
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780137533268
Author: Paula Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON+
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.9, Problem 19P
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the following reaction in which C is the most stable and B the least stable of the three species and the transition state going from A to B is more stable than the transition state going from B to C:
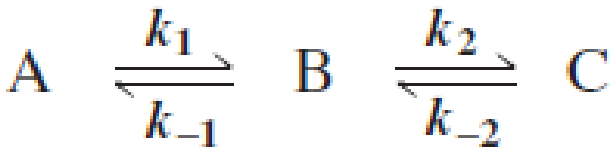
- a. How many intermediates are there?
- b. How many transition states are there?
- c. Which step has the greater rate constant in the forward direction?
- d. Which step has the greater rate constant in the reverse direction?
- e. Of the four steps, which has the greatest rate constant?
- f. Which is the rate-determining step in the forward direction?
- g. Which is the rate-determining step in the reverse direction?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In the normal hydrogen electrode, the balance potential difference in the interface is 0 and the current flow across the electrode when the interface potential difference is +5 mV. Explain briefly. Is the overvoltage 5 mV?
In the normal hydrogen electrode, the balance potential difference in the interface is 0 mV, the maximum potential is 5 mV. Explain briefly.
utron
eutro
cle
TH
tro
(Na
(b) Atoms are said to be electrically neutral. Explain.
(c)
Distinguish
between the following:
(i) Atomic number and mass number.
(ii) Mass number and relative atomic mass.
2. An isotope Q, has 18 neutrons a mass number of 34.
(a) (i) Draw the atomic structure of Q.
(ii) Write its electron arrangement
(b) To which period and group does Q belong? Explain your answer.
(c) How does Q form its ion? Explain.
3. (a) Determine the relative atomic mass of the following elements =
compositions occur in the proportions given.
(i) Neon
20
21
22.
Ne (90.92%), 10Ne (0.26%), and 10Ne (8.82%)
(ii) Argon
36
38
40
18 Ar (0.34%), 18 Ar (0.06%) and 18 Ar (99.6%)
Chapter 5 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 5.1 - Draw the structure for each of the following: a....Ch. 5.1 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 5.4 - a. For which reaction in each set below will S be...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 5.6 - How many different alkenes can be hydrogenated to...Ch. 5.6 - The same alkane is obtained from the catalytic...
Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 12PCh. 5.6 - Rank the following compounds in order from most...Ch. 5.7 - The rate constant for a reaction can be increased...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 16PCh. 5.9 - Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step...Ch. 5.9 - Prob. 18PCh. 5.9 - Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the...Ch. 5.10 - Which of the following parameters would be...Ch. 5 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 5 - Draw the structure of a hydrocarbon that has six...Ch. 5 - Which of the following compounds is the most...Ch. 5 - Prob. 24PCh. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - Prob. 26PCh. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - Name the following:Ch. 5 - Prob. 29PCh. 5 - Prob. 30PCh. 5 - Prob. 31PCh. 5 - Prob. 32PCh. 5 - Prob. 33PCh. 5 - Prob. 34PCh. 5 - Prob. 35PCh. 5 - Name each of the following:Ch. 5 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - Given that the twist-boat conformer of cyclohexane...Ch. 5 - a. The G for conversion of axial fluorocyclohexane...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1PCh. 5 - Prob. 2PCh. 5 - Prob. 3PCh. 5 - Prob. 4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5PCh. 5 - Prob. 6PCh. 5 - Prob. 7PCh. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - Prob. 9PCh. 5 - Prob. 10P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the normal hydrogen electrode, the balance potential difference in the interface is this, the maximum potential is 5 mV. Explain briefly.arrow_forwardThe electrode balance potential is -0.118 V and the interface potential difference is +5 mV. The overvoltage n will be 0.005 - (-0.118) = 0.123 V. Is it correct?arrow_forwardIn the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), if the electrode balance potential is -0.118 V and the interface potential difference is +5 mV. The current voltage will be 0.005 - (-0.118) = 0.123 V ¿Correcto?arrow_forward
- In the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1) at 298K is 0.79 mA cm-2. If the balance potential of the electrode is -0.118 V and the potential difference of the interface is +5 mV. Determine its potential.arrow_forwardIn one electrode: Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density at 298K is 0.79 mA·cm-2. If the voltage difference of the interface is +5 mV. What will be the correct intensity at pH = 2?. Maximum transfer voltage and beta = 0.5.arrow_forwardIn a Pt electrode, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density of an electrode is 0.79 mA cm-2. ¿Qué corriente flow across the electrode of área 5 cm2 when the difference in potential of the interface is +5 mV?.arrow_forward
- If the current voltage is n = 0.14 V, indicate which of the 2 voltage formulas of the ley of Tafel must be applied i a a) == exp (1-B). xp[(1 - ß³): Fn Fn a b) == exp B RT RTarrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V. Indicate which of the 2 formulas must be applied a) = a T = i exp[(1 - p) F Fn Fn b) i==exp B RTarrow_forwardTopic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forward
- Two cations that exchange an electron in an interface, the exchange density is worth 1.39 mA/cm2 and the current density is worth 15 mA/cm2 at 25°C. If the overvoltage is 0.14 V, calculate the reaction rate and symmetry factor. Data: R = 8,314 J mol-1 k-1: F = 96500 Carrow_forwardWith the help of the Tafel line, it is estimated that the interchange density of the VO2+/VO2+ system on the carbon paper has a value of 3 mA cm-2. Calculate a) the current density if the voltage has a value of 1.6 mV and the temperature is 25°C. b) the beta value of the anódico process if the Tafel pendulum is 0.6 V at 25°C. Data: R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1, y F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forwardApply the NANSTE law to the MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- ⇄ Mn2+ + 4H2Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License