. What are four derivatives of the cranial neural crest that you expect to see in the resulting chimeric embryos?arrow_forwardDoes the neural crest have to undergo epithelial to mesenchymal transition prior to migration through the developing embryo? Does the neural crest differentiate into different cell types based on their axial position along the anterior and posterior axis?arrow_forwardUsing quail and chicken embryos, what kind of experiment would you conduct to test if rib forming somites have their axial identity specified before segmentation? How do we know this phenotype is due to axial identity being specified before segmentation and not due to our experimental method?arrow_forward
- 8. Aerobic respiration of a 5 mM solution of tripeptide that is composed of the following three amino acids; alanine, leucine and isoleucine. Alanine breaks down to pyruvate, leucine breaks down to Acetyl-CoA and isoleucine breaks down to succinyl-CoA. Alanine NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Leucine Isoleucine Totals Show your work using dimensional analysis here: 4arrow_forward9. Aerobic respiration of one lipid molecule. The lipid is composed of one glycerol molecule connected to two fatty acid tails. One fatty acid is 12 carbons long and the other fatty acid is 18 carbons long in the figure below. Use the information below to determine how much ATP will be produced from the glycerol part of the lipid. Then, in part B, determine how much ATP is produced from the 2 fatty acids of the lipid. Finally put the NADH and ATP yields together from the glycerol and fatty acids (part A and B) to determine your total number of ATP produced per lipid. Assume no other carbon source is available. fatty acids glycerol 18 carbons 12 carbons 0=arrow_forwardinfluences of environment on the phenotype.arrow_forward
- What is the difference between codominance and phenotypic plasticity?arrow_forwardExplain the differences between polygeny and pleiotropy,arrow_forwardIf using animals in medical experiments could save human lives, is it ethical to do so? In your answer, apply at least one ethical theory in support of your position.arrow_forward
- You aim to test the hypothesis that the Tbx4 and Tbx5 genes inhibit each other's expression during limb development. With access to chicken embryos and viruses capable of overexpressing Tbx4 and Tbx5, describe an experiment to investigate whether these genes suppress each other's expression in the limb buds. What results would you expect if they do repress each other? What results would you expect if they do not repress each other?arrow_forwardYou decide to delete Fgf4 and Fgf8 specifically in the limb bud. Explain why you would not knock out these genes in the entire embryo instead.arrow_forwardYou implant an FGF10-coated bead into the anterior flank of a chicken embryo, directly below the level of the wing bud. What is the phenotype of the resulting ectopic limb? Briefly describe the expected expression domains of 1) Shh, 2) Tbx4, and 3) Tbx5 in the resulting ectopic limb bud.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





